Abstract
Background
Hypomethylating agents (HMA) remain the backbone for treating higher risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) patients (pts) with less than 20% of pts achieving complete response (CR) and median overall survival (OS) of 12-18 months. Ongoing studies in higher risk MDS are assessing the role of adding venetoclax (Ven) to HMA. Preliminary data have reported promising higher response rate as first line therapy (1L) HMA/Ven) as well as activity in relapsed/refractory MDS to HMA. (R/R MDS).
Method
We analyzed all higher risk MDS pts treated at Moffitt Cancer Center defined by revised international prognostic scoring system (R-IPSS) by ≥ intermediate risk who received HMA as first line therapy after diagnosis. We compared outcomes of those pts who received single agent IL HMA, 1L HMA/Ven combination and HMA with Ven add back strategy after HMA failure (R/R MDS HMA/Ven). OS was defined from time of diagnosis.
Results
We identified 1193 higher risk MDS pts who received HMA 1L, 1158 pts received single agent HMA (1L HMA) (1027 azacitidine (AZA) and 131 decitabine (DAC)), 35 pts received 1L HMA/Ven combination (26 AZA and 9 DAC backbone). Among pts treated with HMA alone as first line, 31 were treated subsequently with HMA/Ven combination for R/R MDS without transformation to AML. The median duration of follow up from diagnosis was 96 months (mo) for 1L HMA, 15 mo for 1L HMA/Ven and 36 mo for HMA/Ven R/R MDS.
Focusing on first line therapy, 1127 received 1L HMA alone with no subsequent Ven add back and 35 pts 1L HMA/Ven. Table-1 summarizes baseline characteristics, 1L HMA/Ven pts were more likely to be MDS-EB2 and more pts harbored ASXL-1 somatic mutation (SM).
The overall response rate (ORR) (HI+) was 77% for 1L HMA/Ven compared to 40% 1L HMA (p<.005). The CR/marrow CR (mCR)/PR/HI were 34%/37%/3%/3% compared to 13%/11%/1%/15% for 1L HMA/Ven and IL HMA alone respectively, p <.005. Among pts with ASXL-1 SM, The ORR was 87% (CR 44%) and 32% (CR 8%) for IL HMA/Ven and 1 L HMA alone respectively, p < .005. Among pts with TP53 SM the ORR was 75% and 44% for IL HMA/Ven and 1 L HMA alone respectively, p = .038, however CR rates were 25% versus 17%, p = .47.
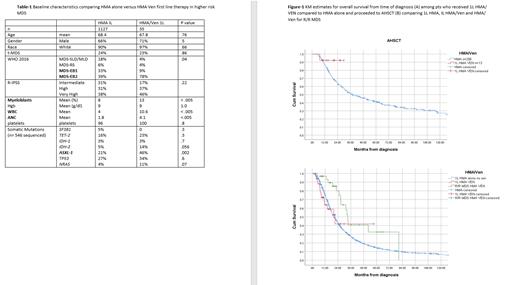
The rate of AML transformation was 23% and 37% for IL HMA/Ven and 1 L HMA alone respectively, p = .08. The overall survival was 21 mo (95% CI 11-32) and 20 mo (95%CI 19-22) for IL HMA/Ven and 1 L HMA alone respectively, p= .86. Among patients who proceeded to allogeneic stem transplantation (AHSCT) (n=269) 13 pts received 1L HMA/Ven, the median OS was not reached compared to 38 mo (95%CI 27-50) among who received 1L HMA alone (p=.2). The 2-year survival probability rate was 91% and 51% for IL HMA/Ven and 1 L HMA alone who proceeded to AHSCT respectively. (Figure 1 A)
Among pts who received 1L HMA alone as first line, 31 pts later received HMA/Ven for R/R MDS. The median number of 1L HMA therapy alone was 6 cycles. The ORR was 61% (CR 13% and mCR 48%). The median OS from time of diagnosis for pts who received HMA/Ven for R/R MDS was 33 mo (95% CI 31-36) compared to 21 mo (95% CI 11-32) for those who had IL HMA/Ven and 20 mo (95%CI 19-22) for those who received 1L HMA alone with no subsequent Ven therapy. (p=.02). (Figure-1 B) Nine of 31 pts who received HMA/Ven R/R MDS underwent AHSCT compared to 22 who did not proceed to transplant with median OS 31 and 33 mo respectively, (p = .7).
Conclusions
Among higher risk MDS patients, 1L HMA/Ven combination yields significantly higher complete response rates including ASXL-1 mutant MDS compared to 1L HMA alone. The OS survival benefit for 1L HMA/Ven in higher risk MDS pts can only be addressed in randomized clinical trial but our data suggest promising activity among those who received 1L HMA/Ven and proceeded to AHSCT (2-year OS 91%). Ven add back strategy to HMA after 1L HMA failure has clinical activity and was associated with OS benefit.
Komrokji: Novartis: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Acceleron: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Agios: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; JAZZ: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Geron: Honoraria. Padron: Taiho: Honoraria; Stemline: Honoraria; BMS: Research Funding; Blueprint: Honoraria; Kura: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Sweet: Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AROG: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bristol Meyers Squibb: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Kuykendall: Protagonist: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pharmaessentia: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Blueprint: Honoraria; Incyte: Consultancy; Celgene/BMS: Honoraria; Abbvie: Honoraria. Lancet: AbbVie: Consultancy; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy; ElevateBio Management: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy; BerGenBio: Consultancy; Agios: Consultancy; Millenium Pharma/Takeda: Consultancy; Astellas: Consultancy; Jazz: Consultancy. Sallman: Shattuck Labs: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Magenta: Consultancy; Syndax: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Intellia: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Takeda: Consultancy; AbbVie: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Agios: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Aprea: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Incyte: Speakers Bureau; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau.
Venetoclax for treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes