Abstract
Introduction Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is the most common subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma with a prognosis highly dependent on the stage of the disease. The mainstay of front-line therapy for limited-stage DLBCL is R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) or R-CHOP-like immunochemotherapy (IC). The impact of combined modality therapy (CMT) with radiation therapy (RT) after IC remains uncertain in the rituximab era. In the pre-rituximab era, studies comparing the efficacy of chemotherapy with or without RT showed heterogenous results. To date, only a few single institutional studies have compared IC versus CMT. The aim of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of standard IC compared to CMT in patients with stage I DLBCL in the rituximab era.
Methods Adult patients with stage I DLBCL diagnosed between 2002 to 2015 and seen at Mayo Clinic Rochester were identified. Data were obtained from medical records. All patients were treated with IC (R-CHOP or R-CHOP-like), or IC followed by radiation (CMT). The student's t-test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to analyze between-group differences, as appropriate. Chi-square or Fisher's exact test was used for categorical variable comparisons. Progression-free survival (PFS) was defined as the time from the date of diagnosis to the date of relapse, death or the date of the last follow-up and was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time from the date of diagnosis to the date of last follow-up or death. Response to treatment was evaluated by treating physicians.
Results The study included 123 patients diagnosed with stage I DLBCL with a median follow-up time of 65.9 months for IC arm and 56.2 months for CMT arm. Overall, 78 patients were treated with six cycles of IC, and 45 patients were treated with 2-4 cycles of IC followed by involved-site radiation (2 cycles in 4 patients, 3 cycles in 25 patients, 4 cycles in 16 patients). There were no significant differences in age, sex, or extranodal involvement. In the IC group, 59 patients had cell of origin data available: 44 (56.41%) were GCB subtype and 15 patients (19.23%) were non-GCB subtype. In the CMT group, 21 patients (47%) and 9 patients (20%) had GCB and non-GCB subtypes, respectively. Double-hit lymphoma (defined as rearrangement of MYC together with rearrangement of BCL2 and/or BCL6) was reported in 4 out of 78 patients in the IC arm and 2 out of 45 patients in the CMT arm.
There was no significant difference in response rates to frontline treatment between groups. In the IC group, the overall response rate (ORR) was 92% (n=72), and the rate of complete response (CR) was 87% (n=68), partial response (PR) was 5% (N=4), stable disease (SD) was 5% (n=4), and progressive disease (PD) was 5% (n=4). In the CMT group, the ORR was 96% (n=43, all CR); 2 patients achieved SD (4%) and no patients had a PR or PD.
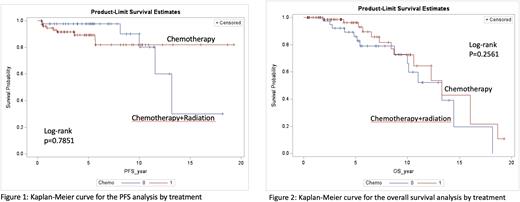
With a median follow-up time of 65.9 months for IC arm, 14 patients had died. With a median follow-up of 56.2 months for the CMT arm, 14 patients had died. Median PFS was not reached in the IC group while PFS was more than 10 years in the CMT group (p=0.7851) [Figure 1]. There was no significant OS difference observed in both groups (p=0.2561) [Figure 2].
Conclusion Our study showed no significant difference in OS and PFS between patients with stage I DLBCL treated with IC or CMT. Future research on a larger patient population is needed to evaluate the role of consolidation radiotherapy in early stage DLBCL.
Disclosures
Wang:TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; MorphoSys: Research Funding; Genmab: Research Funding; InnoCare: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Eli Lilly and Company: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Loxo@Lilly: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Kite Pharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Nowakowski:Bantam Pharmaceutical: Consultancy; Blueprint Medicines Corporation: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation/Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Curis, Inc.: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo Inc: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Kite Pharma Inc.: Consultancy; Kymera Therapeutics: Consultancy; MorphoSys US Inc: Consultancy; NanoString: Research Funding; Ryvu Therapeutics: Consultancy; Selvita: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Zai Lab: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.