Abstract
Tenascin-C (TN-C), a member of the extracellular matrix (ECM) glycoprotein family, is expressed on the surface of stromal cells in the hematopoietic system or lymphoid organs. Recently, TN-C–deficient mutant mice produced by TN-C gene targeting through homologous recombination were shown to develop normally, although TNs have been reported to play important roles in organogenesis and carcinogenesis. In the present study, we found that colony-forming capacity of bone marrow (BM) cells was considerably lower in TN-C–deficient mice (a decrease of ∼35% from control), although their mononuclear cell count and BM architecture showed no significant difference from those of normal mice. Furthermore, in long-term BM culture in vitro, hematopoietic cell production (a decrease of ∼40% in Dexter's condition and of ∼65% in Whitlock-Witte's condition from control), colony-forming capacity of the produced cells (a decrease of ∼60% from control), and longevity of the cultures were markedly lower in the TN-C–deficient mice than in control mice, whereas hematopoiesis in the TN-C–deficient mutant mice was sustained. The addition of TN-C glycoprotein to long-term BM cultures of TN-C–deficient mice clearly induced the recovery of hematopoietic cell production and colony-forming capacity of hematopoietic progenitor cells. Thus, these results provide direct evidence that an ECM glycoprotein component, TN-C, plays a relevant role in hematopoiesis through interactions between stromal cells and hematopoietic progenitor cells.
THE HEMATOPOIETIC microenvironment plays an essential role in hematopoiesis through cell-to-cell, cell-to-extracellular matrix (ECM), and cell-to-growth factor interactions.1,2 Hematopoietic microenvironment is a complex structure in which stem cells, progenitor cells, stromal cells, growth factors, and ECM molecules each interact to regulate hematopoietic cell growth and differentiation. It remains a major quest to determine how the components of mictoenvironment regulate lineage-specific blood cell differentiation. Previous studies showed direct evidence of interaction between hematopoietic stem cells and stromal cells by the finding of the expression of tyrosine kinase receptor family on hematopoietic stem cells and their ligands which stimulate the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells in molecular level. The evidence in hereditarily anemic mice3 that hematopoietic stem cells from heterozygote anemicSl/Sld mouse4 can repopulate the stroma and rescue a lethally irradiated wild-type (+/+) host, but +/+ stem cells fail to rescue theSl/Sld anemia showed that the defect of Sl locus resulted in the defective hematopoietic microenvironment.5,6 White spotting (W) and steel (Sl) mutations have been identified4 and it has been shown that W encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene, a tyrosine kinase membrane receptor,7,8 and Slencoded the mast cell growth factor (also known as Steel factor [SLF], stem cell factor, or kit ligand).9,10 A novel tyrosine kinase receptor specific to hematopoietic stem cells, called flt3/flk-2, has been identified,11,12 and its ligand, flk-ligand (FL), has recently been cloned and characterized as proliferative factor for primitive hematopoietic cells.13
On the other hand, to clarify the function of each molecule related to hematopoietic regulation, a series of the mouse model of the null mutation of the gene has been generated by disruption of the gene using homologous recombination in embryonic stem (ES) cells. The knockout mice disrupting hematopoietic growth factor receptor genes and growth factor genes have been reported. Mice deficient in flk2 showed deficiencies in primitive B-lymphoid progenitors and in T-cell and myeloid reconstitution by mutant stem cells using bone marrow transplantation (BMT) experiments.14 Furthermore, double-mutant mice of both flk2 and c-kit showed more severe hematopoietic deficiency.14 Mice deficient in flk-1, the receptor tyrosine kinase, playing an important role in endothelial development, showed an early defect in the development of hematopoietic cells characterized by the absence of yolk-sac blood islands and vasculogenisis in the mouse embryo.15 Disruption of erythropoietin (EPO) or EPO receptor gene resulted in reduced primitive erythropoiesis in mouse embryo, but committed erythroid progenitors were present in homozygous fetal liver,16 and disruption of common β subunit of the receptors for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) and interleukin-3 (IL-3) and IL-5 caused impaired signaling of growth factors to hematopoietic progenitors.17 Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signal is mediated through two types of receptors, type I (TGF-βRI) and type II (TGF-βRII ),18 and TGF-β1 has been shown as an inhibitor of hematopoietic stem cell growth.18,19 TGF-β receptor type II–deficient mice showed deficiency of yolk sac hematopoiesis and vasculogenesis.20 TGF-β1-knockout mice also showed retardation of yolk-sac vasculature and hematopoietic system.21 Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α) is a chemokine that has pro-inflammatory activity. In the hematopoietic system, MIP-1α enhance colony formation stimulated by GM-CSF and M-CSF and suppress colony formation by more immature progenitor cells.22 However, MIP-1α knockout mice resulted in no overt hematopoietic abnormalities.23
Gene disruptions of cell-adhesion–related molecules have extensively been studied. Integrin family are thought to be critical in controlling differentiation and migration of blood cell precursors. Hirsch et al24 reported that hematopoietic stem cells lacking β1 integrins could form and differentiate into different lineages but could not colonize the fetal liver. Arroyo et al25 showed that disruption of α4 integrin gene resulted in impaired T and B lymphopoiesis, but in normal monocyte and natural killer cell development. These reports indicate that the maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells in BM may require unidentified molecule(s) related to adhesive interaction other than β1 and α4 integrins. Furthermore, p53 tumor suppressor gene-deficient mice showed that mice homozygous for the null allele appeared normal but were susceptible to the spontaneous development of a variety of neoplasms including hematopoietic malignancy (20 malignant lymphoma cases of 30 examined),26 suggesting that p53 has an important role in the maintenance of normal hematopoiesis by the regulatory effect of cell-cycle control.
Gene targeting of ECM component has not been fully examined yet. It is reported that fibronectin-knockout mutant mice caused early embryonic lethality, and blood island formation was impaired in endodermal component of the yolk sac.27 We have previously shown that the ECM glycoproteins TN, fibronectin, and laminin were expressed in established stromal cells by murine BM adherent cell cultures.28 Furthermore, when stromal cells were cocultured with nonadherent BM cells, which resulted in the formation of active hematopoietic areas in culture, the expression of TN was markedly enhanced during lymphoid differentiation under Whitlock-Witte's culture conditions.28 These findings suggest that the ECM component might play a substantial role in lineage-specific hematopoiesis. Tenascins are ECM glycoproteins that have been postulated to be regulators of cell-to-cell interaction, embryogenesis, and the process of malignant transformation.29-33 A recent study on the establishment of TN-C gene-deficient mutant mice showed that homozygous null mutant mice were born live and developed normally.34 Forsberg et al35 also reported normal development of newly generated TN-C knockout mice, and showed that the healing process of skin wounds and severed nerves was not diminished in the TN-C gene-deficient condition. However, little is known about regulation of hematopoiesis in TN-C–deficient mice. In the present study we examined the hematopoietic activity of mutant mice in which TN-C gene expression was completely disrupted to clarify the physiological roles of this molecule in hematopoiesis, using so-called long-term BM cultures (LTBMCs) as a model system of in vitro hematopoiesis. In this system, stromal cells and hematopoietic cells derived from whole BM were maintained in culture, and hematopoietic stem cells migrated within the adherent stromal layer via microenvironmental homing, forming hematopoietic focus-like cobblestones in appearance. In this culture, the relationship between the stromal cells and stem cells is maintained, and in the presence of the hematopoietic cell and stromal cell interactions, proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells and specific progenitor cells can be maintained over several weeks.36 Our results show that TN-C–deficient mice retained their capacity for hematopoiesis; however, the extent of the colony-forming capacity of hematopoietic progenitor cells and production of hematopoietic cells in LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice were significantly lower than in those of TN-C–expressing control mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice.
TN-C–deficient mutant mice were created by TN-C gene-targeting in murine (ES) cells as described previously.34 In the present study, C57BL/6 mice were used as the control mice because ES cells used in the targeting (TT2 cells) were derived from an F1 embryo of C57BL/6 and CBA mice. C57BL/6 mice were obtained from The Japan SLC Co (Shizuoka, Japan). Mice were housed at the Department of Experimental Medicine, Jichi Medical School, Tochigi, and at the Institute of Animal Experimentation, Hokkaido University School of Medicine. This experiment was performed in accordance with the Jichi Medical School Guide for Laboratory Animals and with the Hokkaido University Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Basic data.
Both TN-C–deficient mice and control mice were weighed. Blood was drawn from the tail vein for hematocrit, white blood cell count, and hemogram. Spleen and liver weight was measured after killing of the mice by cervical dislocation. BM obtained from a femur was fixed for histological examination.
Continuous BM cultures.
LTBMCs were established as described previously.37 In each experiment, age-matched 7-week-old (young) and 50-week-old (aged) TN-C–deficient mice and C57BL/6 mice were used. For investigation of the myeloid and macrophage hematopoietic system, we used culture conditions based on Dexter's method36 with modifications.38 Briefly, the contents of an adult mouse femur and tibia were flushed into a 25-cm2 culture flask (Falcon no. 3109; Becton Dickinson Labware, Franklin Lakes, NJ) using an 18-gauge needle in Fisher's medium supplemented with 20% horse serum (Life Technologies, Inc, Grand Island, NY) and 10−6 mol/L hydrodortisone sodium hemisuccinate (Sigma Chemical Co, St Louis, MO). Cultures were incubated at 33°C in humid air containing 7% CO2 and the medium was changed weekly by removal of all nonadherent cells and medium and replacement with 6.0 mL fresh medium. For investigation of the lymphoid hematopoietic system, we used the method originally established by Whitlock et al39 with some modification. Briefly, the flushed BM cells were prepared at the concentration of 4 × 105 cells /mL and seeded into a 25-cm2 culture flask in 5-mL RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 5% fetal calf serum (FCS; HyClone Lab Inc, Logan, UT) and 5 × 10−5 mol/L 2-mercaptoethanol (Sigma). Cultures were incubated at 37°C in humid air containing 5% CO2, medium was changed weekly, and BM nucleated cells were recharged once at day 14. Nonadherent cells were counted weekly and stained with Wright-Giemsa staining solution for morphological assessment.
Crossover reconstitution of cocultures of stromal cells and hematopoietic cells.
Stromal cell lines were established from adherent cells from LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient and control mice. On day 30 after establishment of LTBMCs, adherent cells were removed by treatment with 0.25% trypsin (Life Technologies, Inc, Rockville, MD) and replated in tissue culture plate (Falcon no. 3001) in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (MEM) (Life Technologies, Inc) supplemented with 10% FCS. Cultures were maintained at 37°C, 5% CO2 and passaged twice a week. After several passages, growing cells were plated at a limiting dilution and cloned by using penicylinders to separate single cell–derived colonies.40 To evaluate the supportive ability of stromal cell lines for hematopoiesis, we used the technique of marrow transplantation in vitro. Donor cells were prepared by the method described previously.40 Briefly, fresh BM cells obtained from age-matched 7-week-old mice were suspended in RPMI-1640 medium. To prepare the adherent cell–depleted BM fraction, BM cells were passed through a fine mesh and were applied on a Sephadex G-10 (Pharmacia, Uppsala, Sweden) column as described previously.41 The pass-through fraction was collected and washed with the medium. Recipient stromal cells were plated in 12-well plate (Falcon no. 3043) in 1.5-mL culture medium per well at the density of 2 × 105 cells/well in Dulbecco's MEM supplemented with 5% FCS. After 48 hours of cultures when the stromal culture grew subconfluent, 8 × 105 donor cells/well in Dexter's condition or 2 × 105 cells/well in Whitlock-Witte's condition were engrafted in the specified medium as described above.
Colony-forming assay.
Progenitor cell assays were performed with BM cells from the femur and tibia before the initiation of LTBMCs and nonadherent cells produced by murine LTBMCs. Previously described assay conditions required for growth of multilineage colonies (colony-forming unit in granulocyte-erythroid-megakaryocyte-macrophage, CFU-GEMM)19,37 were used with some modifications. Briefly, cells were plated in methylcellulose (Methocel A-4A, premium; Dow Chemical Co, Midland, MI) cultures at a concentration of 5 × 104 cells/mL at 37°C in humid air containing 5% CO2. One milliliter of a methylcellulose culture was added to each 35-mm Petri dish. Cultures contained 1.0% methylcellulose, 1% bovine serum albumin, 30% FCS, 40 μmol/L 2-mercaptoethanol, 2 U/mL of erythropoietin (Kirin Brewery, Tokyo, Japan), and 1% pokeweed mitogen–stimulated mouse spleen cell–conditioned medium (SCCM) as a source of IL-3. Triplicate plates were cultured for 14 days, and colonies (>50 cells) were counted using an inverted microscope. Macroscopic hemoglobinized colonies were counted as erythroid bursts (burst-forming unit-erythroid, BFU-E). Spleen colony-forming assay (colony-forming unit in spleen, CFU-S) was performed as described previously.42 Briefly, hematopoietic cells from BM or LTBMCs were washed and resuspended at 2 × 106cells/mL in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)(−). Recipient C57BL/6 mice were exposed to 9-Gy total body irradiation and 0.25 mL of the cell suspension was injected to recipient mice via the lateral tail vein. At day 12, the macroscopic colonies were counted after fixation of the spleens in Bouin's solution.
Addition of TN-C glycoprotein to LTBMCs and colony-forming assay.
To confirm the biological role of TN-C, TN-C purified from human melanoma cells (A375) was added to the LTBMCs and colony assay system. TN-C was purified by a series of biochemical procedures including Sepharose CL4B (Pharmacia Biotech, Tokyo, Japan) gel filtration, gelatin Sepharose 4B (Pharmacia) gel affinity chromatography, and DEAE-5PW (Toyo Soda, Tokyo, Japan) ion-exchange high-performance liquid chromatography using the method described by Oike et al.43Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) under reducing conditions showed that finally purified TN-C consisted of a protein band with an apparent molecular weight of 250 kD with over 95% purity. No fibronectin immunogenicity was detected (data not shown). LTBMCs were set in 12-well plates (Falcon no. 3043) in 1.5 mL culture medium per well with an appropriate concentration of TN-C, and medium with TN-C was changed weekly. In the colony assay system, TN-C was added to the methylcellulose medium. TN-C derived from human glioma cell line U-251MG (Life Technologies, Inc) was also used in a series of experiments. Mouse plasma fibronectin (FN) (UCB-Bioproducts S.A., Brussels, Belgium) or heparan sulfate (HS) derived from bovine kidney (Seikagaku Corp, Tokyo, Japan) was used as a control for TN-C.
RESULTS
Hematologic parameters in vivo.
Hematologic parameters of both mutant and control mice were examined in vivo at weeks 7 and 50. No statistical differences were observed between TN-C–deficient mutant and control mice at week 7 in the data of either parameter (P > .05, Student's t-test), body weight (22.0 ± 0.8 v 22.8 ± 1.0 g), hematocrit (51.3% ± 1.3% v 48.4% ± 2.9%), white blood cell count (7,300 ± 300 v 7,400 ± 200/μL), BM mononuclear cell count (39.2 ± 0.7v 38.0 ± 1.1 × 106/femur and tibia), spleen weight (0.1 v 0.1 g), and liver weight (1.1 ± 0.2v 1.1 ± 0.1 g). No statistical differences were observed in both mice group at week 50 (data not shown). However, colony-forming capacity of BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice was considerably lower than that of control mice (Tables 1and 2, week 0). Histological assessment using hematoxylin-eosin staining showed that the microscopic architecture of BM, spleen, thymus, and liver was the same in mutant and control mice (data not shown).
Longevity of LTBMCs.
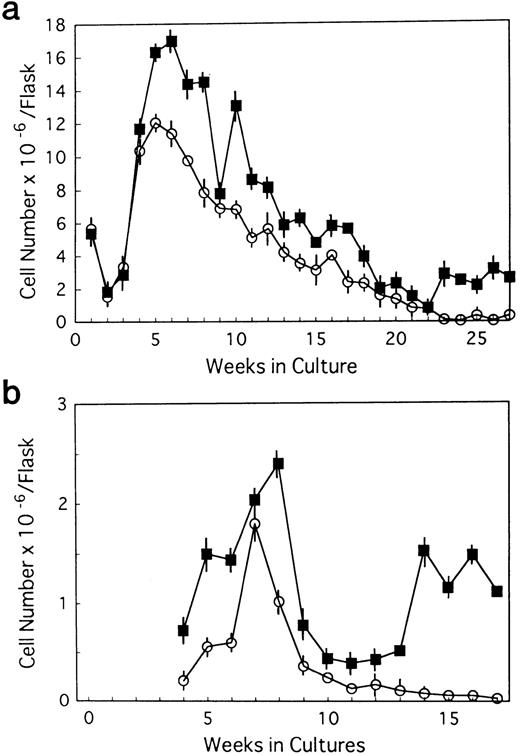
BM cells from 7-week-old mice were subjected to LTBMCs in vitro using two culture conditions: Dexter's culture system for myeloid-lineage cell growth and differentiation, and Whitlock-Witte's for B-lymphoid lineage. In the initiation of Dexter's condition, cultures from the mutant and control mice showed stable hematopoietic focus formations (cobblestone islands) consisting of hematopoietic progenitor cells adhering to stromal layers. LTBMCs started to produce hematopoietic cells from the foci 7 days after culturing. The number of hematopoietic cells produced was more markedly decreased in the course of LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice than in those of controls (Fig 1a). No significant difference was observed in the hemograms of the cells produced in each group during active hematopoiesis (produced hematopoietic cells consisted of 3% to 5% immature blasts, 10% immature myeloid, 85% mature myeloid, and ∼5% monocytoid cells in Wright-Giemsa–stained preparations). As the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice got older, the formation of hematopoietic foci diminished in comparison with control mice. The cells produced from LTBMCs predominantly consisted of monocytoid cells with few mature myeloid cells, and the adherent stromal cell layers gradually became sparse (Fig 2a). After 20 weeks of culture, almost all hematopoietic foci disappeared in the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice (Fig 2a), whereas the LTBMCs of control mice continued to maintain active hematopoiesis (Fig 2b). Under the Whitlock-Witte culture condition, after the stable formation of hematopoietic foci 4 weeks after culturing, prominent decreases of hematopoietic foci and cell production (Figs 1b and 2c) was observed in comparison with control cultures (Figs 1b and 2d), as in Dexter's culture system. The cells produced by the LTBMCs of the mutant and control mice conditioned according to the Whitlock-Witte method showed similar hemograms (produced cells consisted of approximately 5% to 10% immature blasts, ∼2% myeloid, 5% to 8% monocytoid, and 70% to 80% small lymphocytes). Cell-surface marker analysis of the predominant small lymphocytes showed positive reactivity against mouse B-cell marker, anti-mouse antibody RA3-6B2 (B220; Caltag La. Inc, South San Francisco, CA), using the indirect immunofluorescence method with a FACScan instrument (Becton Dickinson, Lincoln Park, NJ) (data not shown). Fifty-week-old mice were used to examine the effect of aging. The longevity of TN-C–deficient mutant cultures were also lower than that of control cultures. In both culture systems after 20 weeks of culture, adherent stromal cell number did not differ from LTBMCs of control and TN-C–deficient mice (15.6 ± 1.8 v 16.2 ± 2.0 × 105 cells/flask in Dexter's condition, and 10.3 ± 2.0v 9.6 ± 2.5 × 105 cells/flask in Whitlock-Witte's condition, P > .05, Student'st-test).
Weekly nonadherent cell production by LTBMCs in Dexter's culture condition (a) and in Whitlock-Witte's culture condition (b) from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice (□) and of control mice (▪) obtained at 7 weeks of age. In Dexter's culture condition, hematopoietic foci formation and cell production became active 1 week after culturing, and in Whitlock-Witte's culture condition, active hematopoiesis began 4 weeks after the crisis phase.39Results represented as mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly by at least six cultures per group per week. Results were significantly different between TN-deficient mouse group and controls (P < .01) in both culture systems. Two other identical experiments gave comparable results.
Weekly nonadherent cell production by LTBMCs in Dexter's culture condition (a) and in Whitlock-Witte's culture condition (b) from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice (□) and of control mice (▪) obtained at 7 weeks of age. In Dexter's culture condition, hematopoietic foci formation and cell production became active 1 week after culturing, and in Whitlock-Witte's culture condition, active hematopoiesis began 4 weeks after the crisis phase.39Results represented as mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly by at least six cultures per group per week. Results were significantly different between TN-deficient mouse group and controls (P < .01) in both culture systems. Two other identical experiments gave comparable results.
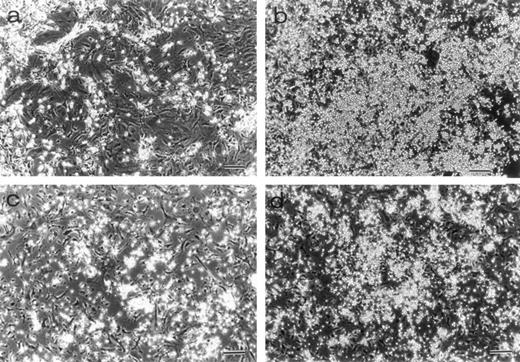
Morphology of LTBMCs obtained from 7-week-old mice. Dexter's cultures of TN-C–deficient mice (a) and of control mice (b) were photographed under an inverted microscope at week 25 after culturing. Large hematopoietic foci were seen in the control culture. Whitlock-Witte's cultures of TN-C–deficient mice (c) and of control mice (d) were photographed at week 15. Bar, 100 μm. Significant decrease in hematopoietic activity was observed in LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mutant mice.
Morphology of LTBMCs obtained from 7-week-old mice. Dexter's cultures of TN-C–deficient mice (a) and of control mice (b) were photographed under an inverted microscope at week 25 after culturing. Large hematopoietic foci were seen in the control culture. Whitlock-Witte's cultures of TN-C–deficient mice (c) and of control mice (d) were photographed at week 15. Bar, 100 μm. Significant decrease in hematopoietic activity was observed in LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mutant mice.
Crossover reconstitution of cocultures of stromal cells and nonadherent hematopoietic cells.
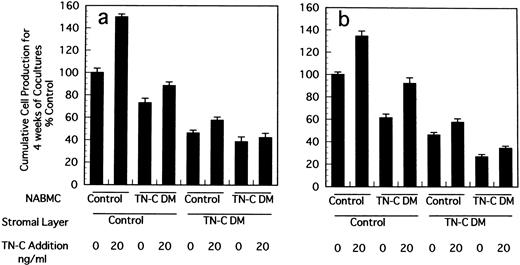
Stromal cells in LTBMCs are not clonal ones because they are derived from whole contents of BM of mice. We established stromal cell lines from LTBMCs of control and TN-C–deficient mice and constituted crossover cocultures of stromal cells and nonadherent BM hematopoietic cells to confirm the decreased supporting activity of hematopoiesis in TN-C–deficient condition. As shown in Fig3, when stromal cells derived from TN-C–deficient mice were cocultured with hematopoietic cells from control or TN-C–deficient hematopoietic cells, cell production from formed hematopoietic foci was markedly decreased compared to that from cocultures with stromal cells from control mice and hematopoietic cells from control or TN-C–deficient mice. Again it was clearly shown that cell production from coculture of stromal cells from control mice and hematopoietic cells from TN-C–deficient mice was lower than that of both stromal cells and hematopoietic cells from control mice.
Crossover reconstitution of cocultures of stromal cells and nonadherent hematopoietic cells derived from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant and control mice obtained at 7 weeks of age. Results represented as the percentage of the value obtained in cumulative mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly for 4 weeks by triplicate cultures per group, which gave 11.8 × 105cells/well in Dexter's condition (a) and 1.7 × 105cells/well in Whitlock-Witte's condition (b) in coculture of stromal cells and hematopoietic cells from control mice. Two other identical experiments gave comparable results.
Crossover reconstitution of cocultures of stromal cells and nonadherent hematopoietic cells derived from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant and control mice obtained at 7 weeks of age. Results represented as the percentage of the value obtained in cumulative mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly for 4 weeks by triplicate cultures per group, which gave 11.8 × 105cells/well in Dexter's condition (a) and 1.7 × 105cells/well in Whitlock-Witte's condition (b) in coculture of stromal cells and hematopoietic cells from control mice. Two other identical experiments gave comparable results.
Colony formation by the produced hematopoietic cells from LTBMCs.
Multi-lineage colony-forming capacity of nonadherent cells produced in Dexter's cultures was evaluated using the colony-formation assay. Nonadherent cells formed multilineage colonies as well as macroscopic hemoglobinized erythroid bursts in the presence of IL-3 and EPO in semisolid medium. In comparison with control mice, significantly diminished colony formation was observed in TN-C–deficient mice characterized by a lower number of multilineage colonies and erythroid bursts (Table 1). To exclude the possibility that there may be a shift of progenitor cell compartment between nonadherent progenitor cells produced by cobblestone islands and adherent progenitors in cobblestones, we tested the colony formation of adherent progenitors. Adherent hematopoietic progenitors were obtained by procuring the adherent cell layer of LTBMCs at 4 weeks of culture followed by passing through the Sephadex G-10 column as described in Materials and Methods. Nonadherent cells formed 81 ± 4 and 58 ± 2/5 × 104 total colonies in control and in TN-C–deficient condition, respectively (P < .001, Student's t-test) and adherent hematopoietic cells formed 35 ± 4 and 26 ± 2/5 × 104 in control and in TN-C–deficient condition, respectively (P < .01, Student's t-test). Thus, decreased colony-forming ability in LTBMCs of TN-C was not simply a shift in progenitor cell compartments. Spleen colony formation (day 12 CFU-S), another assay that indicates colony formation of more primitive progenitor cells, was significantly lower in TN-C–deficient mice (Table 2). These results indicate that colony-forming capacity of nonadherent cells produced in the cultures was lower in TN-C–deficient conditions.
Addition of TN-C to LTBMCs of TN-deficient mice.
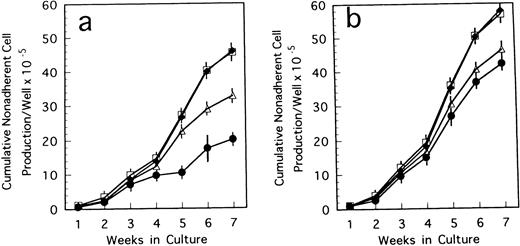
To confirm the biological role of TN-C on hematopoietic activity in TN-C deficient mice, we performed a series of experiments. When 4 to 100 ng/mL TN-C derived from a melanoma cell line was added to the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice both in the Dexter's condition and Whitlock-Witte's condition, hematopoietic focus formations, cobblestone islands, recovered rapidly in a TN-C dose-dependent manner. The number of hematopoietic cells produced was markedly higher in the TN-C-added LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice than in the LTBMCs without TN-C (Figs 4a and5a). The level of cell production by LTBMCs in TN-C–deficient mice supplemented with 20 to 100 ng/mL TN-C recovered to the level of control mice without TN-C addition (Fig 4av 4b and Fig 5a v 5b). Furthermore, TN-C–added LTBMCs of control mice also showed enhanced production of hematopoietic cells (Figs 4b and 5b). However, addition of TN-C to LTBMCs at the concentration over 500 ng/mL resulted in disruption of the stromal layer and hematopoietic focus followed by decreased production of hematopoietic cells. Glioma-derived TN-C had the same effect on the production of hematopoietic cells produced by TN-C–deficient LTBMCs (data not shown). These results indicated that the addition of TN-C to the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice induces a recovery from the impaired hematopoiesis that is observed in TN-C–deficient mice. In crossover reconstitution of coculture systems, it was also shown that TN-C addition had same effect of recovery from the impaired hematopoiesis in TN-C–deficient mice (Fig 3).
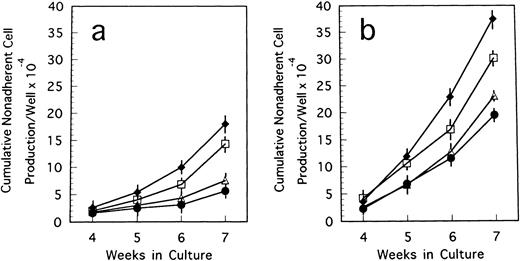
Cumulative nonadherent cell production by LTBMCs treated with TN-C glycoprotein in Dexter's culture condition from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice (a) and control mice (b) obtained at 7 weeks of age. Results represented as cumulative mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly by at least four cultures per group per week. TN-C was added to LTBMCs at final concentration of 4 ng/mL (▵), 20 ng/mL (□), 100 ng/mL (⧫), and without TN-C (•). Results were significantly different between TN-C–treated and TN-C–nontreated cultures (P < .01) in both culture systems. Two other identical experiments yielded comparable results.
Cumulative nonadherent cell production by LTBMCs treated with TN-C glycoprotein in Dexter's culture condition from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice (a) and control mice (b) obtained at 7 weeks of age. Results represented as cumulative mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly by at least four cultures per group per week. TN-C was added to LTBMCs at final concentration of 4 ng/mL (▵), 20 ng/mL (□), 100 ng/mL (⧫), and without TN-C (•). Results were significantly different between TN-C–treated and TN-C–nontreated cultures (P < .01) in both culture systems. Two other identical experiments yielded comparable results.
Cumulative nonadherent cell production by LTBMCs treated with TN-C glycoprotein in Whitlock-Witte's culture condition from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice (a) and control mice (b) obtained at 7 weeks of age. Results represented as cumulative mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly by at least four cultures per group per week. TN-C was added to LTBMCs at final concentration of 4 ng/mL (▵), 20 ng/mL (□), 100 ng/mL (⧫), and without TN-C (•). Results were significantly different between TN-C–treated and TN-C–nontreated cultures (P < .01) in both culture systems. Two other identical experiments gave comparable results.
Cumulative nonadherent cell production by LTBMCs treated with TN-C glycoprotein in Whitlock-Witte's culture condition from BM cells of TN-C–deficient mutant mice (a) and control mice (b) obtained at 7 weeks of age. Results represented as cumulative mean ± SD of nonadherent cells produced weekly by at least four cultures per group per week. TN-C was added to LTBMCs at final concentration of 4 ng/mL (▵), 20 ng/mL (□), 100 ng/mL (⧫), and without TN-C (•). Results were significantly different between TN-C–treated and TN-C–nontreated cultures (P < .01) in both culture systems. Two other identical experiments gave comparable results.
Furthermore, when 2 to 10 μg/mL soluble fragment of FN or 5 to 50 μg/mL HS was added to the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice both in the Dexter's condition and Whitlock-Witte's condition, the number of hematopoietic cells produced was markedly higher in the FN- or HS-added LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice than in the LTBMCs without FN or HS. This increment of hematopoietic cell production was less than that observed in TN-C-added LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice (data not shown). Addition of FN to LTBMCs at the concentration over 50 μg/mL and of HS over 200 μg/mL also resulted in disruption of the stromal layer and hematopoietic focus.
Effect of TN-C-added LTBMCs on colony formation by the produced cells from LTBMCs.
In comparison with TN-C deficient mice, significantly greater colony formation was observed in nonadherent cells produced by TN-C-added LTMBCs of TN-C–deficient mice, characterized by an increased number of multilineage colonies and erythroid bursts (Fig 6). As with cell production from LTBMCs, the level of colony formation of nonadherent cells from LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice added with 20 to 100 ng/mL TN-C recovered to the level of control mice without the addition of TN-C to the LTBMCs (Fig 6). Furthermore, colony formation of nonadherent cells from control LTBMCs treated with TN-C also increased (Fig 6). In addition to TN-C effect to LTBMCs on colony formation, FN or HS was added to LTBMCs to see the effects of these molecules on colony formation. As shown in Fig 7, nonadherent cells produced by FN- or HS-added LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice formed greater colonies compared with those by control LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice. Again, colony formation of nonadherent cells from control LTBMCs treated with FN or HS also increased. To exclude the possibility that ECM molecule itself acts on the progenitor cells to enhance colony-forming capacity of hematopoietic progenitor cells, we evaluated the influence of TN-C on the colony-forming assay using BM cells or nonadherent cells from LTMBCs of both control and TN-C–deficient mice. As shown in Table 3, TN-C did not affect the number of colonies in terms of the formation of multilineage colonies or erythroid bursts in the presence or absence of the growth factors, IL-3 and EPO. Furthermore, other ECM molecules examined, FN or HS as control to TN-C, also did not affect the colony formations (Table 4). These results clearly show that the exogenous addition of TN-C to LTBMCs changes stromal cell-mediated hematopoiesis, but that TN-C did not directly act on hematopoietic progenitor cells. Glioma-derived TN-C had the same effect on the formation of hematopoietic colonies in a series of experiments described above (data not shown).
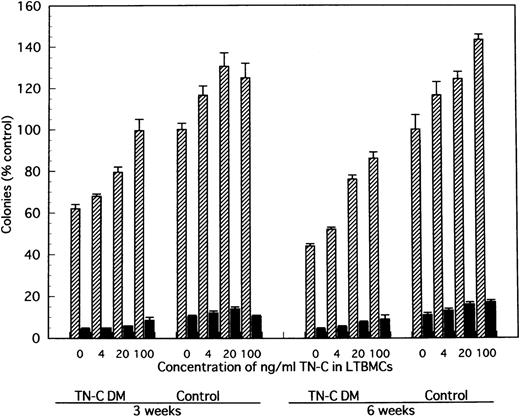
Effect of TN-C–added LTBMCs on colony formation by the produced cells from LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice and of control mice. At weeks 3 and 6 after induction of LTBMCs with TN-C at the final concentration of 0, 4, 20, and 100 ng/mL, nonadherent cells were obtained and cultured in methylcellulose medium as described in Materials and Methods. Colonies (>50 cells) were counted at day 14. Visualized hemoglobinized colonies were counted as erythroid bursts (BFU-E). Results are mean ± SD of triplicate plates and are expressed as the percentage of the value obtained in nonadherent cells from control LTBMCs without TN-C, which formed 134 ± 4 colonies including 14 ± 1 erythroid bursts per 5 × 104 nonadherent cells at week 3, and 103 ± 7 colonies including 11 ± 1 erythroid bursts at week 6 of LTBMCs. TN-C DM, tenascin-C–deficient mutant mice.
Effect of TN-C–added LTBMCs on colony formation by the produced cells from LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice and of control mice. At weeks 3 and 6 after induction of LTBMCs with TN-C at the final concentration of 0, 4, 20, and 100 ng/mL, nonadherent cells were obtained and cultured in methylcellulose medium as described in Materials and Methods. Colonies (>50 cells) were counted at day 14. Visualized hemoglobinized colonies were counted as erythroid bursts (BFU-E). Results are mean ± SD of triplicate plates and are expressed as the percentage of the value obtained in nonadherent cells from control LTBMCs without TN-C, which formed 134 ± 4 colonies including 14 ± 1 erythroid bursts per 5 × 104 nonadherent cells at week 3, and 103 ± 7 colonies including 11 ± 1 erythroid bursts at week 6 of LTBMCs. TN-C DM, tenascin-C–deficient mutant mice.
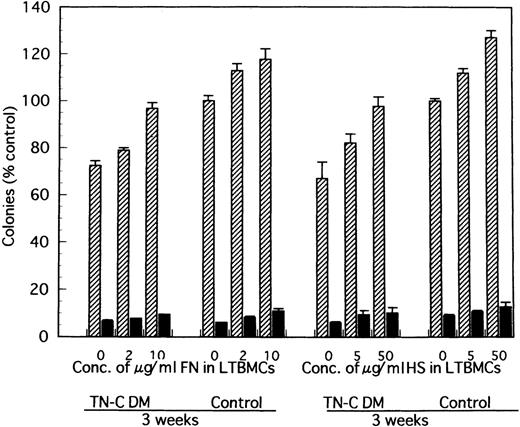
Effect of FN- and HS-added LTBMCs on colony formation by the produced cells from LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice and of control mice. At week 3 after induction of LTBMCs with FN at the final concentration of 0, 2, and 10 μg/mL or HS at 0, 5, and 50 μg/mL, nonadherent cells were obtained and cultured in methylcellulose medium. Results are mean ± SD of triplicate plates and are expressed as the percentage of the value obtained in nonadherent cells from control LTBMCs without FN, which formed 122 ± 3 colonies including 7 ± 1 erythroid bursts per 5 × 104 nonadherent cells at week 3, and from control LTBMCs without HS, which formed 122 ± 2 colonies including 9 ± 2 erythroid bursts per 5 × 104nonadherent cells at week 3. TN-C DM, tenascin-C–deficient mutant mice.
Effect of FN- and HS-added LTBMCs on colony formation by the produced cells from LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice and of control mice. At week 3 after induction of LTBMCs with FN at the final concentration of 0, 2, and 10 μg/mL or HS at 0, 5, and 50 μg/mL, nonadherent cells were obtained and cultured in methylcellulose medium. Results are mean ± SD of triplicate plates and are expressed as the percentage of the value obtained in nonadherent cells from control LTBMCs without FN, which formed 122 ± 3 colonies including 7 ± 1 erythroid bursts per 5 × 104 nonadherent cells at week 3, and from control LTBMCs without HS, which formed 122 ± 2 colonies including 9 ± 2 erythroid bursts per 5 × 104nonadherent cells at week 3. TN-C DM, tenascin-C–deficient mutant mice.
DISCUSSION
In hematopoietic organs, stromal cells such as fibroblasts, epithelial cells, and macrophage-like cells develop networks to maintain hematopoiesis, ie, hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal, proliferation, and growth, by interaction with hematopoietic progenitor cells. ECM glycoproteins produced by the stromal cells are known to play a critical role in the regulation of cell growth and differentiation.1,2 Recent evidence that TN-C is expressed in the stromal cells of the hematopoietic system1,44,45 or lymphoid organs46,47 and that anti–TN-C antibody blocks the attachment of hematopoietic progenitor cells to the stromal layer45 suggests the involvement of TN-C in the regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cells by interaction with the stromal cells. By the assessments of colony-forming capacity and longevity of continuous BM cultures and crossover reconstitution assay, we showed that hematopoietic activity in TN-C–deficient mutant mice is markedly lower than in control mice in which TN-C gene is normally expressed. The addition of TN-C glycoprotein to the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice clearly induced the recovery of hematopoietic cell production and colony-forming capacity. In the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice both in Dexter's and Whitlock-Witte's condition, TN-C glycoprotein was not detected at all in the stromal layer or conditioned media using metabolic labeling and immunoprecipitation methods (data not shown). This finding confirmed that TN-C was not induced in the LTBMCs of TN-C–deficient mice by exogenous stimuli such as culture conditions and concomitant hematopoietic progenitor cells. Furthermore, TN-C did not induce the hematopoietic progenitor cells to enhance colony-forming capacity indicated by the colony-forming assay coexistent with TN-C. Thus, the impaired hematopoiesis in TN-C–deficient mice might be affected by stromal cell–mediated hematopoiesis. We showed direct evidence of the critical involvement of ECM in the maintenance of multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells in TN-C–deficient mutant mice. As mentioned by Forsberg et al,35 indicating that a number of ECM proteins might be compensatory and exchangeable during the processes of tissue repair in TN-C–deficient mice, we also demonstrated that the addition of FN or HS to LTBMCs induced a recovery from the impaired hematopoiesis that was observed in TN-C–deficient mice. FN, one of the components of ECM molecules, plays an important role in the regulation of hematopoietic differentiation,48,49 and glycosaminoglycan side chains, especially HS, has been shown to be a key molecule as selective compartmentalization of growth factors to regulate hematopoiesis through stroma-stem interaction.1 50 The mechanism(s) of action of TN-C on hematopoietic stem cell and microenvironment remain to be determined; however, TN-C may possibly act by increasing binding of hematopoietic cells to stromal cells and by increasing the utilization of hematopoietic growth factors by the stem cells cooperating with other ECM molecules. Our results imply that the redundant supplementary ECM components other than TN-C such as FN influence the interaction between the hematopoiesis-supportive microenvironment and hematopoietic stem cells under TN-C–deficient condition by the modification of behavior of stroma–stem cell and stroma–growth factor–stem cell networks. Further studies are required to clarify the function of the TN families in vivo with special reference to organogenesis of hematopoietic tissues during development and are also required to generate specific knockout mutant mice of other ECM genes to evaluate the effects of defective gene(s) on concordant hematopoietic regulation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Drs T. Osanai and J. Arikawa (Institute of Animal Experimentation, Hokkaido University School of Medicine), and Drs Y. Hakamata and M. Murata (Laboratory of Experimental Medicine, Jichi Medical School) for their valuable advice on animal care and handling. We are also grateful to J. Yamanoi-Saito, Y. Fukuda, and M. Yamane for excellent technical assistance.
Supported in part by the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas No. 05274106 from the Education, Science and Culture of Japan, and a grant from the Yamanouchi Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders.
Address reprint requests to Masatsugu Ohta, MD, Division of Biochemistry, Cancer Institute, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, N-15, W-7, Kita-Ku, Sapporo 060 Japan.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" is accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.