Abstract
Introduction: Pulmonary complications constitute a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the post-hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) period. While Chest X-ray (CXR) is customarily used for screening, we have utilized chest computed tomography (CT) within one month of transplant. Here we aim to characterize the prevalence of abnormalities and their impact on the eligibility for allogenic (allo) HCT and outcomes post-transplant.
Methodology: We conducted a single center retrospective study of all patients who were evaluated for allogenic HCT from January 2013 through December 2020 in New York Presbyterian Hospital - Weill Cornell Medicine (NYP-WCM). All patients who had chest CT as part of their pre-transplant evaluation were included for analysis.
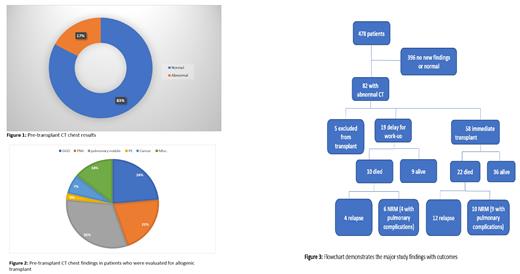
Results: We identified 478 patients who had Chest CT screening. In 396 CT chest was normal or confirmed previous abnormalities. Eighty-two patients (17%) had previously undetected abnormalities (Figure 1). The most frequent abnormalities were pulmonary nodules (defined as nodules of 4 mm or greater) in 27 patients (31%), ground-glass opacities (GGO) in 21 patients (25%), Pneumonia in 18 patients (21%). Miscellaneous findings not related to the primary disease were found in 12 patients (14%) including thyroid nodules, breast nodules and hemangioma of the liver. A new malignancy was found in 6 patients (7%) and incidental pulmonary embolism (PE) in 2 patients (2%) (Figure 2). There were 5 (6%) patients who were ultimately excluded from transplant due to CT chest findings (simultaneous CXR showed abnormalities in only 1 out of 5). Three of those patients were found to have invasive fungal infection, and the other two had unrecognized metastatic lung cancer. For 19 patients (23%), transplant was delayed for diagnostic procedure and/or treatment of pulmonary findings (CXR showed abnormalities in only 3 patients out of 19). The most common reason for delay was lung infection requiring treatment. Thirty-two patients (41%) out of 77 patients with abnormal CT scan who eventually underwent transplant, have died . Sixteen died after relapse, and 16 from non-relapse mortality (NRM) with pulmonary complications playing a role in 13 patients (Figure 3).
Conclusion: 17% of patients who had a pre-transplant CT chest had abnormalities that warranted further evaluation. In 23% of these patients, these findings led to a delay in transplant for further optimization. Six percent were deemed ineligible for transplant due to absolute contraindications that were incidentally discovered on chest CT. Initial screening CXR failed to identify a significant number of abnormalities. Our data suggests that chest CT imaging should be part of the routine pre-transplant evaluation.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.