Abstract
The selectins are membrane glycoproteins promoting adhesive events between leukocytes, platelets, and endothelial cells. We have previously demonstrated that platelets roll on P-selectin expressed on stimulated endothelium. In this study, we wished to examine the function of both the platelet and endothelial selectins, P- and E-selectins, in mediating platelet-endothelial interactions during inflammation. We demonstrate, using intravital microscopic examination of venules inflamed with tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), that resting platelets interact with both P- and E-selectins and that the leukocyte α(1,3)fucosyltransferases FucT IV and FucT VII do not provide platelets with selectin ligand activity. We also show that after thrombin activation of wild-type (+/+) platelets, platelet P-selectin can mediate interactions on a TNF-α–inducible endothelial ligand. To evaluate the potential role of platelet P-selectin in the recruitment of leukocytes to inflammatory sites, we reconstituted the bone marrow of mice deficient in both P- and E-selectins (P/E−/−) with wild-type (+/+) or P-selectin–deficient (P−/−) bone marrow containing megakaryocytic precursors. Providing +/+ platelets to P/E−/− mice by bone marrow transplantation did not rescue the immunodeficient phenotype, suggesting that platelet P-selectin does not have an active function in the recruitment of leukocytes into inflammatory sites. To participate in inflammatory or hemostatic responses, platelets may use the endothelial selectins.
MAINTENANCE OF VASCULAR integrity requires the normal function of both the vascular endothelium and circulating platelets. Although endothelial cells normally act as a nonthrombogenic surface, they may become procoagulant in certain circumstances.1 For example, after stimulation with endotoxin, interleukin-1 (IL-1), or tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), endothelial cells synthesize tissue factor and other procoagulant proteins, which may promote acute thrombosis in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases. In contrast, inherited defects in platelet adhesion molecules are associated with bleeding diathesis.
Stimulated endothelial cells also express a variety of adhesion molecules. Among these are two selectins, members of a family of receptors involved in adhesive interactions among leukocytes, platelets, and the endothelium. P-selectin is stored in Weibel-Palade bodies in the endothelial cells and in the α-granules of platelets. It is rapidly translocated to the surface of both cell types after stimulation with various secretagogues.2-4 E-selectin expression is induced by endotoxin or inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1 and TNF-α.5 Endothelial selectins bind carbohydrate ligands expressed on the surface of leukocytes. Sialylated and fucosylated oligosaccharides, such as sialyl-Lewis,x appear crucial for binding activity.6 Most selectin-binding carbohydrate structures are synthesized by α(1,3)fucosyltransferases (FucTs), of which FucT IV and FucT VII are expressed in leukocytes and thought to be crucial for the biosynthesis of selectin ligands. FucT VII, in particular, appears to direct the expression of sialyl-Lewisx.7 8
The generation via gene targeting of animals deficient for these receptors has provided valuable insight into their functions in vivo.9 Whereas P-selectin knockout mice display severe defects in leukocyte rolling and extravasation in the early phases of inflammation,10 E-selectin–deficient mice are remarkably free of such defects.11 However, the ablation of both endothelial selectins produces profound abnormalities in leukocyte dynamics, indicating that P- and E-selectins cooperate in vivo to mount an appropriate inflammatory response and that they are crucial for leukocyte homeostasis.12,13 Similarly, mice lacking FucT VII exhibit severe defects in leukocyte rolling and extravasation and also lymphocyte homing,14 which are further exaggerated in animals doubly deficient in leukocyte FucT IV and FucT VII (Thall et al, manuscript submitted).
Previously, we reported that, in a manner similar to leukocytes, platelets roll on the endothelium of venules stimulated with the secretagogue calcium ionophore A23187 and that this interaction depended on endothelial P-selectin, with little contribution from platelet P-selectin.15 Consistent with a role for P-selectin in hemostasis, we subsequently detected a 40% prolongation of the tail bleeding time and greater hemorrhage after a local Shwartzman reaction in P-selectin–deficient mice compared with wild-type controls.16 The local Shwartzman reaction, a model of intravascular coagulation induced by successive doses of endotoxin and TNF-α, illustrates the intricate relations between inflammatory and hemostatic systems. TNF-α administered alone does not produce intravascular coagulation but induces leukocyte rolling in the mouse that is dependent on both P- and E-selectins.12 13 Here, we report on selectin-mediated platelet-endothelial interactions during inflammation induced by TNF-α as observed by intravital microscopy of mesenteric venules. We also examine whether wild-type platelet P-selectin can ameliorate the immunodeficient characteristics of P- and E-selectin doubly null mice.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals.
Male C57BL/6J/129Sv mice, wild-type (+/+) or deficient in P-selectin (P−/−),10 E-selectin (E−/−),12 or both P- and E-selectins (P/E−/−),12 weighing 18 to 22 g (aged 5 to 6 weeks) were used for intravital microscopy. Animals were housed at the Center for Blood Research of Harvard Medical School or the Center for Cancer Research of Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Blood for platelet preparation was harvested from +/+, P−/−, or FucT IV/VII −/− mice (Thall et al, manuscript submitted) of any sex or age. The experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Center for Blood Research.
Blood sampling and platelet preparation.
Mouse blood was obtained as previously described.15Briefly, blood was collected from the retro-orbital venous plexus in acid-citrate-dextrose ([ACD] 38 mmol/L citric acid, 75 mmol/L trisodium citrate, and 100 mmol/L dextrose, 1/10 vol), and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was obtained by two sequential centrifugations (280g for 8 minutes and 280g for 3 minutes). Platelets were isolated by filtering the resulting PRP through a Sepharose 2B (Sigma, St Louis, MO) column equilibrated with PIPES buffer (25 mmol/L PIPES, 137 mmol/L NaCl, 4 mmol/L KCl, and 0.1% wt/vol dextrose), pH 7.0 for experiments using resting platelets, and pH 7.4 to optimize activation for experiments with activated platelets.
Gel-filtered platelets were fluorescently labeled with calcein AM 0.25 μg/mL (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) as previously described.15 In experiments using activated platelets, the preparation was incubated with human thrombin (Sigma) 0.2 U/mL for 15 minutes at 37°C. Thrombin was then inhibited with hirulog BG8967 1 μg/mL (generous gift from Dr John Maraganore, Biogen, Cambridge, MA). Recipient mice were injected via the lateral tail vein with 5 × 109 platelets/kg in a volume of 200 to 400 μL PIPES buffer.
Intravital microscopy.
Recipient mice were treated with murine recombinant TNF-α (Genzyme Corp, Boston, MA) 0.5 μg in 500 μL phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) intraperitoneally. Such treatment induces P- and E-selectin–dependent leukocyte rolling in the mesentery.12 At 3.5 hours after TNF-α injection, animals were transfused with calcein AM–labeled platelets and immediately anesthetized with 2.5% tribromoethanol 0.15 mL/10 g. Preparation of the mesentery was as previously described.15 A suitable venule for filming (28 to 40 μm in diameter) was found within about 15 minutes following injection of labeled platelets. Venules were visualized using a Zeiss Axiovert 135 inverted microscope (objective 32X, 0.4NA, Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with a 100 W HBO fluorescent lamp source (Opti Quip, Highland Mills, NY) with a narrow-band FITC filter set (Chroma Technology, Brattleboro, VT), and a silicon-intensified tube camera C2400 (Hamamatsu, Tokyo, Japan) connected to a SVHS video recorder AG-6730 (Panasonic, Tokyo, Japan). Recording of one venule per animal was made for 20 minutes for resting and 10 minutes for activated platelets, respectively. Centerline erythrocyte velocity (Vrbc) was measured using an optical Doppler velocimeter (Microcirculation Research Institute, Texas A&M College of Medicine, College Station, TX). The venular shear rate (τ) was calculated based on Poiseuille's Law for a newtonian fluid, τ = 8(Vmean/Dv), where Dv is the diameter of the venule and Vmean is estimated from the measured Vrbc using the empirical correlation Vmean = Vrbc/1.6.17
Image analysis.
The critical velocity (Vcrit) for each venule was calculated using the equation, Vcrit = Dp/Dv × (2 − Dp/Dv), where Dp is the diameter of a platelet (2 μm). Quantitation of platelet-endothelial interactions was made by an investigator blind to the genotype of the platelets or venules. Platelets traveling a distance of at least 30 μm at a velocity less than Vcrit were scored as “rolling.” Any platelet interacting with the endothelium at a velocity less than Vcrit but not fulfilling the criteria for rolling was labeled as “captured.” The average number of rolling or captured platelets per minute over a venular segment of 250 μm was determined by taking 10 counts of 1 minute (five counts in each half of filming for resting platelets and the whole recording for activated platelets).
Bone marrow transplantation.
P- and E-selectin doubly deficient mice and wild-type female mice aged 7 to 8 weeks received whole-body irradiation (9.5 to 11.0 cGy) in two split doses 3 hours apart, from a cesium source (model 143; J.L. Shepherd, San Fernando, CA). These irradiated recipient mice were then injected with 5 × 106 fresh bone marrow cells (in 300 μL minimal essential medium) from +/+ or P−/− male donors. Transplanted animals were transferred to a sterile microisolator unit and fed with sterile chow food and acidified (pH 2.5) sterile water for 4 weeks. After this recovery period, blood cell counts and the expression of platelet P-selectin were assessed and the mice were transferred to a conventional (nonsterile) environment.
Flow cytometry.
To examine P-selectin expression, 3 to 4 drops of blood, obtained by a retro-orbital bleed from P/E−/− transplanted mice and +/+ and P−/− controls were transferred into 1 mL solution containing 9 parts Hanks balanced salt solution (without calcium and magnesium) and 1 part ACD. PRP was isolated by centrifugation (280g for 5 minutes at room temperature), and the platelets were washed five times (centrifugation 2,000g for 6 minutes) in PIPES buffer (pH 6.1) and resuspended in 500 μL PIPES buffer at physiologic pH (7.4) for activation with thrombin (0.2 U/mL) at 37°C for 15 minutes. Thrombin was removed by a single wash with PIPES buffer, and the platelets were resuspended in PBS-0.01% bovine serum albumin (BSA). Activated platelets were stained for P-selectin using a rabbit polyclonal antibody 1:100 (PharMingen, San Diego, CA) and fluorescein-conjugated sheep anti-rabbit antibody 1:250 (Cappel, Durham, NC). Analysis of 10,000 events was performed on a FACSCaliber flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Mountain View, CA).
Thioglycollate-induced peritonitis.
Mice were injected intraperitoneally with 1 mL 2.95% thioglycollate (Sigma). Blood was obtained by retro-orbital sampling 6 hours after thioglycollate injection. The animals were killed, and peritoneal lavage was performed using 10 mL PBS containing 0.5 mmol/L EDTA, 1 U/mL heparin, and 0.1% BSA. Total cell numbers were determined with a Coulter (Hialeah, FL) counter. The absolute number of neutrophils, eosinophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes were calculated from differential counts of Wright-stained cytospin preparations.
Statistical analysis.
All values are reported as the mean ± SEM. Statistical significance for continuous variables was assessed by Student's t-test. The log-rank test was used to determine statistical significance between probability curves (prevalence of dermatitis).
RESULTS
Platelets interact with both endothelial selectins in inflamed venules.
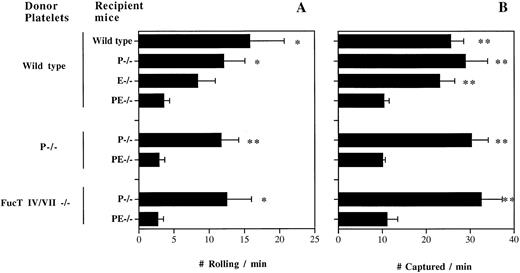
To examine whether selectins are important in platelet-endothelial interactions in venules during inflammation, we transfused fluorescently labeled resting +/+ platelets into TNF-α–treated +/+ or P/E−/− recipient mice and rapidly prepared the animals for intravital microscopy. We observed rolling interactions with the endothelium (Fig 1A) similar to what we described in calcium ionophore (A23187)-stimulated +/+ venules.15 Significantly lower numbers of rolling platelets were seen in TNF-α–treated P/E−/− recipient mice, suggesting that platelets roll on at least one of the endothelial selectins during inflammation. To investigate which endothelial selectin mediates platelet rolling, we transfused resting +/+ platelets into P- or E-selectin singly deficient mice. Venules of P−/− mice treated with TNF-α displayed a reduced flux of rolling platelets compared with that of +/+ recipient mice (Fig 1A). In TNF-α–treated E−/− venules, the rolling activity was reduced further in comparison to +/+ venules, suggesting that under these experimental conditions platelets interact preferentially with E-selectin (Fig 1A). To evaluate whether platelet P-selectin contributed to this interaction, we transfused P−/− platelets into TNF-α–treated P−/− and P/E−/− recipients. The frequency of P−/− platelet rolling was similar to that of +/+ platelets, confirming that platelets roll on endothelial selectins in inflammation.
Resting platelets interact with both endothelial P- and E-selectins in TNF-α–stimulated venules. Gel-filtered fluorescent wild-type, P−/−, or FucT IV/VII−/− platelets were transfused into wild-type, P−/−, E−/−, or P/E−/− recipient mice. The number of platelets (A) rolling and (B) captured over a 250-μm venular segment was determined; n = 5 to 9. *P < .05, **P < .01: v P/E−/−.
Resting platelets interact with both endothelial P- and E-selectins in TNF-α–stimulated venules. Gel-filtered fluorescent wild-type, P−/−, or FucT IV/VII−/− platelets were transfused into wild-type, P−/−, E−/−, or P/E−/− recipient mice. The number of platelets (A) rolling and (B) captured over a 250-μm venular segment was determined; n = 5 to 9. *P < .05, **P < .01: v P/E−/−.
Along with the rolling activity, we noted that many platelets stuck to the venular wall or interacted briefly without fulfilling our criteria for rolling. Although the majority of these interactions were of a transient-sticking type, some platelets adhered for a prolonged duration on TNF-α–treated venules. The fate of sticking platelets could not be evaluated in this system, due to the rapid bleaching (<1 minute) of the fluorescent dye. We determined the number of platelets captured by the vessel wall but not rolling per minute over the same 250-μm venular segment (Fig 1B). Removing one endothelial selectin does not affect the frequency of platelet capture by the vessel wall compared with that of +/+ mice, but the absence of both selectins diminished these interactions by about threefold. Again, similar numbers were obtained from transfusion of resting P−/− platelets into P−/− and P/E−/− recipients (Fig 1B). These results suggest an overlapping role for endothelial P- and E-selectins in platelet interactions with inflamed venules, similar to what has been seen for leukocyte adhesion in other systems.11-13,18 19 The fact that hemodynamic parameters were similar among venules of various genotypes rules out hemodynamic influences on these findings (Table1).
FucT IV and FucT VII do not endow platelets with selectin ligand activity.
Given the similar dependence on endothelial selectins for leukocyte and platelet rolling, we suspected that the α(1,3)fucosyltransferases responsible for leukocyte selectin ligand expression (FucT IV and FucT VII20) might contribute to E- and P-selectin ligand activity on platelets. We therefore isolated platelets from FucT IV/VII double knockout mice and transfused them into TNF-α–treated P−/− and P/E−/− recipients. Surprisingly, FucT IV/VII −/− platelets rolled and were captured as frequently as wild-type platelets in P−/− venules, and similarly, the interaction was greatly reduced in P/E−/− venules (Fig 1A and B). These data suggest that FucT IV and FucT VII do not play a significant role in the synthesis of platelet selectin ligands.
P-selectin on activated platelets can mediate their capture and rolling on a TNF-α–inducible endothelial ligand.
Following the release of Weibel-Palade bodies by A23187, a few minutes after the exteriorization of the mesentery, activated platelets (expressing P-selectin) do not interact with P-selectin–deficient endothelium.15 To investigate whether the situation changes in inflammation, we transfused fluorescently labeled thrombin-activated +/+ or P−/− platelets into TNF-α–treated P/E−/− mice. P/E−/− animals are useful to examine interactions between activated platelets and the endothelium during inflammation, since leukocyte rolling is virtually absent in P/E−/− mice12 (and activated +/+ platelets tend to bind rolling leukocytes15). Resting platelets rolled and were captured minimally under these conditions (Fig 1). We observed numerous interactions of +/+ activated platelets in inflamed venules of P/E−/− mice, whereas very little capture and rolling was seen when activated P−/− platelets were injected or when mice were not treated with TNF-α (Fig 2). These results indicate that activated platelet P-selectin promotes adhesion to inflamed endothelial cells, and that this can occur in the absence of endothelial selectins.
P-selectin of activated platelets can mediate interactions with TNF-α–treated venules in P- and E-selectin double-deficient mice. Number of (A) rolling and (B) captured platelets per minute; n = 5 to 8. *P < .05 v the other 2 groups; **P = .01 v P−/− platelets.
P-selectin of activated platelets can mediate interactions with TNF-α–treated venules in P- and E-selectin double-deficient mice. Number of (A) rolling and (B) captured platelets per minute; n = 5 to 8. *P < .05 v the other 2 groups; **P = .01 v P−/− platelets.
Transplantation of wild-type bone marrow into P- and E-selectin double-deficient mice does not rescue the immunodeficient phenotype.
It has been hypothesized that platelets might be recruited in numbers large enough to cover segments of inflamed venules and, through their high surface expression of P-selectin, actively participate in the recruitment of leukocytes. Supporting this concept, recent studies have demonstrated that leukocytes can roll and extravasate in vitro on a monolayer of activated platelets expressing P-selectin.21-23 To test whether platelet P-selectin could mediate leukocyte recruitment to sites of inflammation in vivo, we transplanted wild-type bone marrow (containing +/+ megakaryocyte precursors) into P/E−/− mice. We asked three questions: Would platelets expressing P-selectin (1) reduce the severe leukocytosis of P/E−/− mice, (2) limit the incidence of bacterial dermatitis in these mice, and (3) improve the extravasation of leukocytes in the thioglycollate model of peritonitis?
In two independent experiments, a total of 38 P/E−/− female mice were divided into two groups (by littermate pairs) and received either +/+ or P−/− bone marrow after a lethal dose of irradiation. The mice were allowed to recover for 4 weeks before expression of platelet P-selectin was assessed by flow cytometry. All mice survived the procedure. Platelets of mice transplanted with +/+ marrow displayed mean fluorescence levels of P-selectin comparable to wild-type nontransplanted controls, and animals reconstituted with P−/− marrow remained negative for P-selectin (data not shown). At week 5 after reconstitution, blood cell counts were determined. P/E−/− mice harboring +/+ circulating platelets displayed total leukocyte and differential counts comparable to those of mice transplanted with P−/− bone marrow (Table 2). This suggests that, unlike endothelial P-selectin, platelet P-selectin does not play a significant role in leukocyte homeostasis. Reconstituted animals were observed periodically for occurrence of the typical spontaneous bacterial dermatitis seen in P/E−/− mice.12No significant difference in the incidence of skin infection was observed over a 4-month period regardless of whether mice carried platelet P-selectin (Fig 3).
Probability of spontaneous occurrence of infectious dermatitis in P- and E-selectin double-deficient mice after bone marrow transplantation. Lethally irradiated P/E−/− recipient mice were reconstituted with either +/+, (□) or −/− (◊) bone marrow. Mice were periodically observed for the presence of dermatitis; n = 19. P = .31 (log-rank test).
Probability of spontaneous occurrence of infectious dermatitis in P- and E-selectin double-deficient mice after bone marrow transplantation. Lethally irradiated P/E−/− recipient mice were reconstituted with either +/+, (□) or −/− (◊) bone marrow. Mice were periodically observed for the presence of dermatitis; n = 19. P = .31 (log-rank test).
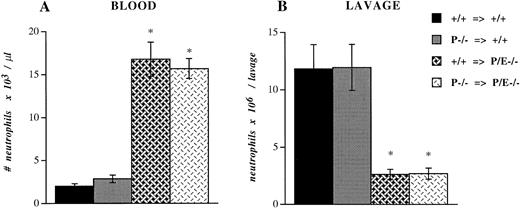
To investigate if platelet P-selectin would influence the recruitment of leukocytes during experimental inflammation, we performed bone marrow transplantation using +/+ and P−/− bone marrow cells in another cohort of +/+ and P/E−/− lethally irradiated mice. Five weeks after transplantation, P-selectin expression in platelets of mice reconstituted with +/+ marrow was similar to that of wild-type controls, while the platelets of mice transplanted with P−/− marrow, predictably, were negative (data not shown). These bone marrow–reconstituted mice were injected intraperitoneally with thioglycollate. After 6 hours, blood samples were collected and peritoneal lavage was performed. P/E−/− mice reconstituted with +/+ megakaryocyte precursors did not show any difference in the circulating neutrophil count (Fig 4A) or the number of neutrophils recruited into the peritoneum (Fig 4B) compared with P/E−/− animals transplanted with −/− megakaryocyte precursors. The proportions of monocytes, eosinophils, and lymphocytes also were not significantly different (data not shown). Similarly, neutrophil emigration to inflamed peritoneum was not altered in +/+ mice harboring P−/− platelets compared with +/+ mice transplanted with +/+ platelets (Fig 4B). As previously demonstrated,12 the recruitment of neutrophils into the thioglycollate-inflamed peritoneum of both groups of P/E−/− mice was significantly impaired compared with that of wild-type animals. Taken together, these results indicate that despite its interactions with inflamed endothelium, platelet P-selectin does not appear to participate in leukocyte homeostasis or in the recruitment of leukocytes into infected or inflamed sites in P- and E-selectin doubly deficient mice. In addition, platelet P-selectin does not appear to potentiate neutrophil efflux to inflamed peritoneum.
Peripheral neutrophil count and peritoneal neutrophil influx after thioglycollate administration. +/+ or P−/− bone marrow cells were transplanted (⇒) into irradiated +/+ or P/E−/− recipients. Mice were allowed to recover for 4 weeks before being challenged with thioglycollate for 6 hours. Blood cell counts were obtained with a Coulter counter, and (A) the absolute neutrophil number/μL was determined from Wright-stained smears. Nucleated cell numbers were also determined by Coulter counter on lavage fluids from the peritoneum, and (B) the neutrophil number per lavage was calculated from differential counts performed on Wright-stained cytospin preparations; n = 7 to 8. *P < .0005 versus wild type.
Peripheral neutrophil count and peritoneal neutrophil influx after thioglycollate administration. +/+ or P−/− bone marrow cells were transplanted (⇒) into irradiated +/+ or P/E−/− recipients. Mice were allowed to recover for 4 weeks before being challenged with thioglycollate for 6 hours. Blood cell counts were obtained with a Coulter counter, and (A) the absolute neutrophil number/μL was determined from Wright-stained smears. Nucleated cell numbers were also determined by Coulter counter on lavage fluids from the peritoneum, and (B) the neutrophil number per lavage was calculated from differential counts performed on Wright-stained cytospin preparations; n = 7 to 8. *P < .0005 versus wild type.
DISCUSSION
During inflammation, several adhesion molecules such as E-selectin, P-selectin, VCAM-1, and ICAMs are induced and/or upregulated on endothelial cells.24 This translates in vivo into an increase in leukocyte rolling and adherence on venules.25Our present study shows that, similar to leukocytes, platelet-endothelial interactions are mediated by endothelial adhesion molecules upregulated during inflammation. We analyzed both the rolling and the capturing rates of platelets on the venular wall and found that either P- or E-selectin could mediate these adhesion events. Although each endothelial selectin captured free-flowing platelets equally well (Fig 1B), the platelet rolling flux was greater on E-selectin (P−/− recipients) during inflammation (Fig 1A). Platelet sticking and rolling did not require platelet P-selectin, since P−/− platelets behaved similarly to +/+ platelets (Fig 1).
Although the behavior of platelets appears to parallel that of leukocytes in many aspects, differences are also highlighted by the present study. Rolling is thought to be mandatory for leukocytes for subsequent firm adhesion, but it did not appear to be a prerequisite for platelets to arrest on venular endothelium under flow in vivo. Indeed, many platelets were captured without prior rolling (Fig 1B). Another main difference is the surprising lack of a need for leukocyte FucT IV and FucT VII for the biosynthesis of platelet selectin ligand(s), as demonstrated by the similar behavior of FucT IV/VII −/− platelets and platelets derived from +/+ mice (Fig 1A and B). These two enzymes have been shown to provide most of the selectin ligand activity expressed by leukocytes.20 However, the fact that mice deficient in both leukocyte α(1,3)fucosyltransferases have a milder phenotype (e.g., they do not develop infectious dermatitis) than P/E−/− mice suggests that other selectin ligands (fucosylated or nonfucosylated) are functional in vivo. Alternatively, the relative protection from skin infections of FucT IV/VII −/− mice still expressing endothelial selectins might also result from normal platelet-endothelial interactions that may be important for normal host resistance to infections. Furthermore, our results indicate that a ligand(s) for E- and P-selectins is constitutively expressed on the surface of platelets. Such a ligand(s) is likely to bear specific carbohydrate moieties carried by a protein or a glycolipid scaffold.26 Interestingly, purified glycolipids (gangliosides) from human platelets contain sialyl-Lewisxepitopes,27 and similar glycolipids isolated from human myeloid cells have been shown to bind E-selectin.28 29
P/E−/− venules stimulated with calcium ionophore15 or with surgical manipulation (Fig 2) show little interaction with transfused +/+ activated platelets. In contrast, TNF-α induces in vivo binding of activated platelets with venular endothelium that is dependent on platelet P-selectin and does not require endothelial selectins (Fig 2). The nature of the endothelial P-selectin ligand in systemic venules is speculative at the moment. Notably, activated platelets were recently described to interact in high endothelial venules with a cognate molecule expressed constitutively that shares characteristics with L-selectin ligands.30 In systemic venules, an inducible endothelial L-selectin ligand has been previously invoked to explain defects of leukocyte rolling in L-selectin–deficient mice.31 This inducible endothelial ligand for L-selectin may therefore be a potential candidate for binding P-selectin in these venules. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 (PSGL-1) represents another candidate counterreceptor for platelet P-selectin. PSGL-1 is expressed constitutively on polymorphonuclear and monocytic cells and may interact with all three selectins.2Although immunohistochemical staining revealed PSGL-1 expression in the venules of some pathologic tissues, it was not detected in tissues undergoing inflammation.32
Thus, platelets may be recruited to the wall of an inflamed venule in different ways. Resting platelets may roll on endothelial selectins or be captured directly. Likewise, activated platelets, through platelet P-selectin, may be captured or roll in a similar fashion on inflamed venules. What are the biologic roles of selectin-mediated platelet-endothelial interactions? Platelets contain a wide range of biologically active materials that may modulate certain inflammatory responses.33 For example, platelet membranes possess IgE receptors that support the cytotoxic functions of platelets in parasitic infections such as Schistosoma mansoniinfection34 and filariasis,35 and additionally, platelet IgE receptors may initiate T-cell–dependent contact sensitivity.36 Although, by itself, platelet P-selectin does not influence the immunodeficient phenotype of P/E−/− mice, it is possible that platelet and endothelial selectins together reinforce sufficiently reciprocal interactions to allow platelets to contribute to inflammatory responses.
As suggested by the P-selectin–dependent fibrin deposition and leukocyte accumulation within a Dacron graft–induced thrombus37 and the greater hemorrhagic tendency seen in P-selectin–deficient mice,16 selectins expressed on the endothelium or on platelets may also participate in hemostatic mechanisms. It is interesting that platelets also roll on von Willebrand factor (vWf) at high shear forces in vitro.38 Complementing the dynamic adhesion of platelets with vWf on injured vessels at high shear, selectin-mediated platelet-endothelial interactions may represent key components of a surveillance system maintaining the integrity of inflamed venules, and upon vascular injury, they may contribute to platelet plug formation. Although the individual functions of selectins, vWf, fibrinogen, GpIb, and GpIIb/IIIa in hemostasis and thrombosis have not yet been fully defined, mice deficient in these adhesion molecules will permit further dissection of these pathways through in vivo experimentation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We are grateful to Mollie Ullmann-Culleré for mouse husbandry.
Supported in part by National Institute of Health Grants No. PO1 HL-56949 (D.D.W.) and PO1 HL-41484 (R.O.H.), an Investigator Award from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (R.O.H.), and a Fellowship from the Medical Research Council of Canada (P.S.F.).
Address reprint requests to Denisa D. Wagner, PhD, Center for Blood Research, 800 Huntington Ave, Boston, MA 02115.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.