Introduction: Individuals with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are often immunosuppressed and at increased risk of infection and secondary malignancies. The primary aim of this study was to determine the incidence of skin cancer amongst the CLL population at Kingston Health Sciences Centre (KHSC), Ontario, Canada. Secondly, we sought to identify the risk factors associated with the development of skin cancer in CLL patients.
Methods: Consecutive patients seen at KHSC with a diagnosis of CLL between 2014 January 1 and 2019 December 31 formed the primary study cohort. KHSC serves a region of ~ 550,000 including a high proportion of older individuals and those living in rural areas. Approval was provided by Queen's University Research Ethics Board. Four independent reviewers conducted retrospective electronic chart review, initially in duplicate with review of any areas of discrepancy to ensure a standardized approach. Data collected included age, sex, CLL date of diagnosis, stage, genetics and treatment; histological diagnoses of other cancers (skin and other), smoking status (ever/never) and date of last follow up or death. The primary outcome was the development of the first skin cancer (squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, or sarcoma) confirmed via pathology reports that are available in our local institution. All statistical analysis was performed using SAS Enterprise v. 7.15. Categorical variables were compared using chi-square or Fisher exact tests, medians using Wilcoxon and Mann-Whitney tests, and continuous variables using t-tests. Risk factors for development of skin cancer were assessed using multivarable Cox-proportional hazard models.
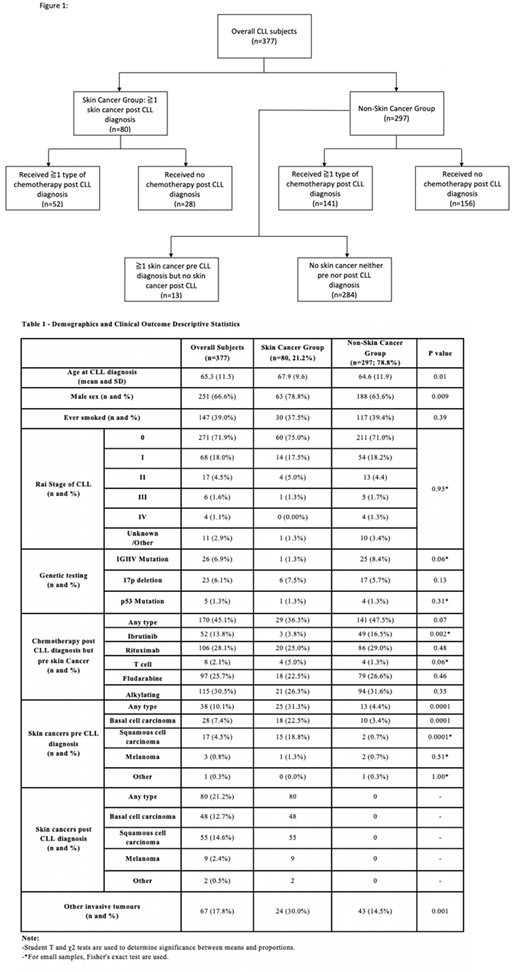
Results: Of the total cohort of 377 individuals with CLL, 251 (67%) were male. Median age at diagnosis of CLL was 65 years (range 36 - 93 years of age). Median follow-up from the time of CLL diagnosis was 6.5 years (range 0.27 - 30.98). Of these, 80 individuals (21.2%) developed at least one skin cancer after their diagnosis of CLL, with an age-adjusted incidence of 16.96/1000 patient years (95% CI 12.5 - 23). Among the 297 who did not develop skin cancer post-CLL diagnosis, 13 individuals who had documented skin cancer pre-CLL diagnosis only, are included in the non-skin cancer group (Figure 1). Females had a lower incidence of skin cancer compared with males (63 males versus 17 females, p=0.009). There was no difference between the groups based on Rai stage at diagnosis, smoking history, or IGHV /p53 status. Individuals treated with ibrutinib had a lower incidence of skin cancer (3 versus 49, p=0.002). Development of skin cancer was associated with development of other invasive tumours including CLL transformation (p=0.001) (Table 1).
Conclusion: Limitations of this study include its small size, and single institution setting. Our data likely reflect a conservative estimate as skin cancers may be diagnosed outside of the institution, and not all CLL is treated at tertiary care centres. Consistent with other studies we found that males with CLL are at increased risk of developing skin cancer, as compared to females. Individuals with CLL and skin cancer were more likely to develop another malignancy or Richter's transformation. The finding of lower incidence of skin cancer with ibrutinib treatment is novel; further investigation in larger populations is needed to determine if it may offer a protective effect.
Asai:Sanofi Canada: Honoraria, Research Funding; AllerGen NCE: Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria; Leo Pharma: Honoraria; Eli Lilly: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Canadian Institutes of Health Research: Research Funding. Hay:Roche: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.