Introduction
Hypomethylating agents (HMAs), azacitidine (Aza) or decitabine, are standard treatment (Tx) for patients (pts) with higher-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (HR-MDS) not candidates for immediate allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). However, complete remission was only reported for 17% receiving Aza, and only half the pts are alive after 2 yrs (Fenaux et. al., 2009).
Venetoclax (Ven), a selective, potent, orally bioavailable BCL-2 inhibitor, has been shown to synergize with HMAs in preclinical studies in HR-MDS (Jilg et. al., 2016) and clinical studies in AML (DiNardo et. al., 2016), suggesting that the combination of Ven+Aza may be a promising approach for HR-MDS Tx. This ongoing, open-label, Phase 1b, dose-escalation study is evaluating the safety and preliminary efficacy of Ven+Aza for Tx-naive HR-MDS.
Methods
The study (NCT02942290) initially included a 3-arm randomized cohort. Data from this cohort included 10 pts treated with Ven (400 mg or 800 mg for 28 days) + Aza and 2 pts treated with Aza alone. Following two deaths (Ven 400 mg=1/5 and Ven 800 mg=1/5), the study was amended to a dose-escalation and safety expansion design to determine the recommended Phase 2 dose (RP2D) of Ven+Aza. Key inclusion criteria were age ≥18 yrs, no prior therapy for MDS, IPSS score of ≥1.5, bone marrow blasts <20%, ECOG score of ≤2, and excluded pts with chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and pts who were candidates for undergoing intensive chemotherapy or allogeneic HSCT. In the dose escalation portion, cohorts were enrolled with escalating doses of Ven administered orally for the first 14 days of each 28-day cycle with cohorts from 100 mg daily up to 400 mg daily. Pts started at 100% of the prescribed Ven dose without intraindividual ramp up. Aza was administered at the std dose (75 mg/m2, subcutaneously or IV) from Day 1-7 per 28-day cycle. Primary study objectives were to evaluate safety and determine the RPTD schedule of Ven+Aza. Key secondary efficacy outcomes include objective response rate (ORR[complete remission (CR) + marrow complete remission (mCR) + partial remission]), progression free survival (PFS), time to response (TTR), duration of response (DOR), and overall survival (OS).
Results
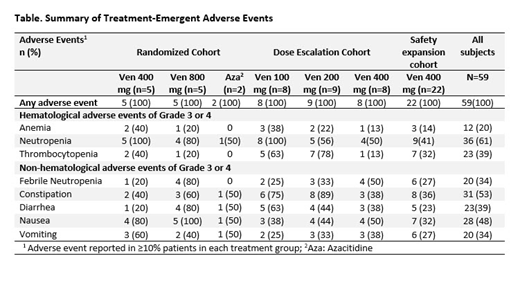
As of April 9, 2019, 59 pts have been treated and dose-escalation is complete. These included 12 pts in the initial randomized cohort. The dose-escalation cohort included 25 pts (Ven 100 mg=8, Ven 200 mg=9, Ven 400 mg=8) and the safety expansion included 22 pts. Results are presented for all 59 pts [75% male, median age 71 yrs (range 26-85)]. At baseline, 15 (25%) pts had an overall IPSS score of 1.5, 29 (49%) had a score of 2, 8 (14%) had a score of 2.5, 6 (10%) had a score of 3.0, and 1 (2%) pt had a score of 3.5. Eleven (19%) pts had intermediate and 24 (41%) pts had poor baseline cytogenetic risk.
In treated pts, the most common treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAE's) were anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia (Table). Common gastrointestinal symptoms were constipation, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting. Infection was predominantly febrile neutropenia. Predominant Grade 3 or 4 AEs included neutropenia (61%), thrombocytopenia (39%), leukopenia (31%), and anemia (20%). Major SAEs were febrile neutropenia (31%). There were 10 deaths of which 4 were due to infections (pneumonia-2, neutropenic sepsis-1 and septic shock- 1). Other causes of death were multiorgan failure (n=1), respiratory failure (n=1), progressive disease (n=3), and unexplained death (n=1). Twenty pts discontinued the study including 10 who underwent transplantation.
Among 57 pts evaluable for response, the ORR with (CR) was documented in 18, mCR in 22 , and stable disease (SD) in 11. Disease progression was observed in 2 pts. Median TTR for ORR was 1.0 mos (range 0.7-3.5 mos). At this data cut, the median time to FU was 4.3 mos (range 3.3-6.5 months). Median DOR, PFS and OS were not reached. With this short follow up, the 12-mo estimates for DOR for ORR was 74% (95% CI: 34%, 92%) and PFS was 59% (95% CI: 31%, 79%). The 18-mo estimate for OS was 74% (95% CI: 50%, 87%). Among 56 pts eligible for hematological improvement (HI), 28 (50%) patients achieved HI as either HI-erythroid, HI-platelet, or HI-neutrophil.
Conclusion
The combination therapy of Ven+Aza demonstrated a tolerable safety profile and promising efficacy in pts with HR-MDS. The maximum tolerated dose of Ven without dose-limiting toxicities was determined to be 400 mg in this HR-MDS population.
Wei:Pfizer: Honoraria; Astellas: former employee, Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; AbbVie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Research Funding; Walter and Eliza Hall Institute: Other: former employee, Patents & Royalties: receives a fraction of its royalty stream related to venetoclax; Macrogenics: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria. Garcia:Abbvie: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding. Borate:Pfizer: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy. Fong:Novartis: Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Astellas: Consultancy. Baer:Al Therapeutics: Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Forma: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Nolte:Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding. Peterlin:AbbVie Inc: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Jazz Pharma: Consultancy; Daiichi-Sankyo: Consultancy. Jurcic:Incyte: Consultancy; AbbVie Inc: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy; Astellas: Research Funding; Syros Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Actinium Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; Forma Therapeutics: Research Funding; Kura Oncology: Research Funding. Garcia-Manero:Amphivena: Consultancy, Research Funding; Helsinn: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; AbbVie: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astex: Consultancy, Research Funding; Onconova: Research Funding; H3 Biomedicine: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding. Hong:Roche: Equity Ownership; Genentech Inc.: Employment, Equity Ownership. Platzbecker:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Odenike:Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Research Funding; Oncotherapy: Research Funding; Astra Zeneca: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Janssen Oncology: Research Funding; NS Pharma: Research Funding; CTI/Baxalta: Research Funding; Astex Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Dunbar:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Zhou:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Harb:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Tanwani:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Wolff:AbbVie Inc: Employment, Other: Stock/stock options. Jacoby:Celgene: Speakers Bureau; Novo Nordisk: Consultancy; Jazz Pharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Venetoclax is a BCL-2 inhibitor that is FDA-approved in some indications. This presentation will focus on venetoclax for treatment in myelodysplastic syndromes, which is not an approved indication.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract