There are errors in the western blots for the MM.1S cell line in Figures 3 (page 3894) and 5 (page 3895).
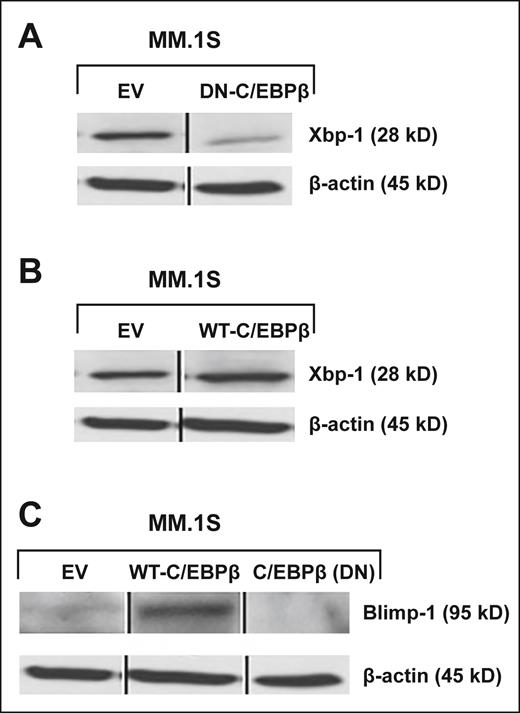
C/EBPβ regulates IRF4-dependent transcription factors such as XBP1 and BLIMP1. MM cells were transfected with EV, (A) DN-C/EBPβ, or (B) WT-C/EBPβ. Transfected cells were selected for 10 days by G418 (500 μg/mL). The selected cells were analyzed for expression of XBP1 by Western blotting with the anti-XBP1 antibody. (C) EV- and WT-C/EBPβ–transfected and selected cells were analyzed for the protein expression of BLIMP1. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane.
C/EBPβ regulates IRF4-dependent transcription factors such as XBP1 and BLIMP1. MM cells were transfected with EV, (A) DN-C/EBPβ, or (B) WT-C/EBPβ. Transfected cells were selected for 10 days by G418 (500 μg/mL). The selected cells were analyzed for expression of XBP1 by Western blotting with the anti-XBP1 antibody. (C) EV- and WT-C/EBPβ–transfected and selected cells were analyzed for the protein expression of BLIMP1. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane.
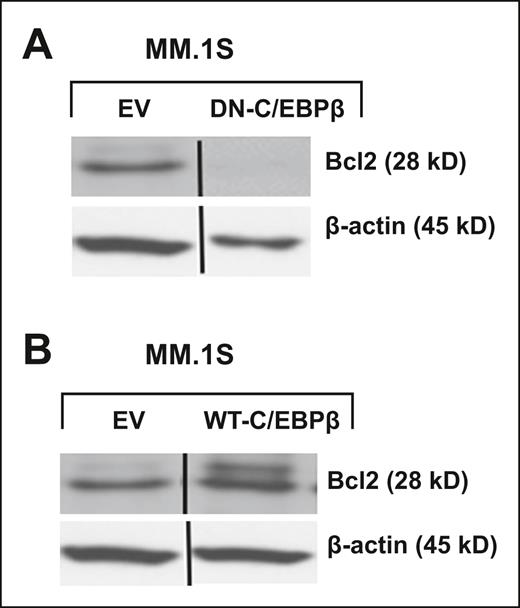
BCL2 is regulated by C/EBPβ. MM cells were transfected with EV, (A) DN-C/EBPβ, or (B) WT-C/EBPβ. Transfected cells were selected for 10 days with G418 (500 μg/mL). Lysates of transfected cells were subjected to Western blotting using anti-BCL2 antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane.
BCL2 is regulated by C/EBPβ. MM cells were transfected with EV, (A) DN-C/EBPβ, or (B) WT-C/EBPβ. Transfected cells were selected for 10 days with G418 (500 μg/mL). Lysates of transfected cells were subjected to Western blotting using anti-BCL2 antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Vertical lines have been inserted to indicate a repositioned gel lane.
In Figure 3, the β-actin band is mistakenly shown from the wrong lane and gel. In addition, in Figure 3C, “pcDNA” should be “EV.” The corrected MM.1S blots for Figure 3 are shown below.
In Figure 5, the β-actin band is mistakenly shown in the wrong lane. The corrected MM.1S blots for Figure 5 are shown below.
The authors repeated key experiments shown in Figures 3 and 5. The original C/EBPβ plasmid was no longer available to them. Therefore, they designed a new lentiviral construct expressing dominant-negative C/EBPβ (DN-C/EBPβ; deletion of amino acids 41 to 205). They also used a LIP isoform that lacks the N-terminal trans-activating and central regulatory regions and therefore also functions as the inactivated form of C/EBPβ. Both constructs were stably transduced into MM.1S and RPMI-8266 cells. The effects on the key transcription factors were examined by western blotting. The experiments confirmed the original study’s finding that C/EBPβ controls several key transcription factors in multiple myeloma.