Pregnancy in CML patients (pts) is becoming a reality due to the increase in information from published cases or larger multicentric database (GIMEMA and ELN). Interferon (IFN) has been used during pregnancy, but little is known about the use of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), which should be stopped early due to their teratogenic effects.
Female pts can ideally plan a pregnancy if they are in a deep, stable, molecular response (DMR=MR≥ 4, ≤0.01%IS) and treatment free remission (TFR) parameters are satisfied. Molecular remission can be maintained throughout the pregnancy, but how to proceed if the remission is rapidly lost, or if the patient is not in DMR, or when CML is discovered during pregnancy?
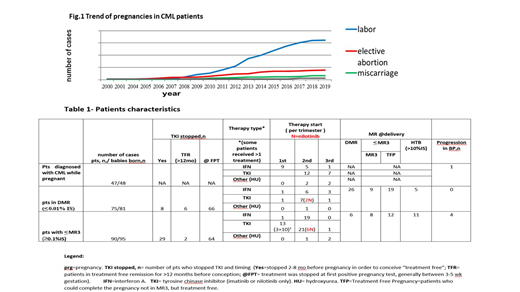
To address these questions, we analyzed more than 300 pregnancies registered through the ELN database. Pts completing pregnancy were grouped as follow:
1) pts diagnosed with CML while pregnant
2) pts in DMR
3) pts with ≤MR3 (≥ 0.1%IS)
In 47 patients CML was diagnosed during pregnancy, 21 during the 1st trimester, 15 in the 2nd , and 11 in the 3rd (range 3-38 wk). Sixteen patients were not treated until delivery, 15 were treated with IFN; 19 with Imatinib (IM), 12 in the 2nd trimester (>16 wk), and 7 in the 3rd. Forty-eight children were born (one set of twins). Three were preterm (35-37 wk), and one pregnancy is ongoing. No births defects were observed. Seven newborns had a low birth weight (< 2.5 Kg) 6 of them were exposed to IM at late pregnancy and 3 were preterm. Follow-up was uneventful. The majority of pts achieved ≥ MR3 after starting TKI. Two pts died: 1 in blast crisis (BC) after 9 years, but she was not adherent to treatment; 1 of transplant complication (resistant to>2TKI).
Seventy five pts had 80 pregnancies in DMR. Six were in TFR (no therapy) for more than 12 mo, while 8 stopped TKI in order to conceive (2-8 mo before conception). Twenty two pts were treated during pregnancy: 12 with TKI (8 IM, 4 nilotinib, NIL) 1 in the 1st trimester (never stopped IM), 7 in the 2nd and 4 in the 3rd; 10 pts received IFN. Eighty one children were born (6 patients had 2 pregnancies, 1 had twins) with one baby born preterm (wk 35). No births defects were observed and two pregnancies are ongoing. Fifty eight pregnancies were carried without any CML treatment. Twenty six maintained DMR, 28 ≤ MR3 and considered in "treatment free pregnancy" (TFP), and 5 had >10% transcript levels at delivery, considered as high tumor burden (HTB). None of the patients progressed after pregnancy, 4 patients maintained TFR. Four patients did not return to MR3 <12 months after restarting TKI; 3 were switched to a more potent TKI rapidly achieving ≥ MR3, while 1 pt, who did not, is in hematologic remission after 3 years.
Pts belonging to ≤MR3 do not satisfy TFR criteria, and were discouraged from starting a pregnancy. However 95 pregnancies (90 pts) were reported; 29 had stopped TKI prior to conception (5 of them had HTB at pregnancy onset). Fifty eight (61%) were treated with IFN (20), TKIs (35), or HU (3). Thirteen patients were treated with IM during 1st trimester (10 throughout the pregnancy). Among the untreated pts, 6 were surprisingly in DMR at delivery, 20 were in TFP, and 11 had HTB. Two babies were born with polydactyly and hypospadias (IFN treatment since 1st trimester), and 2 exhibited a non-closed foramen ovale (IM during 2-3rd trimester) which was considered unlikely to be related to treatment. Four pts progressed in BC and died after pregnancy but all were not compliant to therapy.
This is the first, large, multicenter report focusing on treatment during pregnancy. Results suggest that CML patients can pursue a normal life including planning a family, with several caveats. Based on the different situations examined, treatment with IFN is confirmed safe. In contrast TKIs should not be used during pregnancy. Selected TKIs, specifically IM and NIL which have little placental transfer, can be started after organogenesis. Pts at onset can delay therapy without jeopardizing the future CML outcome. If therapy during pregnancy is deemed necessary, IFN can induce and maintain hematologic remission, or, if introduced earlier, preserve molecular remission after TKI interruption, while TKIs can reduce HTB. Caution should be taken when considering stopping TKI prior to conception due to the possibility of losing response, while an early stop (at first positive pregnancy test, 4-5 wk) could be considered. Detailed results, mother and child follow up and practical management will be presented.
Abruzzese:BMS: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy. Turkina:Pfizer: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; fusion pharma: Consultancy. Apperley:Bristol Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Kim:Novartis: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Il-Yang co.: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Garcia-Gutiérrez:Novartis: Honoraria, Other: Advisory Committees. Mauro:Novartis Oncology: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy. Milojkovic:Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Moriaghi:novartis: Speakers Bureau; BMB: Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Speakers Bureau. Nicolini:Incyte Biosciences: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Sun Pharma Ltd: Consultancy. Rea:Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Honoraria; Incyte Biosciences: Honoraria. Rousselot:Pfizer: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Shacham:novartis: Consultancy. Trawinska:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria. Chelysheva:Fusion Pharma: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria.
informations on the use of interferon and/or TKIs (imatinib, nilotinib) during pregnancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.