Abstract
Background: Despite novel therapies for relapsed/refractory (R/R) DLBCL, outcomes among this cohort remain poor. A prior study suggested that CD20 loss is a mechanism of therapeutic resistance and disease progression in patients treated with rituximab. Whether CD20 loss leads to inferior outcomes is unknown. We hypothesized that CD20 loss in the setting of R/R DLBCL is associated with inferior survival and response rates.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of R/R DLBCL patients seen at the University of Michigan, Mayo Clinic and University of Illinois Hospital between 2003-2021. Inclusion criteria were patients ≥ 18 years old, diagnosis of CD20 positive (+) DLBCL (de novo or transformed), relapsed/refractory disease, and CD20 status available at relapse on flow cytometry or immunohistochemistry. CD20 status was reviewed by the pathology department of each individual institution without central review. Overall survival (OS) was defined as time from first relapse to death and event-free survival (EFS) was time from first relapse to death or next treatment; both of which were estimated with Kaplan Meier analysis. Overall response rate (ORR) was complete response or partial response after first salvage therapy. Descriptive statistics with univariate and multivariate analyses were also performed.
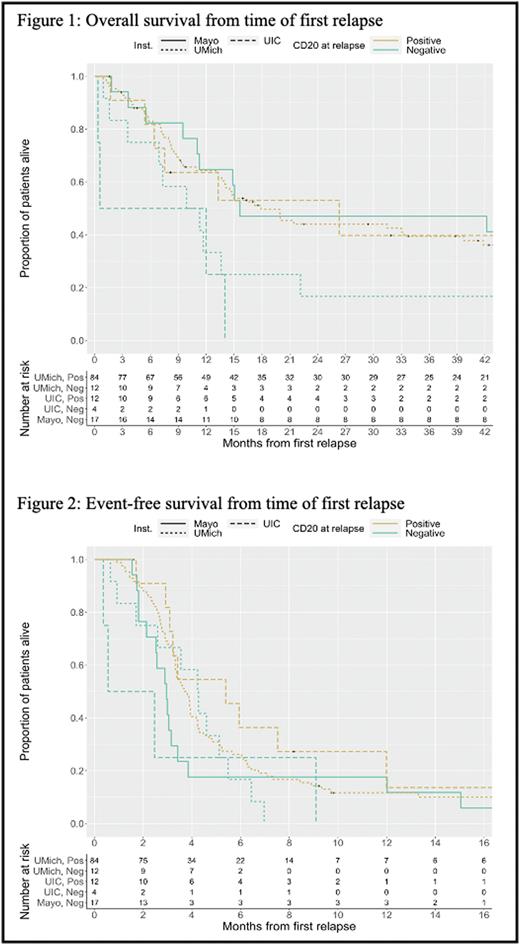
Results: 129 patients were included (64% male) with median age at diagnosis of 62 years. Majority of patients had stage III/IV disease at diagnosis (85%) and 15% had transformed DLBCL. At diagnosis, all patients had CD20+ disease. Median time from diagnosis to first relapse was 21.9 months (interquartile range 9.6, 53.6). Among the 129 patients, 96 were classified as CD20 positive at their time of first relapse (84 from Michigan, 12 from UIC) and 33 were classified as CD20 negative (12 from Michigan, 4 from UIC, and 17 from Mayo). The estimated median time from first relapse to death in the CD20+ group was 17.9 months (95% CI 14.0, 39.7) compared to 12.0 months (95% CI 9.9, 42.2) among the CD20 negative group. An overall (unstratified) log-rank test suggested there were no differences in OS between CD20 groups (p = 0.311).The estimated median EFS in the CD20+ group was 3.8 months (95% CI 3.3, 4.3) compared to 3.0 months (95% CI 2.5, 4.3) in the CD20 negative group, this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.063). Of patients who became CD20 negative at relapse, 79% received anti-CD20 directed therapy thereafter, as part of salvage or with conditioning prior to transplant.
Conclusion: Patients with DLBCL who relapse and maintain CD20 positivity seem to have a trend towards improved EFS and OS, though this was not statistically significant. We also found that for the majority of patients, loss of CD20 did not alter use of anti-CD20 directed therapy. Our study was limited given the retrospective data collection, variation in data collection methodology among institutions and small sample size which may have limited our ability to detect a statistical significance in outcomes. We will plan on expanding our data set in a future analysis.
Disclosures
Takiar:AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Morphosys: Consultancy; Epizyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche/Genentech: Consultancy; Epizyme Eli Lily: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy; Xencor: Consultancy; Seagen Inc.: Consultancy, Honoraria; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy. Nowakowski:Bantam Pharmaceutical: Consultancy; Blueprint Medicines Corporation: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation/Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Curis, Inc.: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo Inc: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Kite Pharma Inc.: Consultancy; Kymera Therapeutics: Consultancy; MorphoSys US Inc: Consultancy; NanoString: Research Funding; Ryvu Therapeutics: Consultancy; Selvita: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Zai Lab: Consultancy. Phillips:Xencor: Consultancy; ADC Therapeutics: Consultancy; AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Eli Lilly: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy, Other: Travel Expenses ; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy; Beigene: Consultancy; Epizyme: Consultancy; Gilead: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy; Genmab: Consultancy; Genentech: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.