Abstract
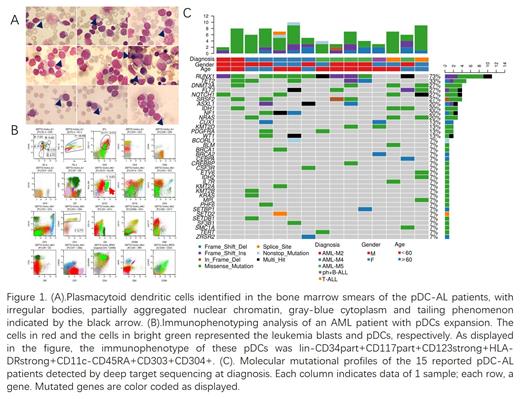
Objective: To improve the understanding of acute leukemia with plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) expansion. Method: Bone marrow smears and flow cytometry immunophenotyping results of patients with acute leukemia and pDCs expansion at diagnosis in our clinical center from August 2018 to January 2021 were retrospectively analyzed. The clinical and biological characteristics were analyzed. Results: Among the 1039 patients with acute leukemia, 15 (1.4%) had pDCs expansion at diagnosis, with a median age of 55 (28-99) years old. The ratio of men to women was 3 to 2. The median proportion of pDCs accounting for all the nucleated cells in bone marrow smear and flow cytometry immunophenotyping were 12.0% (6.0%-50.0%) and 16.6% (4%-28%), respectively. There were 12 cases of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), 11 of them had mutations in RUNX1 and 10 were morphologically classified as AML-M4 or M5. Notably, CD56 was mostly negative (only 1 of the 15 patients expressed CD56 antigen partially) and one of these 15 patients had definite skin lesions, which were significantly different from Blastic plasmacytoid dendritic cell neoplasms. 3 cases were diagnosed as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), of which 2 cases had mutations in NOTCH1 and RAS signaling pathways. 9 out of the 15 cases had consecutive prognostic information and the median follow-up time was 14.9 (2.1-31.9) months, of which 6 received allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation(allo-HSCT) and all were in continuous remission. However, among the 3 non-transplanted patients 2 cases relapsed. Conclusion: Acute leukemia with pDCs expansion is a group of patients with characteristic mutation profiles and relatively poor prognosis, more common in AML with abnormal expansion of the mononuclear system. Allo-HSCT may improve the clinical outcomes of these patients.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.