Abstract
Background: WHIM (Wart, Hypogammaglobulinemia, Infections, Myelokathexis) syndrome is a rare, autosomal-dominant primary immunodeficiency with neutropenia and lymphopenia. The clinical presentation may include recurrent infections, and increased susceptibility to human papillomavirus. In >80% of cases, WHIM syndrome is caused by heterozygous gain-of-function (GOF) mutations in C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4), with >12 variants reported in WHIM syndrome to date (nonsense [NS], frameshift [FS], and missense[MS]) spanning 27 C-terminal amino acids . These mutations cause hyperactivation of downstream signaling and retention of WBC in the bone marrow (McDermott D, et al. Immunol Rev. 2019;287(1):91-102; Beaussant S, et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2012;7(71):1-14). To date, a comprehensive study characterizing the functional abnormalities caused by pathogenic CXCR4 mutations and correlating these measures with clinical presentation in patients has not been conducted. Here, we aimed to establish genotype-phenotype correlations for all known pathogenic variants using in vitro functional assays. These assays characterize CXCR4 receptor trafficking and downstream signaling, which will enable the long-term goal of assessing pathogenicity of novel CXCR4 variants of uncertain significance (VUS). We further aimed to assess the in vitro response of each variant to mavorixafor, an investigational CXCR4 antagonist.
Methods: We used the CXCR4-negative K562 cell line as a model system to express all 14 known CXCR4 variants identified in patients diagnosed with WHIM syndrome (previous reports, ClinVar, and genetic screening initiatives [Invitae PATH4WARD]). The effects of the mutations on CXCR4 receptor trafficking (internalization and degradation), downstream signaling (Ca 2+ mobilization, cAMP inhibition, ERK and AKT activation), and chemotaxis were studied in parallel in a series of assays in cells stimulated with the natural ligand CXCL12. All in vitro functional parameters characterized were investigated for potential correlations with the clinical phenotypes reported for each variant, including disease manifestations and biomarkers.
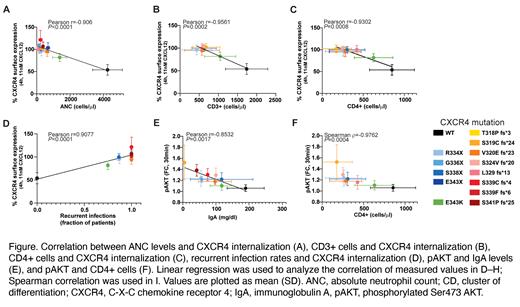
Results: The most conserved feature of the 14 CXCR4 variants was an impaired receptor internalization in response to CXCL12, evidenced by higher percentage of CXCR4 receptors remaining on the cell surface compared to untreated control, with truncated variants showing maximum impairment and the MS variant E343K being least affected. The decreased CXCR4 internalization correlated with both decreased CXCR4 degradation and increased cAMP inhibition. When stimulated with CXCL12, most variants demonstrated a higher amplitude and duration of ERK and AKT activation. Chemotactic responses to CXCL12 were diverse, depending on the variant sequence and subtype. While Ca 2+ mobilization was not enhanced compared to wild-type (WT) CXCR4-expressing cells in this assay, mavorixafor demonstrated inhibition of Ca 2+ mobilization in all CXCR4 mutant cells with a trend toward greater effect in the NS variants. In addition, both ERK and AKT activation decreased with increasing concentration of mavorixafor. Correlation analyses of the functional parameters in cells expressing mutated or WT CXCR4 and clinical manifestations or WBC counts in patients with these mutations revealed that the CXCR4 internalization defect strongly correlated with severity of peripheral blood cytopenias (ie, decreases in absolute neutrophil counts, and in CD3+ and CD4+ T-cell levels), which was paralleled by an increased susceptibility to recurrent infections. In addition, AKT hyperactivation correlated with lower IgA and decreased CD4+ T-cell levels (Figure).
Conclusions: In the current study, we performed a detailed functional analysis of the entire spectrum of CXCR4 WHIM mutations known to date. In vitro CXCR4 receptor internalization correlates with WBC cytopenias and an increased susceptibility to recurrent infections in patients with CXCR4 GOF mutations. These data suggest that CXCR4 internalization and AKT activation may be used as key assays for the assessment of CXCR4 variant pathogenicity in vitro and potentially as WHIM-related disease biomarkers. Additionally, all tested CXCR4 variant cell lines were sensitive to mavorixafor at clinically relevant concentrations, rescuing defective GOF signaling toward that of WT CXCR4-expressing cells.
Zmajkovicova: X4 Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Maier-Munsa: X4 Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment. Maierhofer: X4 Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment. Taveras: X4 Pharmaceuticals: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Badarau: X4 Pharmaceuticals: Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Ended employment in the past 24 months.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract