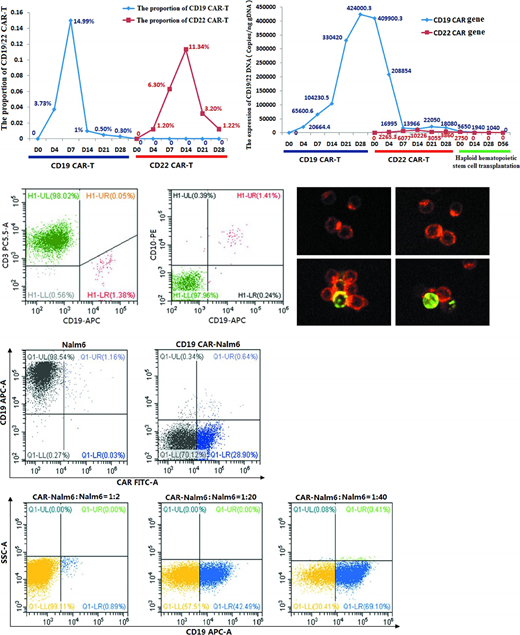
Purpose: To investigate the immunophenotypic characteristics of CD19 CAR transfected into leukemia cells with CD19 expression during CAR-T cell preparation.
Patient andMethods: Here we reported a TP53 positive refractory B-ALL patient relapsed 14 days after Complete response (CR) from the CD19 CAR-T therapy. But her leukemia cells expressed CD19 and expressed aberrantly the anti-CD19 CAR gene at the same time. We transfected CD19 CAR gene into Nalm-6 cells to detect the expression of CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cells and the sensitivity to anti-CD19 CAR T-cell and anti-CD22 CAR T-cell. The binding of CD19 antigen on the surface of CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cells and Nalm-6 cells to CD19 CAR in CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cells was observed by confocal microscopy. The proportion of Nalm-6 cells in the transfection system was increased gradually to observe the change of CD19 expression on CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cells.
Results: The patient received a CD22 CAR-T therapy followed by a haploid hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and achieved CR with vanishment of TP53 mutation. To date, she had leukemia-free survival (LFS) and complete donor chimerism for 8 months. We found that there had 1.41% leukemic cells in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) during anti-CD19 CAR T-cell preparation, which may contribute to the relapse of the first CD19 CAR-T therapy. The CD19 expression was only 1.19% in CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cell culture system with a transfection rate of 46.5±3.78%, while the proportion of CD19 expression increased gradually when we increased the proportion of Nalm-6 cells in the transfection system. CD19 CAR of CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cells occupied the CD19 expression site of the cells themselves, meanwhile occupied the CD19 expression site of Nalm-6 cells. We found that the CD19 CAR Nalm-6 cells were sensitive to anti-CD22 CAR T-cell, althought they were resistant to anti-CD19 CAR T-cell.
Conclusions: There had a presence that CD19 CAR gene was transferred into leukemia cells during T cell manufacturing. The immunophenotype of leukemia cells of these refractory B-ALL patients who relapsed after CR from anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy were CD19+ or CD19-. It was determined by the proportion of CD19 CAR leukemia cells and leukemia cells. Anti-CD22 CAR T-cell therapy could be as a salvage measure to such patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.