Introduction: The activity of immune checkpoint blockade including anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein-4 and anti-programmed cell death protein-1 monoclonal antibodies in hematologic malignancies is limited outside of classical Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. Tumor mutational burden (TMB), programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression, and microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) are well-established biomarkers predicting response to checkpoint blockade in solid malignancies. In addition, tumors with high TMB, defined as ≥10 mutations/megabase (mut/Mb), and/or MSI-H are Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved tissue agnostic biomarkers for treatment with pembrolizumab. The frequencies of high TMB, MSI-H, and expression pattern of PD-L1 across specific hematologic malignancies are undefined.
Methods: Patients with hematologic malignancies who had next generation sequencing (NGS) performed by Foundation One Heme were identified. TMB and MSI were measured by NGS. TMB was classified as high if ≥10 mut/Mb and low if <10 mut/Mb. When available, PD-L1 expression on tumor cells by immunohistochemistry (IHC) was also collected. PD-L1 IHC was performed with either Ventana (SP142) PD-L1 antibody or Dako (22C3) PD-L1 antibody. Scores were classified as high (≥ 50%), low (1-49%), and negative (<1%) based on the percent of tumor cells staining positive for PD-L1. Pathology reports were retrospectively re-reviewed to determine the diagnosis.
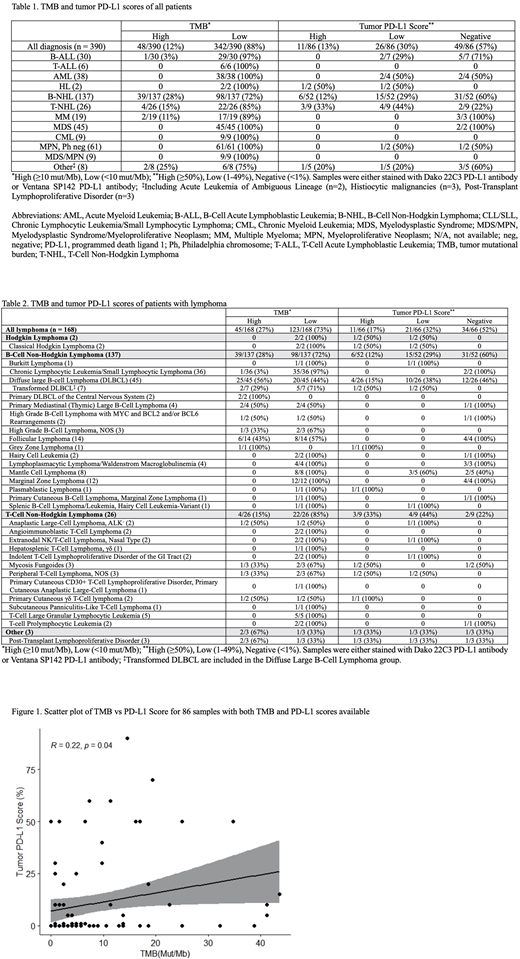
Results: A total of 390 patients with hematologic malignancies with NGS were identified. Forty eight of the 390 samples (12%) had a high TMB (Table 1). Twenty five of 45 (56%) patients with DLBCL had a high TMB (Table 2). The TMB was low in all myeloid malignancies tested. None of the 302 samples tested were MSI-H. PD-L1 IHC was performed on 86 samples. Eleven (13%) had high expression, 26 (30%) had low expression, and 49 (57%) had no expression of PD-L1 on the tumor cells (Table 1). The majority of samples with PD-L1 expression were mature lymphomas (81%). TMB and PD-L1 score had a significant linear relationship (R = 0.22,p= 0.04, 95% CI 0.01 - 0.41) (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This study provides detailed characteristics of TMB, MSI status, and PD-L1 expression for hematologic malignancies. Notably, a subset of lymphomas had high TMB and/or PD-L1 expression. Biomarker driven studies of checkpoint blockade in hematologic malignancies with high TMB and/or PD-L1 expression are warranted.
Sokol:Foundation Medicine:Current Employment;Roche:Current equity holder in publicly-traded company.Kurzrock:Medimmune:Research Funding;Foundation Medicine:Research Funding;Konica Minolta:Research Funding;IDbyDNA:Current equity holder in private company;Pfizer:Consultancy, Research Funding;Sequenom:Research Funding;Bicara Therapeutics, Inc.:Consultancy;Incyte:Research Funding;Takeda:Research Funding;TopAlliance:Research Funding;Boehringer Ingelheim:Research Funding;CureMatch Inc:Current equity holder in private company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;Grifols:Research Funding;Guardant:Research Funding;X Biotech:Consultancy;Neomed:Consultancy;Actuate Therapeutics:Consultancy;Roche:Consultancy;Merck Serono:Research Funding;Genentech:Research Funding;Debiopharm:Research Funding;CureMetrix:Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees;OmniSeq:Research Funding;TD2/Volastra:Consultancy;Turning Point Therapeutics:Consultancy.Goodman:EUSA Pharma:Consultancy;Seattle Genetics:Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.