Abstract
Backgrounds: Relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL) patients have limited treatment options and are associated with poor prognosis. Patients generally receive salvage therapy as rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide (R-ICE), followed by consolidation with high-dose therapy (HDT) and autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). However, only approximately 50% of patients can proceed to ASCT and only half of these achieve durable remission post-transplant. New therapeutic strategies are needed to improve response rates and to prevent recurrence following ASCT. The immunomodulatory agent lenalidomide has demonstrated direct anti-tumor effects in lymphoma. Some studies found that the addition of lenalidomide to the widely used R-ICE salvage regimen is feasible and results in promising response rates in R/R DLBCL patients. Pomalidomide is a third-generation immunomodulatory drug that has shown excellent therapeutic activity against relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) and primary vitreoretinal lymphoma (PVRL) with an acceptable toxicity profile. We aim to determine the safety, tolerability and efficacy of pomalidomide in combination with R-ICE in R/R DLBCL patients.
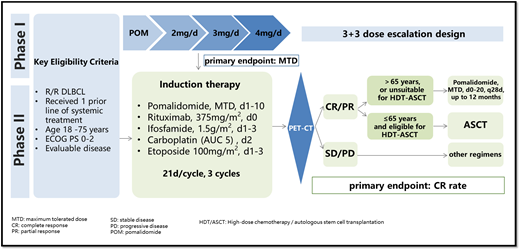
Study Design and Methods: PRIDE (ChiCTR2100049327) is a phase I/II trial of pomalidomide plus R-ICE (PR-ICE) as a salvage regimen for first-relapse or primary refractory DLBCL. In phase I of the study, patients receive escalating doses of pomalidomide (2mg, 3mg or 4mg daily on d1-10) along with R-ICE therapy every 21 days by standard 3+3 design until the MTD has been determined. In stage II, all subjects receive three cycles of R-ICE plus pomalidomide, dosing as RP2D. Patients with CR or PR but not eligible for ASCT receive continuous pomalidomide as maintenance therapy for 12 months. Key eligibility criteria are as follows: histologically confirmed DLBCL; relapsed or refractory after one prior treatment for DLBCL; age 18-75 years; absolute neutrophil count >1500 /mm 3; platelet count > 75,000/mm 3; calculated creatinine clearance of over 60 mL/min by Cockroft-Gault formula; total bilirubin < 1.5×ULN; AST and ALT < 3×ULN. The primary endpoint of phase II is the CR rate after PR-ICE induction treatment. The CR rate for R-ICE in R/R DLBCL was estimated to be approximately 35%. We hypothesize that the addition of POM to R-ICE could increase the CR rate by approximately 20%. For phase II, it requires a sample size of 44 evaluable patients (one-sided alpha = 0.05, power 80%, dropout rate of 15%). Eligible patients who receive at least one dose of PRICE will be included in the efficacy and safety analyses. The 95% CI of CR was calculated using Clopper-Pearson method. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate PFS and OS. All these analyses were conducted using SAS 9.4 software. Enrollment for phase I will begin in Q4 of 2021.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Pomalidomide is indicated for the treatment of adult patients: in combination with dexamethasone, for patients with multiple myeloma (MM) who have received at least two prior therapies including lenalidomide and a proteasome inhibitor and have demonstrated disease progression on or within 60 days of completion of the last therapy in China. The abstract presents the rationale for the use of generic pomalidomide in combination with R-ICE, a combination that is not approved in China at present.