It is still uncertain whether multilineage hematopoietic progenitor cells are affected by human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection in vivo. The SCID-hu Thy/Liv model is permissive of long-term multilineage human hematopoiesis, including T lymphopoiesis. This model was used to investigate the effects of HIV-1 infection on early hematopoietic progenitor function. We found that both lineage-restricted and multilineage hematopoietic progenitors were depleted from grafts infected with either a molecular clone or a primary isolate of HIV-1. Depletion of hematopoietic progenitors (including CD34+ cells, colony-forming units in methylcellulose, and long-term culture-initiating cells) occurred several days before the onset of thymocyte depletion, indicating that the subsequent rapid decline in thymocyte numbers was due at least in part to loss of thymocyte progenitors. HIV-1 proviral genomes were not detected at high frequency in hematopoietic cells earlier than the intrathymic T-progenitor cell stage, despite the depletion of such cells in infected grafts. Proviral genomes were also not detected in colonies derived from progenitor cells from infected grafts. These data demonstrate that HIV-1 infection interrupts both lineage-restricted and multilineage hematopoiesis in vivo and suggest that depletion of early hematopoietic progenitor cells occurs in the absence of direct viral infection.
ALL MODELS OF T-CELL depletion in human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) disease must invoke the failure of hematopoietic organs to produce sufficient T cells to match the rate of their destruction. Several lines of evidence implicate impaired thymopoiesis as a causative factor in HIV-1–associated T-cell depletion.1 HIV-1 infection of thymus in vivo has been demonstrated.2 Intrathymic T progenitor cells have been shown to be infectable by HIV-1 in vitro3,4 and in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv model.5 The thymic pathology induced by HIV-1 in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv model may be strain-dependent5-7 and includes both thymocyte depletion and destruction of thymic epithelium.8 Prethymic progenitor cells in bone marrow may also be infected and depleted by HIV-1, although the frequency of HIV-1 infection of primitive progenitors appears to be low.9-15 In particular, it is uncertain whether HIV-1 effects on central hematopoietic organs such as bone marrow or fetal liver are directly mediated by HIV-1 infection or are the indirect result of altered levels of cytokines and trophic factors.16 17 Animal model systems for HIV-1 infection may assist in defining the pathology of HIV-1 for the design and testing of therapies to reverse or prevent HIV-1–associated cytopenias. In addition, the determination of the earliest stages in thymocyte development affected by HIV-1 infection will be important for the design of therapies to reconstitute immune function.
Among experimental models of HIV-1 infection, the SCID-hu Thy/Liv mouse uniquely allows the study of human hematopoietic function at both the thymic and prethymic stages.18 The conjoint organ formed by transplantation of human fetal thymus and liver not only supports long-term lymphopoiesis, but also maintains a self-replenishing pool of primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells that show potential for development into myeloid and erythroid lineages.
We have used this model to study the effects of HIV-1 infection on early stages of hematopoiesis. Using both a molecular clone and primary strains of HIV-1, we found that depletion of intrathymic T-progenitor cells was a common feature of HIV-1 infection. Using both phenotypic and functional analyses of earlier hematopoietic progenitor cells, we found that HIV-1 infection resulted in depletion of both lineage-restricted and multilineage progenitor cells. Depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells preceded the loss of CD4+CD8+ and CD4+CD8−thymocytes, suggesting that HIV-1 infection interrupted thymocyte development at an early progenitor stage. However, proviral genomes were found to be most concentrated at the stage of the intrathymic T-progenitor cell and were seen in only low copy number in earlier progenitor cells and their progeny in methylcellulose cultures. These in vivo observations support a role for diminished hematopoietic progenitor cell function in the pathogenesis of HIV-1 infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Animals and virus infection.
SCID-hu Thy/Liv mice were constructed as described18-20 and maintained under specific pathogen-free barrier conditions. All animals used in each experiment carried liver and thymus tissue from a single fetal donor. Protocols for the use of fetal tissue were approved by the UCSF Committee on Human Research, and protocols for the care and use of SCID-hu mice were approved by the Committee on Animal Research. Thy/Liv grafts were infected by intragraft injection of 2,000 TCID50 of each isolate or an equivalent volume of medium for mock infection controls, as described.20
Virus stocks.
HIV-1 virus stocks were generated by low passage propagation of primary strains (JD and PD) or molecular clones (NL4-3) in cultures of phytohemagglutinin-activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).20 NL4-3 is an infectious molecular clone of HIV-121 that has been maintained as a plasmid stock and not extensively passaged in tissue culture. JD and PD are uncloned, early passage, syncytium-inducing primary strains of HIV-1. Virus stocks were titrated on PBMC blasts and subjected to endpoint analysis as described.20
Thymocyte immunophenotyping and sorting.
Monoclonal antibodies were obtained from Becton Dickinson Immunocytometry Systems (fluorescein isothiocyanate [FITC]-conjugated anti-CD4, phycoerythrin [PE]-conjugated anti-CD8, biotin-conjugated anti-CD3 and anti-CD8, PE-conjugated anti-CD34, and conjugated isotype controls; Mountain View, CA) and from Caltag (TRI-COLOR-conjugated anti-CD3 and anti-CD8, TRI-COLOR-conjugated streptavidin, and conjugated isotype controls; Burlingame, CA). Cell sorting was performed on a Becton Dickinson FACS Vantage fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS; Becton Dickinson Immunocytometry Systems, Mountain View, CA). Analysis was performed on either the FACS Vantage or on a Becton Dickinson FACScan instrument with CellQuest analysis software. Thymocytes were recovered from grafts by filtration through nylon mesh bags, and the number of total live cells recovered per graft was determined by hemocytometer counting and trypan blue dye exclusion. For sorting of thymocyte subclasses, freshly isolated thymocytes were surface stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD4, PE-conjugated anti-CD8, and TRI-COLOR-conjugated anti-CD3. Percentages of single-positive CD4 and CD8 thymocytes (CD3+CD4+CD8− and CD3+CD4−CD8+), double-positive thymocytes (CD4+CD8+), and intrathymic T-cell progenitors (CD3−CD4+CD8−) were calculated within a live cell lymphocyte gate using forward and side scatter criteria, with positive gates defined by the 99th percentile of isotype staining.
Progenitor cell assays.
Progenitor cells were enriched from bulk thymocytes by negative selection with biotinylated anti-CD3 and anti-CD8 monoclonals and streptavidin-coated magnetic beads (Dynal, Lake Success, NY) and subsequently divided into aliquots for CD34 staining or plating into methylcellulose assays (to measure colony-forming units-cells [CFU-C]) or long-term bone marrow assays (to measure long-term culture-initiating cells [LTC-IC]). The efficiency of bead depletion was assessed by reanalysis using streptavidin-TRI-COLOR. CD34+ progenitor cells were enumerated by surface staining the CD3- and CD8-depleted thymocytes with PE-conjugated anti-CD34 antibody. A total of 100,000 to 500,000 Thy/Liv cells depleted of CD3- and/or CD8-thymocytes were added to methylcellulose cultures (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada) supplemented with 100 ng/mL stem cell factor (SCF) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), 10 ng/mL interleukin-3 (IL-3) and IL-6, and 2 U/mL erythropoietin (EPO; all cytokines were obtained from R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN). Triplicate plates were scored for colony-forming units–granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM), burst-forming units-erythroid (BFU-E), and colony-forming units-granulocyte, erythroid, monocyte, megakaryocyte (CFU-GEMM) after 14 days. LTC-IC were assayed by limiting dilution analysis of CD3- and CD8-depleted cells as previously described,22except that cells were grown on irradiated fetal bone marrow stromal cultures. Cultures were grown for 5 to 6 weeks in the presence of IL-3, IL-6, and SCF and scored for growth-positive wells. Total CFU-C and LTC-IC per graft were calculated as total colonies scored in methylcellulose assay or long-term bone marrow culture, respectively, divided by the fraction of postdepletion cells plated in each assay, divided by the fraction of total cells set aside for bead depletion. The total number of CD34+ cells per graft was calculated as the percentage of bead-depleted cells positive for CD34 staining, multiplied by the number of cells recovered after bead depletion, divided by the fraction of total cells set aside for bead depletion.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of HIV-1 proviral sequence.
Cells recovered from Thy/Liv grafts were stained with monoclonal antibodies to CD3, CD4, CD8, and/or CD34. Live cells were defined by forward and side scatter, and 2,000 cells of each subset (total thymocytes, CD34+, CD3+CD4+CD8−, or CD3−CD4+CD8−) were sorted on a Becton Dickinson FACS Vantage cell sorter. Sorted cells were lysed in 20 μL of PCR buffer with 100 μg/mL proteinase K, digested for 30 minutes at 65°C, and then inactivated at 95°C for 15 minutes. Lysates were serially diluted before 40-cycle PCR amplification of gag sequences, as previously described.23 Methycellulose colonies containing approximately 103 to 104cells were lysed similarly. Lysates of ACH-2 cells served as internal controls to document copy number sensitivity. Endpoint dilution estimates of proviral copy number from replicate samples were derived using the method of Reed and Muench,24 which averages data from replicate samples to interpolate a copy number endpoint.
RESULTS
Time-dependent depletion of mature and immature thymocytes by HIV-1.
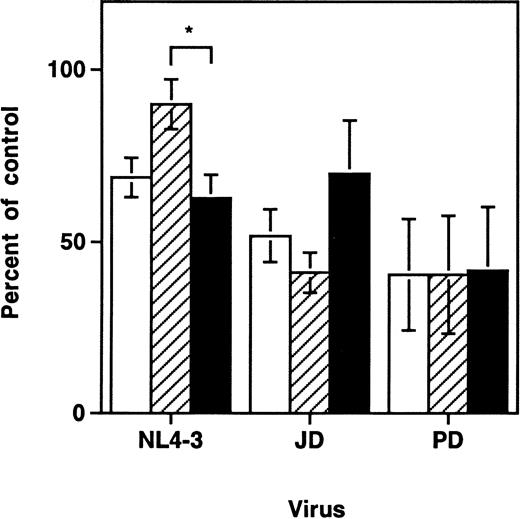
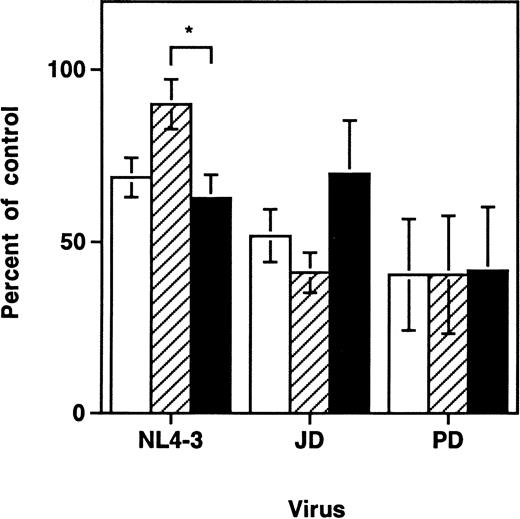
Previous work with the SCID-hu Thy/Liv model demonstrated a time-dependent depletion of CD3+CD4+CD8+ and CD3+CD4+CD8− thymocytes after infection with primary strains of HIV-1 or with the molecular clone NL4-3.6-8,25 In contrast, depletion of intrathymic T-progenitor cells, which carry the surface phenotype CD3−CD4+CD8−, was found to be greater in grafts infected with NL4-3 than in those infected by the primary HIV-1 strain, JD.5 At day 9 to 14 after infection in these experiments, we also found that each of the three viral strains tested (NL4-3, JD, and PD) resulted in depletion of both total thymocytes and intrathymic T-progenitor cells (Fig1). Consistent with earlier findings, only NL4-3 induced significantly greater depletion of the intrathymic T-progenitor cells than of the more mature CD3+CD4+CD8− cells. Thus, viral strain differences accounted for discernible differences in the pattern of thymocyte depletion after infection, but all strains tested resulted in thymocyte depletion of both mature and immature thymocytes.
HIV-1–induced depletion of mature and immature thymocyte subsets in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv mouse. Depletion of thymocyte subsets by HIV-1 strains NL4-3, JD, and PD was assessed at day 9 to 14 after infection. Cell numbers are expressed as percentages of values from mock-infected control grafts (Mean ± SEM). Data for NL4-3 summarize 10 separate experiments with 57 animals; data for JD summarize 5 experiments with 26 animals; and data for PD summarize 2 experiments with 10 animals. Each experiment used SCID-hu mouse cohorts made with fetal tissue from separate donors. *P < .01 (unpairedt-test) for difference between depletion of CD3−CD4+CD8− and CD3+CD4+CD8− cells. (□) Total thymocytes; (▨) CD3+CD4+CD8−; (▪) CD3−CD4+CD8−.
HIV-1–induced depletion of mature and immature thymocyte subsets in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv mouse. Depletion of thymocyte subsets by HIV-1 strains NL4-3, JD, and PD was assessed at day 9 to 14 after infection. Cell numbers are expressed as percentages of values from mock-infected control grafts (Mean ± SEM). Data for NL4-3 summarize 10 separate experiments with 57 animals; data for JD summarize 5 experiments with 26 animals; and data for PD summarize 2 experiments with 10 animals. Each experiment used SCID-hu mouse cohorts made with fetal tissue from separate donors. *P < .01 (unpairedt-test) for difference between depletion of CD3−CD4+CD8− and CD3+CD4+CD8− cells. (□) Total thymocytes; (▨) CD3+CD4+CD8−; (▪) CD3−CD4+CD8−.
Early depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells by HIV-1.
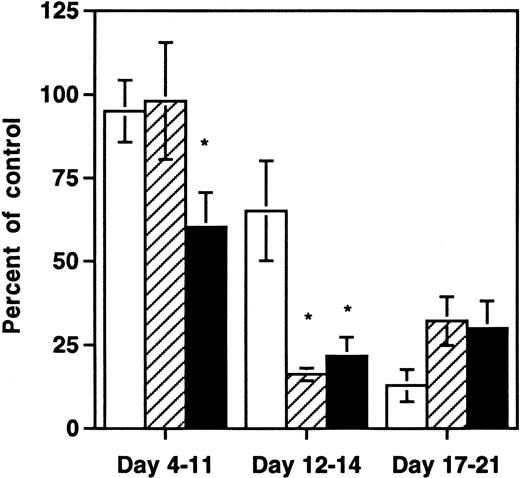
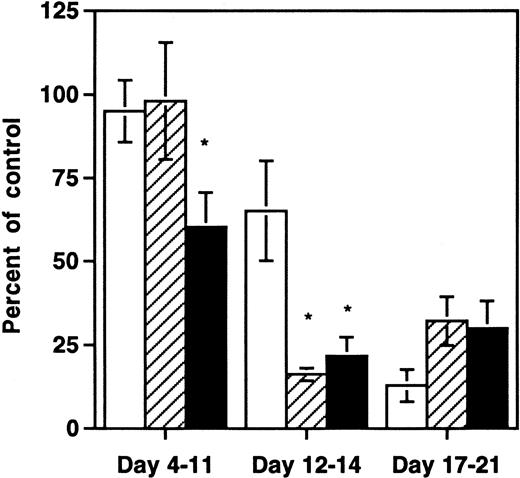
The finding that multiple HIV-1 strains depleted thymic progenitors prompted us to determine whether earlier hematopoietic progenitor cells were also affected by HIV-1 infection in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv mouse. We therefore measured the clonogenic capacity of multilineage and lineage-restricted hematopoietic progenitor cells from grafts infected either with NL4-3 or with medium. At early and late time points after infection, aliquots of harvested thymocytes were subjected to quantitative immunophenotyping with antibodies to CD3, CD8, and CD4 or depleted of mature cells with antibodies to CD3 and CD8 and then either assayed for expression of CD34 or for hematopoietic clonogenic capacity in methylcellulose or in long-term bone marrow cultures. At days 4 to 11 after infection, significantly fewer CD34+ cells remained in grafts infected with NL4-3 compared with controls (Fig2). At this early time point there was no depletion of lineage-restricted progenitor cell activity as measured by methylcellulose colony-forming units (CFU-C) or of total thymocytes. At days 12 to 14 after infection, both CD34+ cells and lineage-restricted progenitors were diminished relative to controls, and the degree of depletion exceeded that of total thymocytes (P < .05). By days 17 to 21 after infection, all hematopoietic elements in the Thy/Liv grafts, including total thymocytes, CFU-Cs, and CD34+ cells, were severely depleted. Thus, depletion of both functional (lineage-restricted) and phenotypic progenitors preceded the rapid decrease in total thymocyte numbers seen between day 11 and 21 after infection in this model.
Early selective depletion of CD34+hematopoietic progenitor cells and CFU-C by NL4-3. Data are shown from three pooled experiments at 8 different time points: three time points with 21 animals from one donor at days 4 to 11, three time points with 23 animals from three donors at days 12 to 14, and two time points with 13 animals from two donors at days 17 to 21. *Depletion values that are significantly different (P < .05, unpaired t-test) from the value for total thymocytes. (□) Total thymocytes per graft; (▨) CFU-C per graft; (▪) CD34+ cells per graft.
Early selective depletion of CD34+hematopoietic progenitor cells and CFU-C by NL4-3. Data are shown from three pooled experiments at 8 different time points: three time points with 21 animals from one donor at days 4 to 11, three time points with 23 animals from three donors at days 12 to 14, and two time points with 13 animals from two donors at days 17 to 21. *Depletion values that are significantly different (P < .05, unpaired t-test) from the value for total thymocytes. (□) Total thymocytes per graft; (▨) CFU-C per graft; (▪) CD34+ cells per graft.
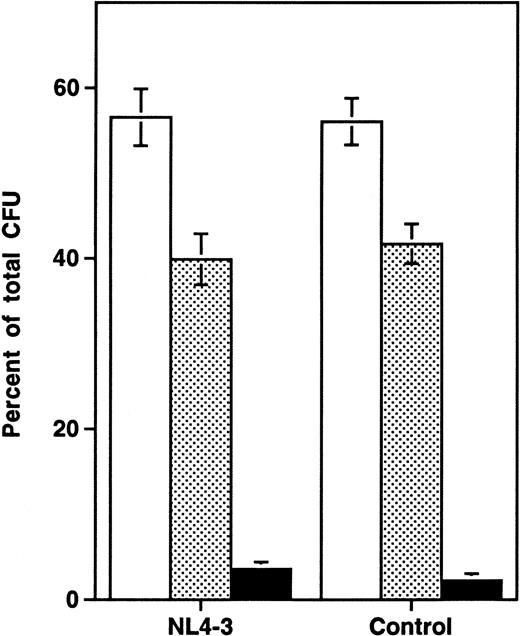
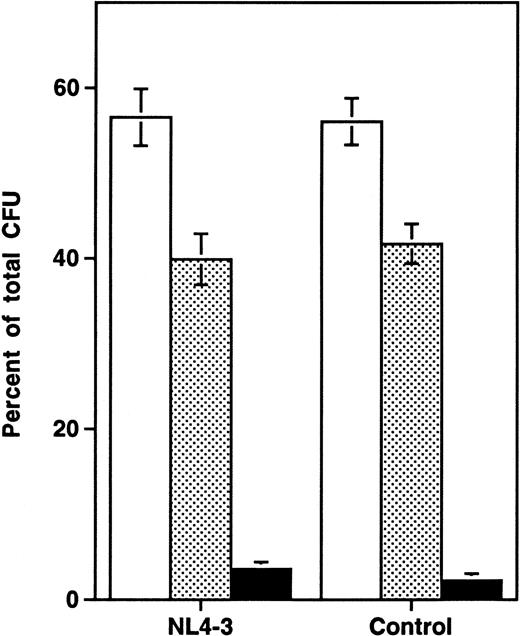
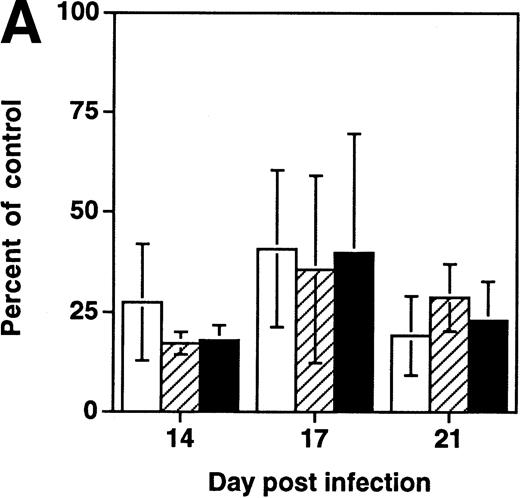
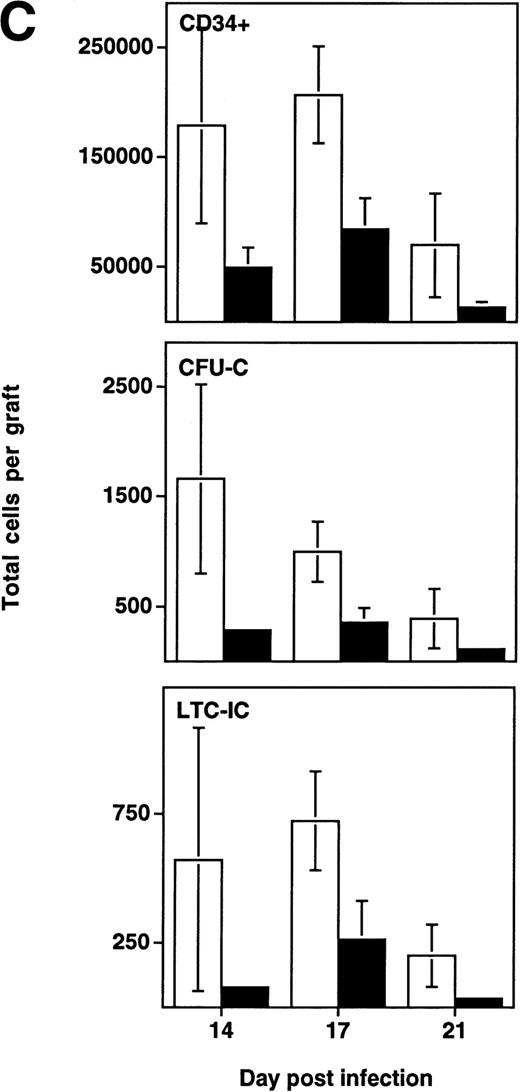
Analysis of the distribution of colonies of specific lineages arising from progenitor cells showed no difference between infected and uninfected grafts (Fig 3), suggesting that the impairment of progenitor activity occurred before the stage of lineage commitment. To determine directly whether HIV-1 infection affects multilineage hematopoietic progenitors, we measured the frequency of LTC-IC in NL4-3 and mock-infected grafts in three experiments performed 14 to 21 days after infection. In each experiment, the absolute number of CD34+ cells, of CFU-C, and of LTC-IC per HIV-1–infected graft (expressed as a percentage of values from uninfected control grafts) decreased equivalently (Fig 4A). Thus, HIV-1 infection resulted in depletion of multipotent hematopoietic progenitor cells contemporary with, and equivalent to, the depletion of lineage-committed progenitor cells.
Lineage-independent depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells by NL4-3. Each colony lineage is expressed as a percentage of total colonies recovered (mean ± SEM). The data are aggregated from 9 time points sampled in three experiments, including 13 animals in week 1, 24 animals in week 2, 18 animals in week 3, and 6 animals in week 4 after infection. Compared with uninfected controls, HIV-1–infected grafts showed a mean reduction of 28% in total thymocytes and of 43% in CFU-C over all time points sampled. (□) CFU-GM; (▧) BFU-E; (▪) CFU-GEMM.
Lineage-independent depletion of hematopoietic progenitor cells by NL4-3. Each colony lineage is expressed as a percentage of total colonies recovered (mean ± SEM). The data are aggregated from 9 time points sampled in three experiments, including 13 animals in week 1, 24 animals in week 2, 18 animals in week 3, and 6 animals in week 4 after infection. Compared with uninfected controls, HIV-1–infected grafts showed a mean reduction of 28% in total thymocytes and of 43% in CFU-C over all time points sampled. (□) CFU-GM; (▧) BFU-E; (▪) CFU-GEMM.
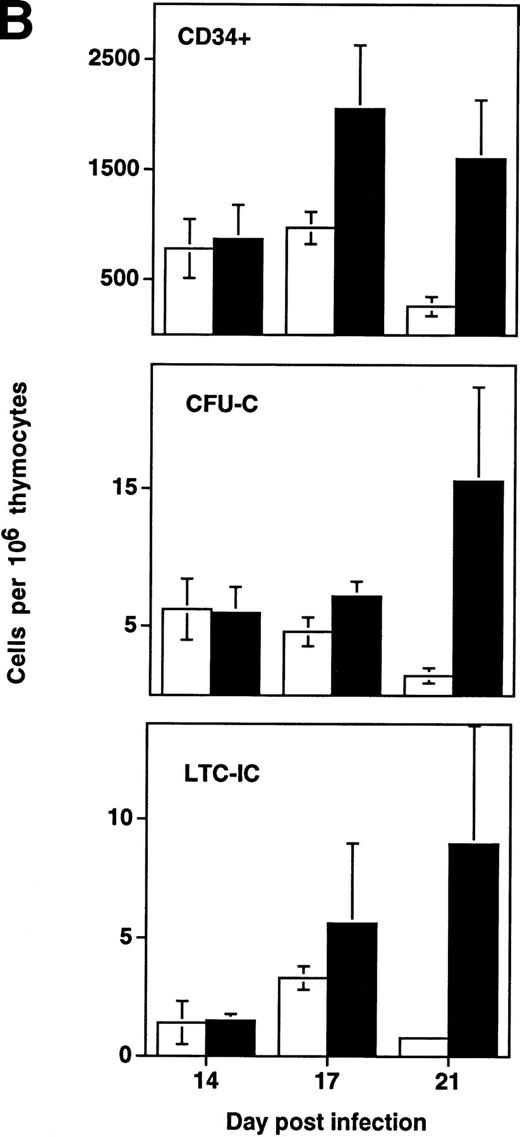
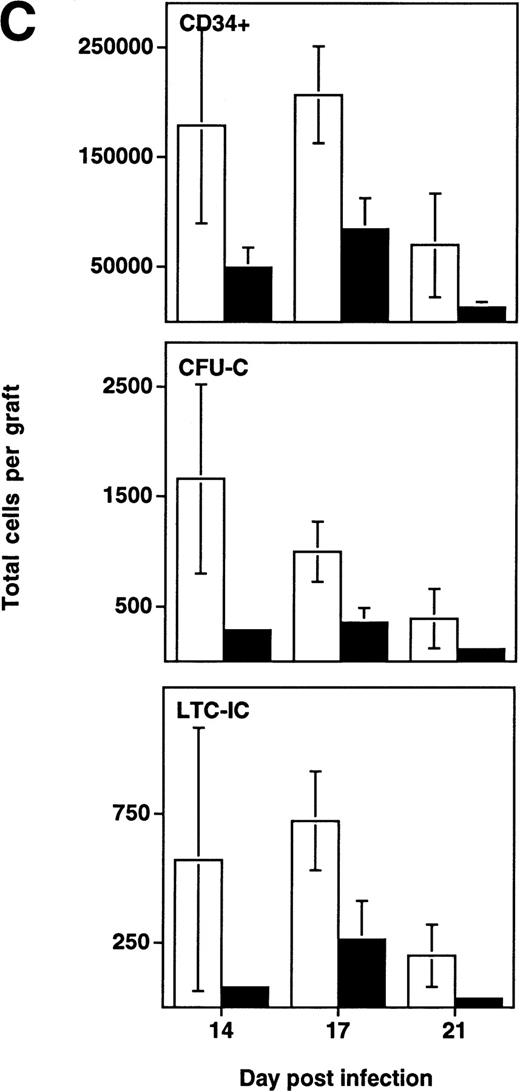
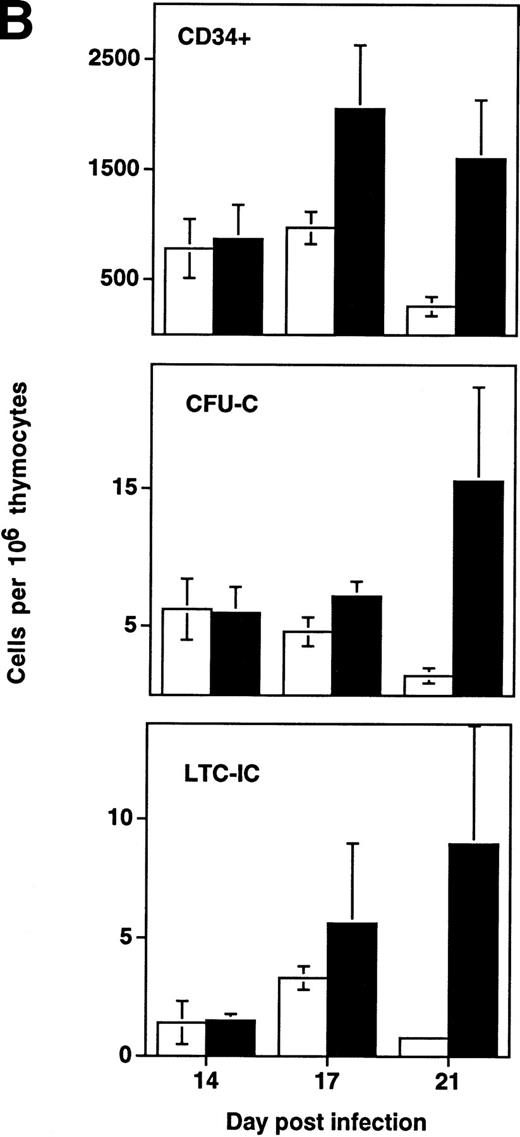
Depletion of LTC-IC, CFU-C, and CD34+ cells by HIV-1 (NL4-3). (A) Primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells (LTC-IC) are depleted synchronously with CFU-C and CD34+ cells in HIV-1–infected SCID-hu Thy/Liv. (□) CD34+ progenitor cells, (▨) CFU-C, and (▪) LTC-IC were determined in parallel 14 to 21 days after infection of grafts with HIV-1 strain, NL4-3. The total number of each is expressed as a percentage of the total number obtained from mock-infected, control grafts. (B) Relative enrichment of all progenitor classes in thymocyte-depleted grafts. Data from experiments in (A) are expressed as cell number per 106surviving thymocytes. (C) Absolute depletion of all progenitor classes in thymocyte-depleted grafts. Data from experiments shown in (A) are now expressed as total number of cells per graft. (□) Control; (▪) NL4-3.
Depletion of LTC-IC, CFU-C, and CD34+ cells by HIV-1 (NL4-3). (A) Primitive hematopoietic progenitor cells (LTC-IC) are depleted synchronously with CFU-C and CD34+ cells in HIV-1–infected SCID-hu Thy/Liv. (□) CD34+ progenitor cells, (▨) CFU-C, and (▪) LTC-IC were determined in parallel 14 to 21 days after infection of grafts with HIV-1 strain, NL4-3. The total number of each is expressed as a percentage of the total number obtained from mock-infected, control grafts. (B) Relative enrichment of all progenitor classes in thymocyte-depleted grafts. Data from experiments in (A) are expressed as cell number per 106surviving thymocytes. (C) Absolute depletion of all progenitor classes in thymocyte-depleted grafts. Data from experiments shown in (A) are now expressed as total number of cells per graft. (□) Control; (▪) NL4-3.
In addition to the early depletion of progenitor cells, HIV-1 infection results in the infection and death of thymocytes at more mature stages.5-8 Depletion of both progenitor cells and more mature thymocytes over time would be expected to result in a more accelerated decline in the numbers of the more mature cells. This was observed to be the case in experiments in which LTC-IC, CFU, and CD34+ phenotypic progenitors were measured from day 14 to 21 after infection (Fig 4B). In HIV-1–infected grafts, the prevalence of all three progenitor subsets (expressed as a fraction of surviving cells) actually increased relative to uninfected controls in a time-dependent fashion. However, even though hematopoietic progenitor cells comprise a greater fraction of the surviving total from HIV-1–infected grafts, these cells clearly undergo early and specific depletion when their numbers are expressed as total cells per graft (Fig 4C).
Progenitor depletion is a property shared by a primary HIV-1 strain and a molecular clone.
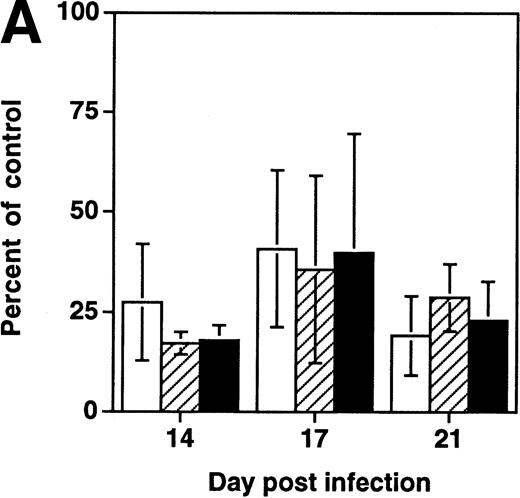
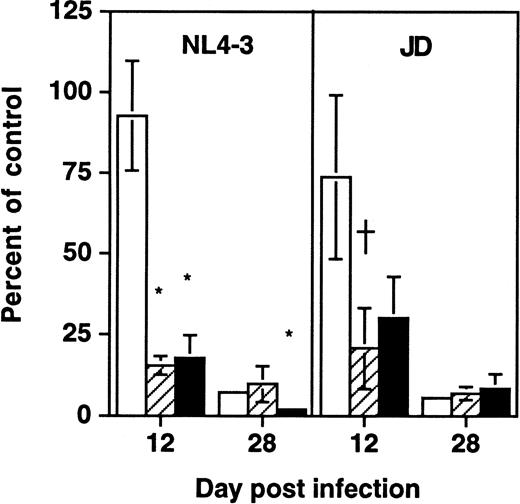
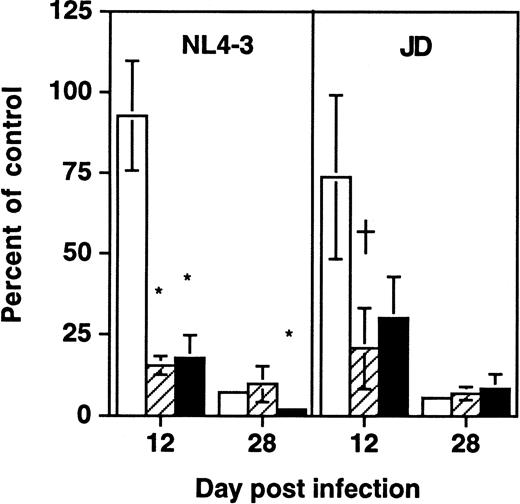
To determine whether depletion of hematopoietic progenitors was a property shared by primary HIV-1 strains, SCID-hu Thy/Liv grafts were infected in parallel with NL4-3 or the primary isolate JD (Fig5). At late (day 28) time points after infection, each virus was found to deplete both total thymocytes and CD34+ progenitor cells as well as colony-forming cells. However, at day 12 after infection, grafts infected with either virus showed normal numbers of total thymocytes but decreased numbers of CFU-C and CD34+ progenitor cells. These data suggest that the ability of HIV-1 to impair thymopoiesis through progenitor depletion is shared by a primary HIV-1 strain and by the molecular clone NL4-3.
Early depletion of CD34+ progenitor cells and CFU-C is a feature of both a primary isolate and a T-tropic molecular clone of HIV-1. Thy/Liv grafts were infected with either NL4-3 or HIV-1 strain JD, as described in the Materials and Methods. Data (mean ± SEM) summarize two experiments with animals from two donors, with 21 animals at day 12 and 21 animals at day 28. †.1 >P > .05 and *P < .05 for difference between value and total thymocytes (unpaired t-test). (□) Total; (▨) CFU-C; (▪) CD34+.
Early depletion of CD34+ progenitor cells and CFU-C is a feature of both a primary isolate and a T-tropic molecular clone of HIV-1. Thy/Liv grafts were infected with either NL4-3 or HIV-1 strain JD, as described in the Materials and Methods. Data (mean ± SEM) summarize two experiments with animals from two donors, with 21 animals at day 12 and 21 animals at day 28. †.1 >P > .05 and *P < .05 for difference between value and total thymocytes (unpaired t-test). (□) Total; (▨) CFU-C; (▪) CD34+.
HIV-1 proviral DNA accumulates in intrathymic T-cell progenitors but not in earlier progenitors.
Because HIV-1 infection may diminish hematopoietic progenitor capacity either by direct means (eg, lytic viral infection of progenitor cells) or by indirect means (eg, upregulation of hematosuppressive cytokines or disruption of stromal cell support), we evaluated the possibility that hematopoietic progenitor cells in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv graft were infected by HIV-1. First, DNA from colonies generated in methylcellulose culture was tested for the presence of proviral HIV-1 DNA using the PCR. Between 5 and 28 days after infection of grafts with NL4-3 or JD, only 4 of 1,293 colonies tested were positive for gag sequences (Table 1). This rate of PCR signal positivity is no higher than what might have arisen from carryover DNA in the culture, suggesting either that progenitor cells are uninfected by HIV-1 or that infected progenitor cells fail to generate colonies in methylcellulose assays. Secondly, sort-purified subpopulations of cells within the Thy/Liv implant were subjected to a quantitative, endpoint-dilution PCR analysis for the presence of HIV-1 proviral genomes. Among various potential target cells, intrathymic T-progenitor cells consistently harbored the highest frequency of HIV-1 genomes (Table 2). Intermediate levels of infection were observed in more mature CD3+CD4+CD8− thymocytes, whereas CD34+ cells showed the lowest frequency of infection.
DISCUSSION
HIV-induced impairment of hematopoietic progenitor function has been studied by a variety of in vitro methods with equivocal results.16,17,26 Major limitations of these methods include lack of control of maturation in tissue culture, nonphysiological development, and incomplete representation of stromal elements that may participate in HIV-1–induced pathology. In this study, we have addressed the effects of HIV-1 infection with an in vivo model, the SCID-hu Thy/Liv mouse, which encompasses the hematopoietic function of both thymus and fetal liver. We were thus able to observe effects on thymopoiesis and multilineage hematopoiesis simultaneously and to measure effects of HIV-1 infection on each. This model has been shown to recapitulate primary HIV-1 strain-specific pathology seen in vivo.6-8 With it, we have shown that HIV-1 infection impairs hematopoietic progenitor capacity in vivo at a stage as early as the multilineage progenitor population. In a kinetic analysis of thymocyte depletion, the impairment of lineage-restricted and multilineage progenitors was found to precede by several days the rapid decline in more mature thymocyte numbers. This observation was valid for both a molecular clone of HIV-1 and a primary strain, suggesting that hematopoietic progenitor cell depletion may be a common feature of HIV-1 pathology. We conclude that the rapid decline in thymocyte numbers seen in the SCID-hu model is likely to be the consequence of concurrent depletion of both thymocyte progenitor cells and more mature CD4+ thymocytes.
Prior studies in this model5-8,27 emphasized that infection and destruction of intrathymic T-progenitor cells and their progeny was the major pathological mechanism of HIV-1–induced thymocyte depletion. Our findings prompt a reappraisal of this model and suggest that destruction of less mature hematopoietic progenitor cells may be as important as infection and death of more mature thymocyte subpopulations. Although experimental data in the SCID-hu model have recently suggested that thymopoiesis can be restored in HIV-1–infected grafts after treatment with potent antiretroviral compounds and/or progenitor cell transplantation,28 the effects of these strategies were not durable. This is consistent with our finding that hematopoietic progenitor cells were the first cells depleted after HIV-1 infection and that such cells remain severely depleted at later stages despite their enrichment relative to other surviving cells. To the extent that this population of cells and/or its supportive microenvironment may be adversely affected by HIV-1 infection, resumption of thymopoiesis may be limited if present at all.
Our studies underscore an important methodologic point pertinent to the interpretation of studies in the SCID-hu mouse model. Thus, markedly different conclusions arise depending on how cell populations are sampled and quantitated: when expressed as a fraction of 106 surviving cells, the percentage of hematopoietic progenitor cells appears to be increasing in the Thy/Liv graft after infection (Fig 4B); measured in absolute terms (Fig 4A and C), the number of such cells per graft is actually decreasing. This dichotomy is the result of the different rates of depletion of different cell subpopulations that occur during a period when the total number of thymocytes is rapidly decreasing. Consequently, studies that rely solely upon percentage data and ignore total cell populations (eg, those studies that use serial biopsies of infected grafts; see, eg, Jamieson et al27 and Withers-Ward et al28) are prone to errors in interpretation that may underestimate the degree of depletion of a relatively spared subpopulation of cells. A similar problem confronts analyses of cell subpopulations in humans; eg, measurements of CD4+ T cells from samples of peripheral blood or of isolated lymph nodes do not permit quantitation of the total body CD4+ T-cell compartment.29
These findings also raise a question critical for treatment strategies: are thymocyte progenitor cells and hematopoietic progenitor cells themselves directly infected by HIV-1 or, alternatively, is their decrease due to indirect factors? We found that the intrathymic T-progenitor cell harbored large numbers of HIV-1 proviruses relative to more mature progeny. Even though CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells had a relatively low viral burden, these cells (as well as LTC-IC and CFU-C) were depleted at early time points after infection. It is therefore likely that HIV-1 destroys earlier hematopoietic progenitors by indirect means. Candidate mechanisms responsible for such destruction include altered cytokine environments in the infected thymus,30-32 dysregulation of other stromal developmental signals,33-35 and/or direct toxic effects of gp120.36 An alternative explanation for the robust and early depletion of progenitors without accumulation of viral genomes is that progenitor cells are rapidly cleared after infection by HIV-1. Our finding of early depletion of thymocyte progenitors differs importantly from other investigations into HIV-1–induced pathology in the SCID-hu model27 in that we demonstrate the death of progenitor cells at a phase of infection before depletion of total thymocytes or CD4+ thymocytes. Diminished thymopoiesis due to death of progenitor cells thus contributes to thymocyte depletion induced by HIV-1. Direct viral killing may be an additional mechanism of HIV-1–induced thymocyte depletion, although it is not the only one. The significance of this finding for treatment in humans is that durable suppression of viral replication may not be sufficient to restore hematolymphoid microenvironments that have been damaged by HIV-1 infection.
The importance of the thymus in peripheral T-cell homeostasis in children is established,37 and the role of the thymus in supporting peripheral T-cell numbers in the HIV-1–infected adult has been recently noted.38 The data presented here suggest that destruction of progenitor cells at the thymic and/or prethymic stage may contribute to the failure to maintain normal CD4+T-cell counts in HIV-1 disease. The depletion of hematopoietic progenitor capacity may explain the preferential loss of naive T cells in during the course of HIV-1 disease.39,40 Impaired progenitor capacity may contribute to peripheral CD4+depletion regardless of whether the rate of CD4+ T-cell loss is high or low.29,41,42 HIV-1 infection in the SCID-hu Thy/Liv model may also model events in late stage HIV-1 disease,25 when T-cell numbers decrease more rapidly and when other hematopoietic lineages are more significantly affected.16 These contributions of HIV-1–induced hematopoietic deficiency to the pathology of HIV-1 infection underscore the importance of augmenting combination antiviral regimens with therapies designed to restore or to improve hematopoietic function.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Robert M. Grant, MD, MPH, for advice on statistical analysis of data in this report.
Supported by grants (to J.M.M.) from the National Institutes of Health (NIH; R01-AI40312) and from the Pediatric AIDS Foundation. M.J. is supported by a grant from the NIH (K08 AI01425). J.M.M. is an Elizabeth Glaser Scientist supported by the Pediatric AIDS Foundation.
Address reprint requests to Joseph M. McCune, MD, PhD, Gladstone Institute of Virology and Immunology, PO Box 419100, San Francisco, CA 94141-9100.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. This article must therefore be hereby marked "advertisement" is accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.