Abstract
Aggressive B cell lymphomas often require prompt steroid treatment prior to baseline 18f-fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography (PET CT) scan and definitive treatment in order to alleviate symptoms and/or prevent organ damage. Since lymphomas are a steroid sensitive malignancy, there is a concern that steroid prophase might affect PET CT results and diagnostic yield.
We conducted a retrospective cohort study to evaluate the effect of steroid treatment prior to baseline PET CT scan on the standardized uptake value (SUV) max and additional PET CT parameters by examining two groups of patients: steroid-naïve and steroid-treated patients. The effect of steroid administration on SUV max was examined across different daily and weekly steroid doses and durations of treatment.
Between January of 2017 and May 2020, 187 newly diagnosed patients with aggressive B cell lymphoma who had a pre-treatment PET CT scan were evaluated. 160 patients (85.5%) had Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL)/ High-grade B-cell lymphoma, 13 patients (7%) had primary mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma, 9 patients (4.8%) had primary DLBCL of the central nervous system and 5 patients (2.7%) had Burkitt lymphoma.
132 patients (70.6%) were included in the steroid-naïve group and 55 patients (29.4%) in the steroid-treated group. In the steroid-treated group, the mean duration of steroid treatment was 10.49 (±9.28) days. Average daily dose of steroid treatment was equivalent to 72.27 (±36) mg of prednisone and the mean cumulative prednisone dose during the week prior to PET CT scan was equivalent to 367.95 (±239.9) mg of prednisone.
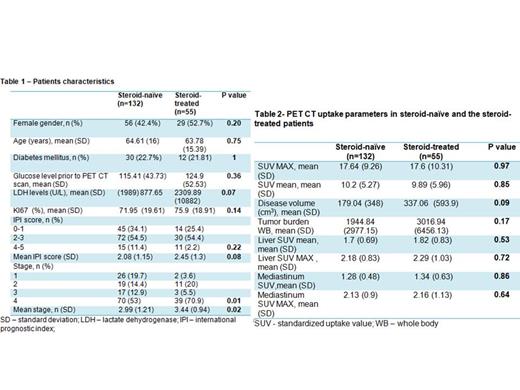
There was no statistical significant difference between the groups in age, gender or KI67. However, patients in the steroid treated group had a significantly higher stage of disease compared to the steroid-naïve group (mean 3.44 compared to 2.99, respectively, p=0.01). The steroid-treated group also had a trend towards a higher IPI score (mean 2.45 versus 2.08, p=0.08) and a trend towards a higher LDH level (mean 2309.89 U/L, range 250-81374 versus mean 877.65 U/L, range 272-22036, p= 0.07), as depicted in table 1.
There was no statistical difference in SUV max between the steroid-naïve and steroid-treated groups (p=0.97). This was consistent across various steroid treatment durations and dosage regimes. Patients in the steroid-treated group had a trend towards a higher tumor burden and a larger tumor volume compared to the steroid-naïve group, however it did not reach statistical significance. Mean tumor volume was 179.04 cm 3 in the steroid naïve group and 337.06 cm 3 in the steroid treated group (p=0.17). Mean tumor burden was 1944.84 in the steroid-naïve group and 3016.94 in the steroid-treated group (p=0.09).
There was no difference in additional PET CT parameters including SUV mean, SUV max and SUV mean of liver and mediastinum between the groups as depicted in table 2.
In conclusion, in aggressive B cell lymphoma, pre-treatment with steroids prior to initial PET CT scan does not affect SUV max or other PET CT parameters and does not reduce PET CT diagnostic yield.
Gurion: Medison: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences: Consultancy; Takeda Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; JC Health Care: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria.