Abstract
Background: Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is associated with an acquired hypercoagulopathy that drives venous thromboembolic comorbidities. The molecular mechanisms underlying NS-associated hypercoagulopathy are incompletely understood, however previous studies proposed marked urinary loss of antithrombin (AT) as a primary etiology. We have previously demonstrated, in rodent NS models, that there is no correlation between AT antigen and thrombin generation, which we have previously used to characterize the hypercoagulopathy. The objective of this study is to examine the association between AT antigen, AT activity, and hypercoagulopathy along with NS disease severity markers (proteinuria and plasma albumin) in 2 cohorts that include both pediatric and adult NS patients.
Methods: Plasma samples were obtained from both cohorts as follows: (1) Samples were obtained on presentation from 147 adult and pediatric patients participating in the NEPTUNE prospective observational cohort study (2) Samples were obtained on presentation and after 7 weeks of glucocorticoid therapy (GC) in steroid sensitive and steroid resistant pediatric patients participating in the PNRC study. AT antigen and activity assays were performed using ELISA and chromogenic assays, respectively. Thrombin generation assay, plasma albumin, and urine protein-to-creatinine ratio were determined as previously described.
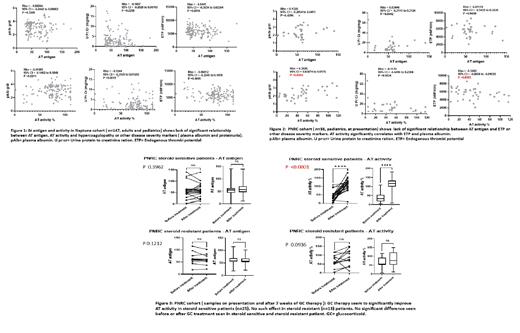
Results: There was no significant relationship between AT antigen or AT activity and thrombin generation parameters. AT antigen and activity also did not correlate with NS severity markers (plasma albumin and proteinuria) in the NEPTUNE cohort (Figure1). In PNRC pediatric cohort, no significant correlation was found between AT antigen and thrombin generation or other disease severity markers. However, AT activity was significantly associated with both plasma albumin and endogenous thrombin potential at presentation (Figure 2) and at follow-up. Interestingly, GC therapy significantly improved AT activity in steroid-sensitive but not steroid-resistant NS patients (Figure 3). A comprehensive literature review and meta-analysis was also performed which revealed that clinically significant AT deficiency (<0.7 IU/mL) is uncommon in both pediatric and adult NS patients.
Conclusion: AT antigen does not correlate with thrombin generation-defined hypercoagulopathy in adult or pediatric NS patients. AT activity does correlate with hypercoagulopathy in pediatric NS patients and improves significantly with successful remission inducing therapy. These data suggest that pediatric NS patients may have a qualitative, but not quantitative, AT deficiency that is responsive to therapy. The mechanism underlying this qualitative deficiency should be characterized in future studies.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.