Background: CPX-351 is a liposomal encapsulation of daunorubicin and cytarabine in a 1:5 molar ratio. In a randomized phase 3 study (CPX-351-301) conducted in older adults (60 to 75 years old) with newly diagnosed, high-risk and/or secondary AML, CPX-351 induction therapy was superior to standard 7+3 with improved rates of complete remission (CR) and overall survival (OS). In both older adults and high-risk AML, allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is frequently the preferred post-remission strategy owing to the high rates of relapse and poor overall survival with conventional chemotherapy approaches. After a median follow-up of 20.7 months, the primary pre-planned analysis found that more patients randomized to CPX-351 underwent HCT and an exploratory landmark survival analysis from the time of HCT favored CPX-351 (HR = 0.46 [95% CI: 0.24, 0.89]; one-sided P = 0.009). However, the initial protocol did not collect data related to HCT and the basis for improved HCT outcomes with CPX-351 was previously unknown. Here we present a detailed analysis of HCT outcomes in patients enrolled in the CPX-351-301 study with 5-years of follow-up.
Methods: Patients age 60 to 75 years with high-risk and/or secondary AML were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive CPX-351 or 7+3 as induction and consolidation chemotherapy (Lancet J et al, JCO 2018). The protocol was amended to collect additional HCT-specific information, including donor and HCT characteristics and post-HCT outcomes, including rates of relapse and GVHD. Post-HCT outcomes including relapse, GVHD, and death were analyzed as competing events.
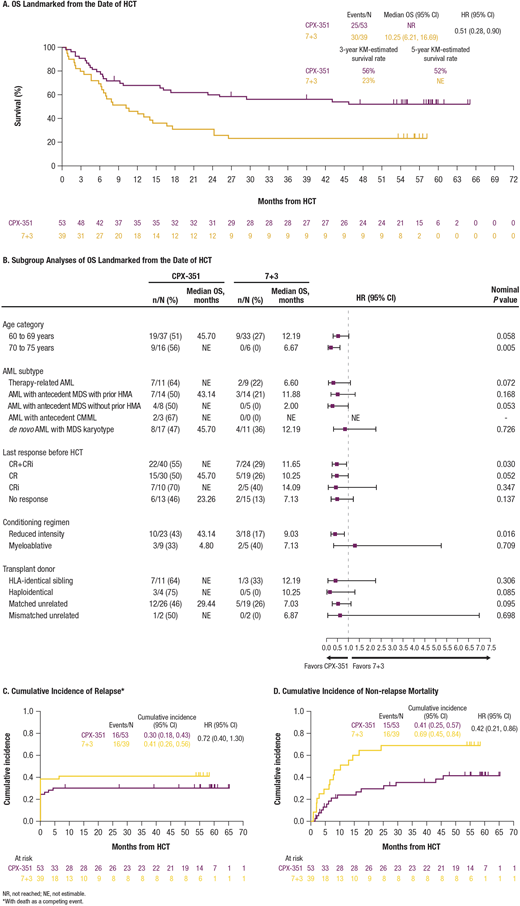
Results: Of 309 randomized patients in the CPX-351-301 study, more patients achieved CR/CRi with CPX-351 vs 7+3 (48% vs 33%) allowing more patients to proceed to HCT (35% vs 25%) and more patients to proceed to HCT in remission (CPX-351: 41/73 [56%]; 7+3: 24/52 [46%]). The median age was 66 years with CPX-351 vs 65 years with standard induction among the transplanted cohorts; 16 patients in the CPX-351 transplanted arm were over the age of 70 compared to only 6 in the 7+3 arm. Other pre-HCT patient characteristics were balanced between the CPX-351 and 7+3 groups, including ECOG performance status (8% vs 5% with ECOG PS of 2), HCT-CI (median 4 vs 3), donor type (matched unrelated donor 49% vs 49%), and conditioning regimen intensity (myeloablative [17% vs 13%] vs reduced-intensity conditioning [43% vs 46%]). The Kaplan-Meier-estimated 3-year survival rate among transplanted patients was 56% with CPX-351 vs 23% with 7+3 (Figure 1A). The differences in survival consistently favored CPX-351 across patient age, AML subtype, disease status, donor type, and conditioning intensity (Figure 1B). Differences in OS were driven by a large reduction in non-relapse mortality (HR = 0.42 [95% CI: 0.21, 0.86]; Figure 1D). The cumulative incidence of acute GVHD with death as a competing event at 6 months from HCT date was 0.49 (95% CI: 0.35, 0.62) in the CPX-351 arm and 0.38 (95% CI: 0.23, 0.53) in the 7+3 arm.
Conclusions: Analysis of HCT outcomes in patients enrolled in the CPX-351-301 study demonstrated that treatment with CPX-351 in older adults with high-risk and/or secondary AML resulted in more patients bridged to HCT and more patients transplanted in CR/CRi compared to 7+3, with improved OS in transplanted patients. The pattern of HCT outcomes suggests improved disease control with CPX-351 induction allowing higher HCT rates, but more importantly improved tolerability with less non-relapse mortality; this data supports the development of CPX-351 in other high-risk AML populations in which allogeneic HCT is the preferred post-remission strategy.
Uy:Genentech: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Astellas Pharma: Honoraria; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy. Lin:Abbvie: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Trovagene: Research Funding; Prescient Therapeutics: Research Funding; Tolero Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Ono Pharmaceutical: Research Funding; Genetech-Roche: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Jazz: Research Funding; Mateon Therapeutics: Research Funding; Gilead Sciences: Research Funding; Celyad: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Bio-Path Holdings: Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Research Funding; Aptevo: Research Funding. Wieduwilt:Reata Pharmaceuticals: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company; Daiichi Sankyo: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Leadiant: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Macrogeneics: Research Funding. Ryan:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Faderl:Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Lancet:Abbvie: Consultancy; Agios Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy, Honoraria; Astellas Pharma: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; ElevateBio Management: Consultancy; Jazz Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.