The epichaperome, which was previously described by our team (Rodina et al. Nature 2016, Joshi et al. Nature Reviews Cancer 2018), is a complex hyper-connected network of chaperones and co-chaperones that are present in a subset of tumors, and its role is to facilitate the survival of malignant cells. We have previously shown abundant epichaperome networks in different tumor types, including AML. PU-H71 is a novel epichaperome inhibitor that selectively targets cells expressing the epichaperome. We hypothesize that personalizing PU-H71 in AML based on epichaperome abundance will significantly improve the clinical efficacy of PU-H71. To investigate this, we assessed the frequency of epichaperome abundance in primary AML samples and sought to develop a method with clinical application to predict response to PU-H71.
We screened 55 de novo and relapsed/refractory primary AML bone marrow and peripheral blood samples for epichaperome abundance and cytotoxicity. Epichaperome abundance was assessed by incubating cells with FITC-bound PU-H71 (labeled F2) for 4 hours followed by analysis by multi-parameter flow cytometry. A chemically similar FITC-bound PU-H71, which does not bind the epichaperome, termed F9, was used as a control (Taldone et al. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2011). MV411 cell lines were also used as positive controls (given known epichaperome abundance and high sensitivity to PU-H71), and intra-sample T-cells were used as negative controls. Furthermore, we assessed cell survival by incubating cells with 0.5uM PU-H71 for 48-hours followed by evaluation by multi-parameter flow cytometry. All analyses were performed in duplicates or triplicates. The ratio of blast F2 to F9 was combined with the F2-F9 blast to T cell ratio to calculate epichaperome abundance.
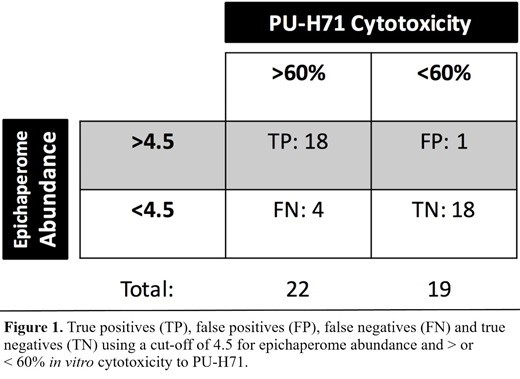
Data on epichaperome abundance was available in 50 patient samples. Cytotoxicity data was available in 41 patients. 22/41 (54%) of patient samples underwent ≥60% cell death, respectively, and 7/41 (17%) were resistant to PU-H71, as defined by < 5% cytotoxicity. An ROC curve using epichaperome cut-offs of 1, 2.5, 4.5, 6, 8 and 15 provided an AUC of 0.97 (95% CI 0.889-1.056, p=0.006). Using a cut-off of 4.5 for epichaperome abundance, 22/50 (44%) of samples expressed high levels of the epichaperome, and sensitivity and specificity for predicting >60% in vitro cytotoxicity to PU-H71 were 81.8% (95% CI 59.7-94.8%) and 94.7% (95% CI 74-100%) (Figure 1). This method's diagnostic accuracy was 87.8%, with positive and negative likelihood ratios of 15.5 and 0.19. Collectively, our data suggests that this flow cytometry-based evaluation of epichaperome abundance is a promising tool for detecting epichaperome abundance and personalizing the treatment of PU-H71 in patients with AML.
Chiosis:Samus Therapeutics: Equity Ownership, Patents & Royalties: Intellectual rights to the PU-FITC assay. Roboz:Trovagene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sandoz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Otsuka: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Orsenix: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MEI Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Jazz: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celltrion: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Actinium: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amphivena: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Argenx: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astex: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Eisai: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Guzman:Samus Therapeutics: Patents & Royalties: intellectual rights to the PU-FITC assay; Cellectis: Research Funding; SeqRx: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.