Background
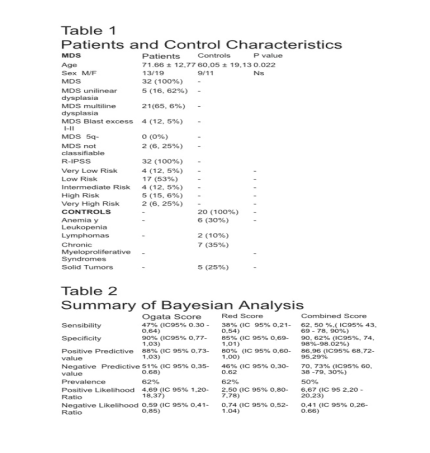
Flow cytometry (CF) is an important diagnostic tool for myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). Different analysis systems have been developed, the "Ogata score" is a simple two-color protocol based on surface expression SSC, CD45 and CD34, which has been validated in a multicentric study showing sensitivity of 69% and specificity of 92% in low risk MDS. Scoring based on erythroid markers by CF (Red) uses the coefficient of variation of CD36 and CD71 in combination with the fluorescence intensity of CD71 and the percentage of CD117 + in erythroid progenitors.
Goals.
To analyze the usefulness of the "Ogata, Red score and combined system" in the diagnosis of MDS of a patient population in Cucuta, the north of Santander, Colombia.
Methods
Case-control study, conducted at the "Unidad Hematológica Especializada" of Cucuta, a total of 32 patients with MDS and 28 control patients were included estimating the "Ogata and Red score", we followed protocols of Euroflow that includes processes of dyeing, analysis and washing using as a Lysis / fixation solution, but it deferred from Leukemia-Net standards. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and prevalence were established in our cohort, in addition we estimated a combined scoring system that integrated "Ogata and Red score"
Results
In "Ogata score" the sensitivity was 47% (95% CI 0.30-0.64) the specificity 90% (95% IC 0.77-1.03), PPV 88% (95% IC 0, 73-1.03), NPV 51% (95% IC 0.35-0.68), prevalence 62%. Red score showed sensitivity of 38% (95% IC 0.21- 0.54), specificity of 85% (95% IC 0.69-1.01), PPV 80% (95% CI 0.60-1.00), NPV 46% (95% IC 0.30-0.62) and prevalence of 62% Combined score of "Ogata plus Red", obtained sensitivity of 62.50% (95%CI 43.69 -78.90), specificity 90.62% (95%CI, 74.98 -98.02), PPV 86.96 (95% CI 68.72-95.29), NPV 70.73% (95%CI 60.38 -79.30) with a prevalence of 50% (95% CI 37.23 -62.77).
Conclusions
In our study, low sensitivity was found in the "Ogata and Red" score, but "Ogata" score showed lower sensibility than the published studies. Both scores had a high specificity and negative predictive value, in accordance with literature. Lysis method could interfere in this results. The Combined Score in FC helped increase the sensitivity of the test for MDS. It is necessary to implement strategies for the harmonization of FC techniques in different laboratories, in order to become a coadjutant tool that contributes to the diagnosis of MDS along with morphology, cytogenetics and molecular biology.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.