Abstract
Multiple Myeloma (MM) is a haematological malignancy characterised by clonal proliferation of plasma cells within the bone marrow (Landgren and Weiss, 2009). Unfortunately, despite the major improvements to the treatment of MM within the last decade, it remains an incurable disease. Therefore, novel innovative combinations of less toxic therapies are warranted, especially for elderly patients with relapsed/refractory disease.
The anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family of proteins (BCL-2, BCL-XL and MCL-1) are critical regulators of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway and determine the survival of human MM cells (Letai et al., 2004, Del Gaizo Moore et al., 2008). Recently, Venetoclax, a selective BCL-2 inhibitor, was FDA approved for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) and acute mylogenous leukemia (AML), in combination with demethylating agents (Roberts et al., 2016, DiNardo et al., 2018, DiNardo et al., 2019) It is known that some MM patients with t(11;14) have a good response to combination treatment with venetoclax, however certain patients who do not have t(11;14) also respond to venetoclax. Therefore, a biomarker for response is urgently required in MM, as it has heterogeneous anti-apoptotic dependencies. In AML, venetoclax is combined with the epigenetic modifier 5-azacytidine. Highlighting, that screening for epigenetic modifier's, maybe a useful approach to identify synergistic combination of treatments with venetoclax in MM.
Methods:
To assess anti-apoptotic protein dependence in MM cell lines (JJN3, RPMI-8226, KMS18, MM1S, U266) and primary patient samples, BH3 profiling was used. Briefly, cells are exposed to a series of BH3-only peptides (20-23 mer in length) following gentle permeabilisation of cell membrane with low concentrations of digitonin. The loss of mitochondrial potential (JC-1) or the release of cytochrome c (cytochrome-c-FITC antibody) was assessed by plate reader or by flow cytometry. Cell death was assessed by Annexin V/ propidium iodide staining by flow cytometry. Using primary patient samples, CD138 + cells were isolated using the Miltenyi MAC sorter. For the epigenetic screen cell viability was assessed by CellTiter-Glo® and death was then confirmed by Annexin V/Pi staining.
Results
BH3 profiling was used to assess anti-apoptotic dependence in a panel of five MM cell lines. It is a functional assay that interrogates BCL-2 protein interactions using synthetic BH3 peptides to measure the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. The BH3 profiling was correlated to the response of the cell lines to a series of BH3 mimetics : venetoclax (selective BCL-2 inhibitor), ABT-263 (BCL-2, BCL-XL and BCL-W inhibitor), WEHI-539 (BCL-XL inhibitor) and AMG-176 (MCL-1 inhibitor). This data highlighted that BH3 profiling is a powerful tool for identifying anti-apoptotic dependnece in MM. It also showed and that there is a diverse anti-apoptotic dependence in MM cell lines and primary patient samples. Remarkably, one patient with plasma cell leukemia showed BCL-2 dependence by BH3 profiling, a t(11:14) translocation and a sustained in-vivo single agent response to venetoclax (Glavey et al., 2020)..
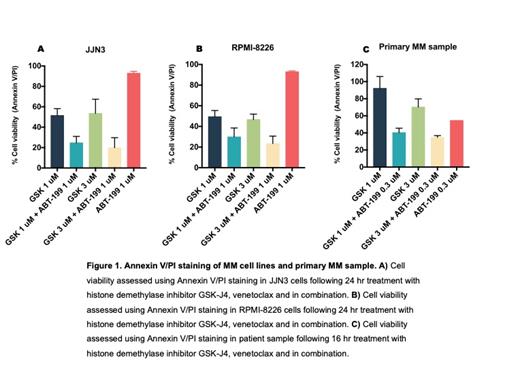
Next, we performed an unbiased epigenetic modifier screen in two MM cell lines JJN3 (MCL-1 dependent cell lines) and KMS-18 (mixed anti-apoptotic dependence) to induce BCL-2 dependence and sensitivity to venetoclax. The screen included the following classes of epigenetic modifiers: histone deacetylase inhibitors, histone methyltransferase inhibitors, DNA methyltransferase inhibitors and histone acetylase inhibitors. Interestingly, two classes of epigenetic drugs were synergistic with venetoclax in three different MM cell lines (CI <0.8). The combination was also validated by dynamic BH3 profiling in cell lines MM patient samples ex-vivo. Further work is required, in the form of a clinical trial, to validate our hypothesis that this provides a highly effective novel combination therapy option for myeloma patients.
Conclusion.
BH3 profiling is a powerful tool to identify the anti-apoptotic dependence in MM cell lines and MM patient samples, which we can exploit pharmacologically to kill MM cells in a personalised medicine approach. Combining epigenetic modifiers with venetoclax induces BCL-2 dependence in MM and enhances response to treatment.
Flanagan: AbbVie: Research Funding. O'Dwyer: Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; ONK Therapeutics: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy. Quinn: Takeda: Honoraria. Glavey: Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene and BMS company: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Amgen: Honoraria, Research Funding. Ni Chonghaile: AbbVie: Research Funding.