Introduction: CLL is the most common chronic leukemia in the US, with nearly 20,000 new cases expected annually. Novel agents, such as ibrutinib, idelalisib, and venetoclax, have been approved in recent years and provide oral options for CLL. However, there is limited data regarding real-world treatment patterns with these novel agents. This study describes dose reduction and discontinuation rates, reasons for both, and outcomes, including overall survival (OS) and duration of therapy (DOT), in CLL patients treated with novel agents.
Methods: This is an analysis of a large retrospective cohort study of adult patients (≥ 18 years old) with CLL, treated with novel agents in the VHA from 10/01/2013 to 3/31/2018. Historical data were examined for up to 20 years prior to the enrollment period (10/01/1993 to 9/30/2013). Index date was defined as the date of novel agent initiation. The follow-up period was a minimum of 6 months post index date. Variables, collected via a structured EMR database, included patient demographics, and clinical and treatment characteristics. CLL diagnosis, molecular profiles, and reasons for dose reduction and discontinuation were abstracted by chart review. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize baseline characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes.
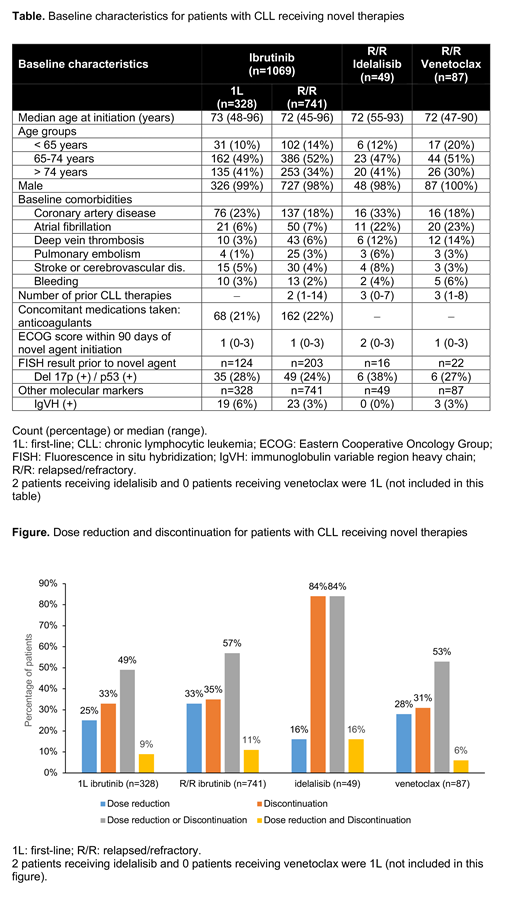
Results: A total of 1205 CLL patients were included in this analysis. Of these, in first observed line, 328 (27%) patients received ibrutinib; in relapsed/refractory observed line (r/r), 741(62%) patients received ibrutinib, 49 (4%) patients on idelalisib, and 87 (7%) patients on venetoclax. Ibrutinib patients in first observed line had a median (range) age of 73 (48-96) years and a median follow-up of 23 (3-54) months after treatment initiation. Dose reduction (n=83, 25%) and discontinuation (n=108, 33%) were frequently due to adverse events (AEs) (93% and 64%). Median DOT to ibrutinib discontinuation was 8 months. The most common AEs leading to dose reduction were major bleed (15%) and rash (15%). The most common AEs leading to discontinuation were atrial fibrillation (20%), major bleed (19%), and infection (11%). The calculated median OS from initiation was 31 (14-49) months. R/R ibrutinib patients had a median age of 72 (45-96) years and had 31 (2-85) months of follow-up after treatment initiation. Dose reduction (n=242, 33%) and discontinuation (n=263, 35%) were frequently due to AEs (89% and 63%). Median DOT to ibrutinib discontinuation was 12 months. The most common AEs leading to dose reduction were thrombocytopenia (13%), arthralgia/myalgia (13%), and infection (12%). The most common AEs leading to discontinuation were atrial fibrillation (19%), infection (15%), and major bleed (11%). the calculated median OS from initiation was 39 (9-57) months. R/R idelalisib patients (n=49) had a median age of 72 (55-93) years and had 27 (3-53) months of follow-up after treatment initiation. Dose reduction (n=8, 16%) and discontinuation (n=41, 84%) were frequently due to AEs (100% and 54%). Median DOT to idelalisib discontinuation was 5 months. The most common AE leading to dose reduction was neutropenia (50%). The most common AEs leading to discontinuation were infection (27%) and pneumonia (18%). R/R venetoclax patients (n=87) had a median age of 72 (47-90) years and had 9 (0-35) months of follow-up after treatment initiation. Dose reduction (n=24, 28%) and discontinuation (n=27, 31%) were frequently due to AEs (100% and 41%). Median DOT to venetoclax discontinuation was 5 months. The most common AEs leading to dose reduction were neutropenia (27%) and thrombocytopenia (27%). The most common AEs leading to discontinuation were neutropenia (36%), thrombocytopenia (18%), and infection (18%). There was not enough follow-up time to have a meaningful OS in this cohort.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the largest EMR/chart review study among CLL patients initiating treatments in the real-world setting. This study provides evidence regarding patient characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes among patients initiating novel agents for the treatment of CLL in the national VHA population. Dose reduction and discontinuation were frequent across all novel agents, with AEs as the most common reason. These data highlight the significant difference in real world data compared with clinical trial data and indicate the unmet need for more tolerable treatment options for CLL patients.
Frei:AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Le:AstraZeneca: Employment, Other: Stocks. McHugh:AstraZeneca: Employment. Elesinmogun:AstraZeneca: Employment, Equity Ownership. Obodozie-Ofoegbu:UT Austin: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.