Introduction. In multiple myeloma (MM), the presence of translocation t(4;14) and/or 17p deletion, found in around 10 to 15% of the patients, is considered as high-risk feature associated with adverse survival. Despite recent advances in the treatment of MM, t(4;14) and del(17p) are still associated with poor outcome. The aim of this study was to analyze the trends of survival in patients with newly diagnosed MM harboring t(4;14) and or 17p deletion over the past two decades.
Methods. Patients from five French centers with newly-diagnosed MM from 2001 to 2019 and displaying del(17p) and/or t(4;14) were retrospectively included. Cytogenetics abnormalities were detected by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and del(17p) positivity cut-off was 30%. New agents were defined as: pomalidomide, carfilzomib, ixazomib and anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies.
Results. 246 patients carrying either t(4;14) (n=106 patients), del(17p) (n=121 patients) or both (n=19 patients) were included. Median age was 64 years (range, 35-91). ISS and R-ISS score were 3 in 88 patients (36%). Eighty-seven patients (35%) were diagnosed in 2001-2010 period, and 159 (65%) in 2011-2019 period. Front-line autologous stem-cell transplantation (ASCT) was performed in 121 (49%) patients. Among transplant eligible patients, 112 patients (n=93%) received triplet induction, 78 patients (64%) a consolidation regimen and 15 patients (12%) a maintenance therapy. Double-ASCT was decided in 21 patients (17%). Among transplant ineligible patients, 61 patients (49%) received melphalan-based regimen in first line, 36 (29%) a bortezomib-based and 15 patients (14%) a lenalidomide-based regimen. At any line, 92 patients (37%) received at least one of the new agents with only 12 patients (5%) in frontline therapy.
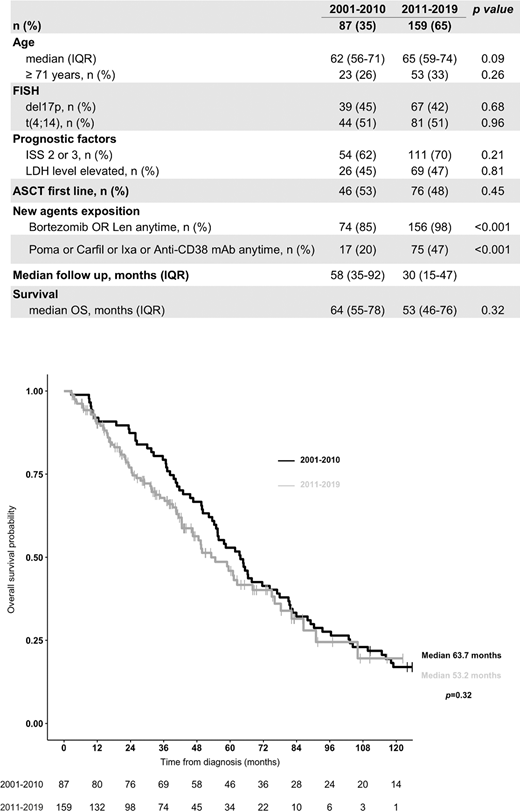
Median follow-up was 41 months (IQR: 21-69). Median overall survival (OS) was 58.4 months (IQR: 50.1-66.5) for the entire cohort, 55.5 months (IQR: 46.6-78.3) for del(17p), 62.5 months (IQR: 54.2-76.1) for t(4;14) and 48.6 months (18.1-not reached) for patients with both (p=0.2). Median of first progression-free survival (PFS1) was 25.6 months (IQR: 22.2-29.8), with no difference between del(17p), t(4;14) or both (p=0.57). Importantly, no improvement of median OS was observed in patients diagnosed between 2001-2010 in comparison with patients diagnosed between 2011-2019 (63.7 versus 53.2 months, p=0.32). In univariate and multivariate analysis: age (continuous and cut-off 71 years-old) and ASCT significantly were associated with risk of death (HR: 1.03, 1.09 and 0.45, respectively). Median OS of patients eligible to ASCT was 76.1 months (IQR: 62.5-90.3) vs 42.5 months (IQR: 36.8-54.6) for patients not eligible (HR 0.45, 95%CI 0.28-0.0.71; p<0.001). Double-ASCT did not improve significantly OS (75 vs 81.1 months ; p=0.41) and PFS1 (31.6 vs 47.8, p=0.30) compared with single-ASCT.
Conclusion. This large multicenter real-world study confirms that patients with newly diagnosed MM carrying del(17p) and/or t(4;14) remain a therapeutic challenge with no significant overall survival improvement in the past decades despite the use of novel agents. The definition of high-risk MM patients is evolving with incorporation of new markers (i.e chromosome 1 abnormalities, PET-imaging). Minimal-residual disease achievement will also re-defined risk stratification. Nonetheless, the need for innovative approaches such as earlier strategies using new agents or immunotherapy (CAR-T cells, bispecific T-cell engager antibodies) may significantly improve outcomes.
Figure captions
Table 1. Clinical, biological characteristics, treatment and survival of the 246 included patients based on period of diagnosis.
IQR: interquartile range; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization; ISS: international score system; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; ASCT: autologous stem cell transplantation; len: lenalidomide; Poma: pomalidomide; Carfil: carfilzomib; Ixa: ixazomib; mAb: monoclonal antibodies; OS: overall survival
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curves for overall survival for the 246 included patients based on period of diagnosis.
Moreau:Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria. Touzeau:Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; GlaxoSmithKline: Honoraria, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.