Introduction:
Anti-CD20 antibody plus chemotherapy is one of the standard treatments for follicular lymphoma (FL) patients in need of therapy. Obinutuzumab-based regimens demonstrated improved progression- free survival (PFS) compared to rituximab plus chemotherapy (NCT01332968). Recently, the course of treatment of FL patients was disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic due to immunosuppressive nature of therapy, in particular, of the maintenance treatment with the anti-CD20 antibody.
Patients and Methods:
We report on the results of obinutuzumab combined with different chemotherapy induction regimens in consecutive FL patients who started treatment at hemato-oncology centers in Poland between August 2018 and December 2022.
The choice of chemotherapy (CVP, CHOP or bendamustine) was left to the discretion of the centre providing the treatment. Obinutuzumab maintenance was given to patients who achieved at least partial response (PR) after induction immunochemotherapy. Patients, who developed signs or symptoms suggesting acute COVID-19 infection were tested for the presence of SARS-COV 2. In other cases tests were performed according to local policy.
The response was evaluated with computed tomography or positron emission tomography according to Lugano 2014 Criteria. Chi-square test was used to compare percentages. Survival analyses were based on the Kaplan-Meier method.
Results:
The study group included 257 treatment-naive FL patients. The median age (range) was 55 (27-89) years, 42.4% of patients were males. 65.0% (n=167) of patients had comorbidities. According to FLIPI 47.1% of patients were classified as high risk, 33.9% as intermediate and 19.1% as low risk, whereas 39.5%, 23.2% and 37.3% of patients were in PRIMA PI high, intermediate and low risk groups, respectively. Median number of GELF criteria was 3 (range 0-9). Induction chemotherapy included: CVP in 52.1% (n=134), CHOP in 33.1% (n=85) and bendamustine in 14.8% (n=38) of patients. Median number of cycles was 6 (range 1 - 8).
After induction immunochemotherapy complete response (CR), PR, stable disease (SD) and progression disease (PD) rates were: 66.0%, 29.6%, 0.4% and 4.0%, respectively. Maintenance treatment was given to 217 patients (85.1%). Progression within 2 years of the start of treatment (POD24) occurred in 5.8% (n=15) of patients.
With a median follow up of 23.7 months, 7.4% patients (n=19) relapsed, 13.2% of patients died (n=34). Death was caused by COVID-19 in 20, and by other infection in 2 cases. Three patients died from FL, 2 patients - due to other malignancy, and one each from myocardial infarction and treatment toxicity. Cause of death was unknown in five cases.
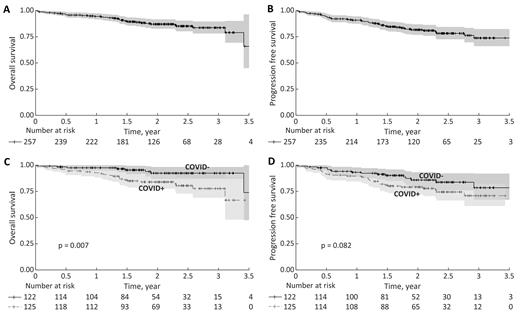
The SARS-CoV-2 infection was detected in 125 patients with no apparent relation to the type of chemotherapy regimen (p=0.762). COVID-19 severity was unknown in 8.1% (n=9) and defined by investigators as asymptomatic in 23.4% (n=26), mild in 44.1% (n=49), severe 19.8% (n=22) and critical in 4.5% (n=5). The highest increase in the number of COVID-19 occurred in the first six months of 2022. 13.8% of patients (n=17) had SARS-COV-2 infection prior to immunochemotherapy, 28.5% (n=35) during induction immunochemotherapy, 53.7% (n=66) during maintenance, and 4.1% (n=5) after completion of the treatment. 3-year OS and PFS was 84% (95%CI: 78%-90%) and 74% (95%CI: 66% - 82%), respectively (Figure 1AB). 3-year OS of patients without COVID-19 was 92% (95%CI: 87% - 98%), while 3-year OS of patients with COVID-19 was 78% (95%CI: 69% - 88%) (p = 0.007), (Figure 1C).
Conclusions:
The survival of our real-world series of patients treated with obinutuzumab-based regimens was apparently worse than in the original study. These results may have been influenced by more prevalent high and intermediate risk factors, high tumor burden, as well as high frequency of SARS-COV 2 infection in our group of patients. OS was particularly lower among patients who had symptomatic COVID disease . These results seem to support a recommendation to initiate treatment in strictly symptomatic FL patients only, even if they formally meet GELF criteria. In the context of COVID-19 pandemic, CVP or CHOP might be preferred over more immunosuppressive bendamustine, and obinutuzumab maintenance treatment should be considered with caution as appropriate.
Disclosures
Paszkiewicz-Kozik:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Giza:Roche: Honoraria, Other: Travel; takeda: Honoraria, Other: travel; abbvie: Honoraria, Other: travel. Dabrowska-Iwanicka:Gilead: Other: travel; Abbvie: Other: Travel. Bolkun:Abbvie: Speakers Bureau. Wasik-Szczepanek:janssen: Speakers Bureau; roche: Speakers Bureau; abbvie: Other: travel. Domanska-Czyz:Roche: Other: Travel. Ostrowska:Roche: Other: Travel. Swierkowska:Roche: Other: Travel. Krzanowski:Roche: Other: Travel. Mroz-Zycinska:Roche: Other: Travel. Romejko-Jarosinska:takeda: Other: Travel; gilead: Honoraria, Other: travel. Dlugosz-Danecka:Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Speakers Bureau; Servier: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: travel, Speakers Bureau; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Zaucha:MSD: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Medical University of Gdańsk: Current Employment; Pierre Fabre, Takeda, BMS, Gilead, Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Astra Zeneca, Abbvie: Honoraria. Walewski:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria; GSK/Novartis: Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria.