Abstract
Background: Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT) is a severe prothrombotic complication of adenoviral vaccines including ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 (AstraZeneca) vaccine. The putative mechanism involves formation of pathological anti-PF4 antibodies that activate platelets via the FcγRIIa receptor to drive thrombosis and the associated thrombocytopenia. Functional assays are important in the VITT diagnostic pathway as not all detectable PF4 antibodies are pathogenic. Detection of procoagulant platelets (platelets supporting thrombin generation) in presence of PF4 has been proposed as a diagnostic assay for VITT (Althaus et al). Procoagulant platelets are not typically generated in response to low level agonist stimulation; however, combination of ligand binding of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR) (eg. PAR1) and ITAM linked receptors (eg. GPVI, CLEC2 and FcγRIIa) synergistically induce procoagulant platelet formation. Here, we describe an alternative flow cytometric assay to diagnose VITT. We hypothesized that priming of platelets with a PAR1 agonist at a level sufficient to release PF4, but insufficient to generate a significant procoagulant response in donor platelets, would provide a platform in which procoagulant response would be dependent on presence of FcγRIIa dependent procoagulant antibodies in patient plasma, without requirement for additional PF4.
Methods: Our previously established flow cytometry-based procoagulant platelet assay (using cell death marker GSAO and P-selectin) was modified to incorporate exogenous patient plasma and performed on whole blood from healthy donors screened for FcγRIIa responsiveness (aggregation response to anti-CD9 antibody, ALB6), primed with 5 μM SFLLRN. The assay was performed on Australian patients referred for confirmatory VITT testing with probable VITT (confirmed thrombosis within 4-42 days of ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccination, D-Dimer > 5x ULN, platelets < 150 x 10 9/L or falling platelet count) after screening on PF4/heparin ELISA (Asserachrom HPIA IgG Assay, Stago Diagnostics). Procoagulant response was also measured in presence of 0.5 U/mL and 100 U/mL heparin, monoclonal FcγRIIa blocking antibody, IV.3, and intravenous immunoglobulin, IVIg. Some plasmas were incubated with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 or SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Flow cytometry positive patients were also tested by serotonin release assay (SRA) and multiplate aggregometry. Clinical correlation was obtained.
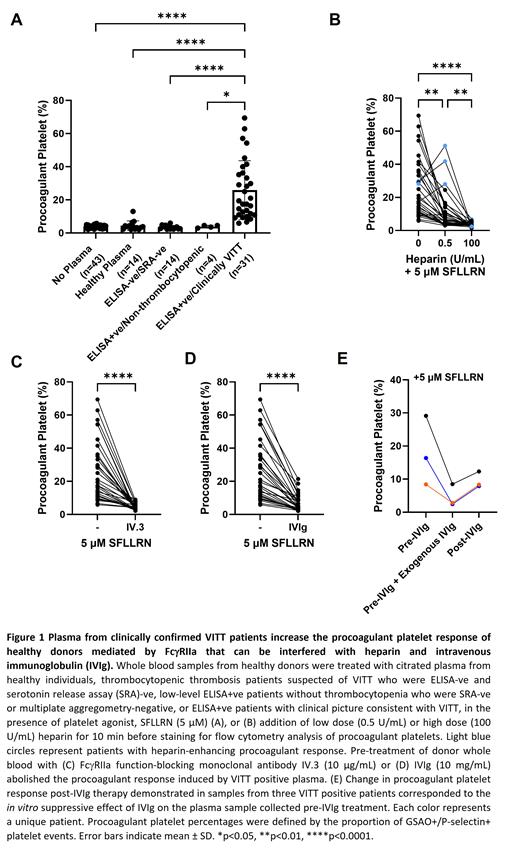
Results: Citrated plasma from 49 unique patients with suspected VITT are reported. Plasma from ELISA+ve patients with clinical picture consistent with VITT (n=31), significantly increased the procoagulant platelet proportions in healthy donors in presence of 5 μM SFLLRN (p<0.0001, Figure 1A). This increase was not seen with plasma from healthy donors (n=14); or individuals exposed to ChAdOx1 nCov-19 vaccine without VITT: thrombocytopenic thrombosis patients who were ELISA-ve and SRA-ve (n=14); or low-level ELISA+ve patients without thrombocytopenia who were negative by either multiplate or SRA (n=4). The procoagulant platelet response induced by VITT positive plasma was reduced with low dose heparin (0.5 U/mL, p<0.01) except for 3 patients who showed a heparin-enhancing effect (Figure 1B). High dose heparin (100 U/mL, p<0.0001), IV.3 (10 µg/mL, p<0.0001) or IVIg (10 mg/mL, p<0.0001) abolished the procoagulant response (Figures 1C-D). The in vitro effect of IVIg was predictive of the in vivo response to IVIg therapy (Figure 1E). Addition of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein had no effect on the procoagulant platelet response. ChAdOx1 nCov-19 had an inconsistent effect on procoagulant platelet formation in presence of VITT plasma. Use of donors without a robust aggregation response to ALB6 resulted in false negative results.
Conclusion: Induction of FcγRIIa dependent procoagulant response by patient plasma, suppressible by high dose heparin and IVIg, is highly indicative of VITT in the correct clinical circumstance. This assay modification of priming donor platelets from known FcγRIIa responsive donors with a GPCR agonist to potentiate the ITAM signaling from platelet activating immune complexes, results in a sensitive and specific assay. This may represent a functional platform that can be adopted into diagnostic laboratories to identify patients with platelet-activating antibodies and potentially predict treatment responses.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.