Abstract
Introduction: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a disease of inhibited cell death, increased proliferation and high importance of interactions with the microenvironment e.g. with T-cells or stromal cells. A central effector in this concert is the activation of B-cell receptor (BCR) signalling pathway, associated with selection of specific BCR qualities (either autonomous signalling or reactivity to chronic (auto)-antigenic stimuli) and these signals play an essential role in CLL disease development and progression, also evidenced by the clinical success of kinase inbibitors directed at this signal. Mechanisms modulating selection of specific BCR types are ill understood, but since checkpoints during BCR selection in B cells are guarded by the Bcl2 family of proteins it is likely that cell death proteins are also influencing these decisions in CLL. To study the importance of microenvironmental interactions and antigen stimulation Tcl1 tg mice, which develop a murine CLL highly similar to the human disease 1,2, were frequently applied in the past, aiming to overcome the limitations of more or less artificial CLL in vitro culture systems. During clonal evolution of CLL, predominantly unmutated and stereotyped IgVH-11 and IgVH-12 BCRs are selected in Tcl1 tg mice which were shown to be specific for the autoantigen phosphatidylcholine (PtC) 3, however, the detailed mechanisms of clonal selection in CLL are still unclear. Here we propose a role of the BH3-only and pro-apoptotic protein Bmf in clonal selection by eliminating CLL cells expressing highly responsive BCRs.
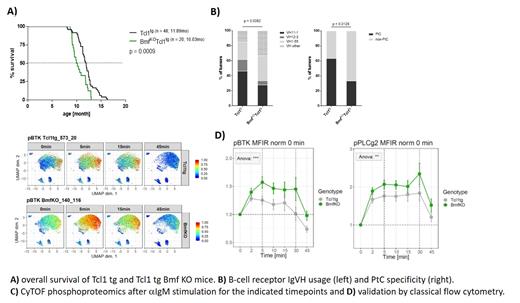
Methods: Tcl1 tg mice were crossed to Bmf knockout (KO) mice and CLL development monitored over time. After establishment of overt leukemia, mice were sacrificed and the overall survival time analysed. Additionally, we performed BCR sequencing, RNA-Seq and phosphoproteomics after 10µg/ml aIgM treatment using mass cytometry (Helios, CyTOF) and flow cytometry.
Results: We found that Tcl1 tg Bmf KO mice developed phenotypically unchanged murine CLL but had an earlier onset of disease (Figure 1A) and an altered usage of BCR IgVH genes. While Tcl1 tg mice usually use PtC specific IgVH genes from the VH11 and V12 family, absence of Bmf led to a skewing to non PtC specific IgVH genes, mainly form the VH1 family (Figure 1B). We thus speculated that lack of Bmf favoured the selection of CLL clones with hyper responsive BCRs, when compared to Tcl1 tg mice with functional Bmf. Indeed we could show that after aIgM stimulation Tcl1 tg BmfKO CLL cells showed increased BCR signalling as measured by mass cytometry (Figure 1C), which was also confirmed by conventional flow cytometry (Figure 1D). Importantly, strong BCR stimulation induces cell death in B cells. Indeed, this can be observed in CLL cells from Tcl1 mice. In Tcl1 tumors that are deficient for BMF this cell death induction is not observed, suggesting that loss of Bmf protects from excessive cell death due to strong BCR stimulation.
Conclusions: Here we report a novel role of Bmf in the selection of BCR clones in murine CLL. The higher BCR signalling capacity and the skewing of IgVH gene usage in the absence of Bmf indicates that highly responsive BCR clones are more often selected instead of eliminated during clonal selection.. Interestingly, a SNP in the Bmf gene has been reported to be susceptibility locud for CLL, suggesting that low expression of BMF may have similar effects in huma CLL. Indeed, in preliminary analyses, we observed a similar contribution of Bmf in clonal selection and BCR responsiveness in human CLL and decreased resistance to the BCR signalling inhibitor ibrutinib. Therefore our findings might also be important in a clinical context.
References:
1. Yan XJ, Albesiano E, Zanesi N, et al. B cell receptors in TCL1 transgenic mice resemble those of aggressive, treatment-resistant human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. ProcNatlAcadSciUSA. 2006;103(31):11713-11718.
2. Hofbauer JP, Heyder C, Denk U, et al. Development of CLL in the TCL1 transgenic mouse model is associated with severe skewing of the T-cell compartment homologous to human CLL. Leukemia. 2011;25(9):1452-1458.
3. Chen SS, Batliwalla F, Holodick NE, et al. Autoantigen can promote progression to a more aggressive TCL1 leukemia by selecting variants with enhanced B-cell receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(16):E1500-1507.
Greil: Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Daiichi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Sankyo: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Sandoz: Honoraria, Research Funding.