Abstract
Background:
Venetoclax plus hypomethylating agents (HMA) (HMA+VEN) is a standard of care treatment for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are unfit for intensive chemotherapy. In the phase 3 VIALE-A trial, azacididine (aza)+VEN compared to aza alone demonstrated an improved overall survival of 14.7 months versus 9.6 months, respectively. A common toxicity with HMA+VEN is myelosuppression. The prognostic implications of incomplete count recovery despite leukemia free state after HMA+VEN treatment in AML is unclear. We aimed to compare the outcomes of those who achieved complete remission (CR), complete remission with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi), or morphologic leukemia-free state (MLFS) in AML patients treated frontline with HMA+VEN.
Methods:
Patients seen at Moffitt Cancer Center between 2019 and 2021 diagnosed with AML and treated with frontline HMA+VEN were retrospectively evaluated and included for analysis. Patients were stratified by best response; either CR, CRi, or MLFS. Baseline characteristics were compared by chi square (categorical variables) and t- test (continuous variables). Survival estimates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method from date of diagnosis and groups were compared using log-rank test.
Results:
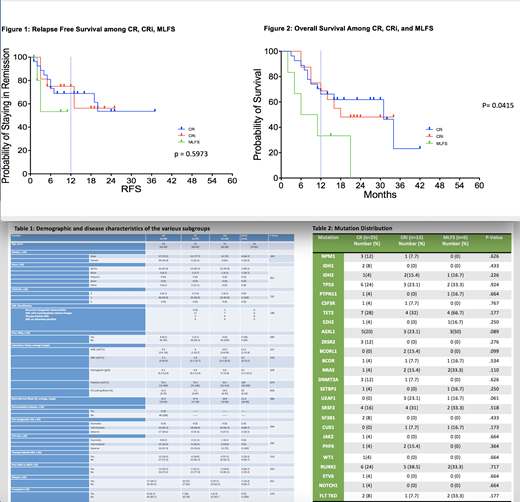
Of the 102 patients treated with HMA+VEN in the frontline setting, 48% (n=49) had blast clearance with a best response of CR in 27/102 (26.4%), CRi in 16/102 (15.7%), or MLFS in 6/102 (5.9%). The remainder had residual disease. Baseline characteristics were similar among the three response groups (Table 1) as was mutational distribution (Table 2). There was no difference between AML WHO classification subtype (p= .148). Decitabine or aza was used at the discretion of the treating physician did not significantly impact responses (p= .225). In those who achieved CR, 14% had prior therapy related AML compared to 37.5% in CRi and 33.3% in MLFS (p= .314). Antecedent MDS or MPN with transformation to AML was seen in 22.2%, 18.8%, and 66.7% of CR, CRi, and MLFS respectively (p= .029). Of those, 3.7% in CR group had HMA use for prior MDS/MPN compared to 0% in CRi and 50% in MLFS (p= .000). The median relapse free survival was not reached for CR, CRi, and MLFS (Figure 1), it is important to note that 3 of the 6 MLFS patients died without relapse . At median follow up of 23 months, median overall survival (OS) in the CR group was significantly longer, 31 months, compared to 18 months in the CRi group and 8.5 months in the MLFS group (p=0.0415) (Figure 2). Transplant was achieved in 26% of CR and 6.3% of CRi and 0% of MLFS and was not significant among the groups (p = .124).
Conclusion:
Patients who received frontline HMA+VEN for AML directed therapy and achieved CR/CRi had better survival compared to those who achieved MLFS. Our data suggest that incomplete recovery of blood counts plays a significant role in overall survival regardless of leukemia free state. Further, the data demonstrate significantly higher secondary AML with antecedent MDS or MPN in the MLFS group compared to CR and CRi groups. Of those, prior HMA therapy was also identified as significantly higher in the MLFS group compared to CR and CRi groups which may contribute to the prolonged cytopenias and worse OS. While the limitation to this study is overall small number of patients, it suggests that a goal of CR over CRi or MLFS is desirable for superior OS. In the future, it would be of interest to incorporate the rates of responses and variables that may have an impact such as therapy dose adjustment, time to response, and delays in therapy due to cytopenia. Additional studies identifying dose adjustments or other ways to improve hematologic recovery would be valuable to potentially improve outcomes in this difficult to treat population.
Padron: Stemline: Honoraria; Taiho: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding; Blueprint: Honoraria; Kura: Research Funding. Sallman: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy; Shattuck Labs: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Intellia: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aprea: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Syndax: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Magenta: Consultancy; Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Komrokji: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AbbVie: Consultancy; Acceleron: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Geron: Consultancy; BMSCelgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Taiho Oncology: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; PharmaEssentia: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Lancet: AbbVie: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Millenium Pharma/Takeda: Consultancy; ElevateBio Management: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy; BerGenBio: Consultancy. Sweet: AROG: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.