Abstract
Background: Double expressor lymphoma (DEL) is a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) defined as having increased expression of MYC (≥40%) and BCL-2 (≥50%) by immunohistochemistry (IHC). Patients with DEL have inferior outcomes when treated with standard immunochemotherapy. Previous studies illustrated that lenalidomide showed a significant clinical response in non-GCB DLBCL, and well tolerated when combined with R-CHOP. This study aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of lenalidomide combined with R-CHOP (R2-CHOP) in newly diagnosed DEL patients.
Methods: Histologic diagnosis of DLBCL and MYC/BCL-2 expression by IHC were confirmed by central pathology prior to study therapy. Treatment regimen included lenalidomide 25 mg/d orally days 1-10 per 21days, plus standard R-CHOP21 for 6 cycles. The primary end point was 2-year progression free survival (PFS) per independent central radiology review. Secondary end points included 2-year event-free survival (EFS), overall response rate (ORR), overall survival (OS), and safety.
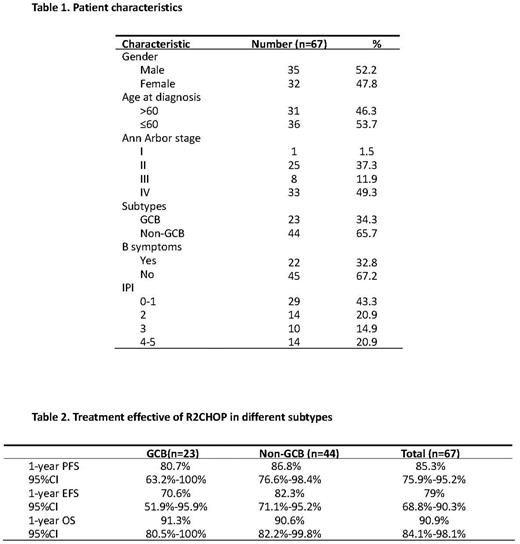
Results: Between Oct 2019 and Aug 2021, 67 eligible patients were enrolled in this study. Median age was 58 (range 27-75) years. Forty-one (61.2%) patients were stage III-IV, and 35.8% of patients were IPI score ≥3. Non-GCB subtype was determined in 44 (65.7%) patients. Three patients detected double-hit lymphoma withdrew from the study per investigator's decision. Sixty patients were evaluable for response. Fifty-seven patients responded to therapy, with overall response rate of 95% (57/60), and complete response rate of 80% (48/60). With a median follow-up of 17.8 months, the estimated 1-year PFS rate was 85.3% (95%CI 75.9%-95.2%). And the 1-year EFS rate was 79% (95%CI 68.8%-90.3%). Median OS was not reached, and 1-year OS rate was 90.9% (95%CI 84.1%-98.1%). Grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicities included neutropenia (67.2%), thrombocytopenia (19.4%), and anemia (4.5%). The most common nonhematologic adverse events were grade 1 to 2, including nausea, vomiting, fatigue, diarrhea, and mucositis. Grade 3 pneumonia occurred in 5 patients. Dose modification of lenalidomide or R-CHOP due to AEs were noted in 43.3% and 20.9% patients. No treatment-related death occurred in the study.
Conclusion: Our preliminary data indicate promising activity of lenalidomide combined with R-CHOP for newly diagnosed DEL patients. R2CHOP regimen was feasible, with predictable and manageable adverse events.
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
OffLabel Disclosure:
Lenalidomide is approved in treating multiple myeloma. However, previous studies illustrated that it showed a significant clinical response in non-GCB DLBCL, and well tolerated when combined with R-CHOP. Double expressor lymphoma (DEL) has aggressive behavior and lacks standard treatment. This study aims to investigate the efficacy and safety of lenalidomide combined with R-CHOP (R2-CHOP) in newly diagnosed DEL patients.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.