BACKGROUND:
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is an adverse complication of unfractionated and low molecular weight heparin caused by antibodies recognizing platelet factor 4-heparin (PF4/hep) complexes leading to platelet activation. The diagnosis of HIT is based on the combination of the clinical picture, using the 4T score along with screening and confirmatory methods to detect platelet activating anti‐PF4/H antibodies.
OBJECTIVES:
Performance was evaluated for two enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs), 1) Asserachrom HPIA , Diagnostica Stago Inc., Parsippany, NJ, USA and 2) LIFECODES PF4 Enhanced, Immucor, Inc., Norcross, GA, USA for screening-based detection of PF4/hep antibodies.
METHODS:
ELISA assays were run per manufacturer recommendations and adapted for automation on a Dynex DS2 automated ELISA platform. Performance characteristics of the two immunoassays were assessed, including sensitivity, specificity, concordance with serotonin release assay (SRA), positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV). 21 samples were used in the study.
Results:
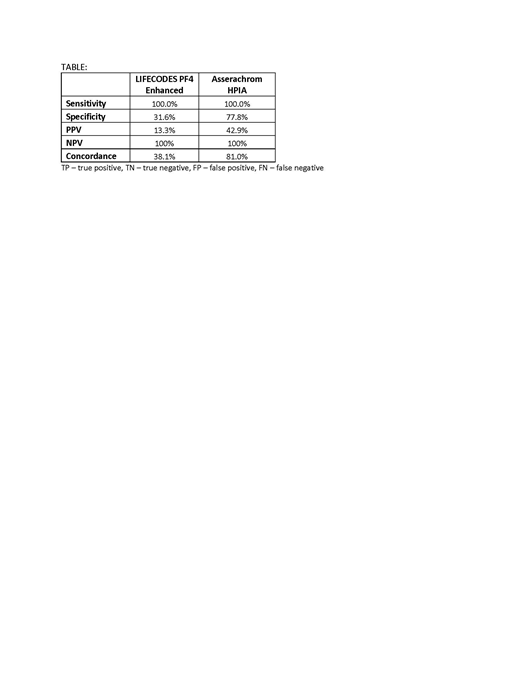
Both assays, Asserachrom HPIA and LIFECODES PF4 Enhanced demonstrated 100% sensitivity and NPV, confirming both assays' reliability to detect and rule out HIT (see table). The diagnostic specificity was significantly higher for Asserachrom HPIA vs. LIFECODES PF4 Enhanced (77.8% vs 31.6%). Asserachrom HPIA showed fewer false positive results, with PPV of 42.9% for Asserachrom HPIA vs. 13.3% for LIFECODES PF4 Enhanced. No false negative results were found for either assay. Asserachrom HPIA demonstrated 81.0% concordance with SRA, vs. 38.1% for LIFECODES PF4 Enhanced.
CONCLUSIONS:
HIT is a life-threatening disorder, with diagnosis depending on clinical findings using the 4T score along with laboratory evaluation. Combining the 4T score with PF4/hep antibody screening increases the accuracy of excluding HIT. Our observations indicate Asserachrom HPIA provides results with high sensitivity and specificity, minimizing false positivess, allowing use of alternative anticoagulants more selectively in at risk patients, to potentially improve patient management while minimizing costs.
Mardovina:Diagnostica Stago, Inc.: Employment. Chromczak:Diagnostica Stago, Inc.: Employment. Riley:Diagnostica Stago, Inc.: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.