Background:
Smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM) was stratified into risk classes based on several models including Mayo clinic and Spanish myeloma working group models. After the revision of diagnostic criteria for multiple myeloma (MM) in 2014, the ultra-high risk SMM patients (>80% clonal plasma cells at two years) were re-classified as active MM patients. Thus, predictors of progression in patients currently diagnosed as SMM are unknown and reassessment of existing models is required. We aim to identify the risk factors associated with progression in SMM patients classified according to updated guidelines.
Methods
We performed a literature search following PRISMA guidelines and used following bibliographic databases: MEDLINE (Ovid and PubMed), EMBASE, The Cochrane Library and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), as well as annual meetings abstracts from inception till 1st,August 2019. We used MeSH and Emtree terms as well as performed open search for "smoldering multiple myeloma", "smoldering myeloma", and "asymptomatic multiple myeloma". Two independent reviewers screened the literature. We used snowballing technique to screen abstracts and reference within articles to include titles. Cochrane collaboration tool was used to asses risk of bias among included studies
Results
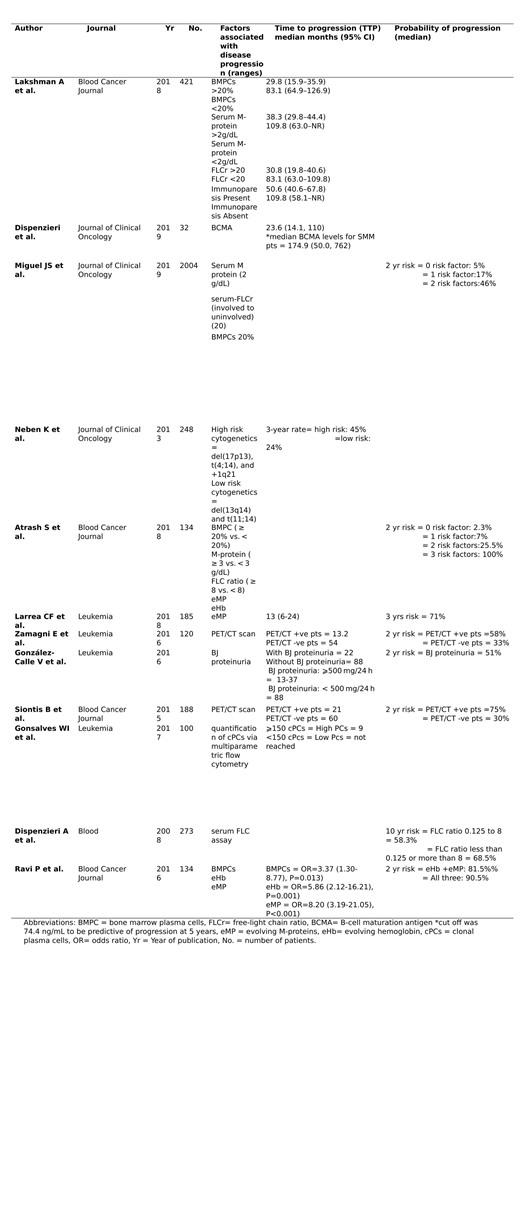
Our search retrieved 419 titles. After going through the titles and abstracts 38 articles were selected for full text review. Final review led to inclusion of 11 articles. Levels of serum M proteins, percentage of bone marrow plasma cells (BMPCs), serum free light chain ratio (FLCr) and PET/CT scan findings of whole body were most consistently and reliably indicated the progression of SMM to MM (Table 1). New studies are suggesting that B-cell maturation levels (BCMA), evolving M-proteins (eMP) and evolving hemoglobin levels (eHb) are also an accurate measure of SMM progression and should be incorporated in the risk stratification models. A study by Gonsalves WI et al. also suggested that levels of circulating clonal plasma cells with a cutoff of 150 was an important prognostic marker in their study. Immunoparesis status and role of Bence Jones proteins in reliably predicting the progression of SMM was debatable because they were significant in univariate analysis but were not significant in multivariate analysis (Table 1).
Conclusion
Serum M protein levels (2 g/dL), percentage of BMPCs (20%), serum FLCr (20) and PET/CT scan were reliable in predicting the prognosis of smoldering MM. New techniques like B-cell maturation levels(74.4 ng/mL), evolving M-proteins and evolving hemoglobin levels can play a significant role in proposing future risk predictive models of SMM. Role of immunoparesis and Bence Jones proteins is debatable.
Anwer:Seattle Genetics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; In-Cyte: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.