Abstract
Interactions between cell surface receptors are important regulatory elements in the complex host responses to infections. In this study, it is shown that a classic chemotactic factor, the bacterial chemotactic peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucylphenyl-alanine (fMLF), rapidly induced a protein-kinase-C–mediated serine phosphorylation and down-regulation of the chemokine receptor CCR5, which serves as a major human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 coreceptor. The fMLF binding to its receptor, formyl peptide receptor (FPR), resulted in significant attenuation of cell responses to CCR5 ligands and in inhibition of HIV-1-envelope-glycoprotein–mediated fusion and infection of cells expressing CD4, CCR5, and FPR. The finding that the expression and function of CCR5 can be regulated by peptides that use an unrelated receptor may provide a novel approach to the design of anti-inflamatory and antiretroviral agents.
Introduction
The chemokine receptor CCR5 is a major fusion cofactor used by most of the primary isolates of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1).1-3 Subjects with an allotypic variant of CCR5 that results in failure to express this coreceptor are largely resistant to HIV-1 infection.4,5Owing to its prominent role in HIV-1 pathogenesis, CCR5 has become a focus of investigation concerning its regulation and the development of antagonists that may interrupt the interaction between HIV-1–envelope and CCR5. Chemokine ligands specific for CCR5 and antibodies recognizing this receptor have been shown to inhibit HIV-1 entry and replication.6-10 Human monocytes express a wide variety of 7-transmembrane (STM), G-protein–coupled chemoattractant receptors including chemokine receptors and the receptors for classic chemotactic factors such as the bacterial chemotactic peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLF), activated complement component 5 (C5a), and leukotriene B4 (LTB4).11-13 These cells are major infiltrating leukocytes in lesions of chronic inflammation, presumably as a consequence of the cell response to locally produced chemoattractants. In addition, monocytes/macrophages are targets of HIV-1 infection by virtue of the expression of both CD4 and CCR5. Since monocyte recruitment and activation under inflammatory conditions are probably the result of a concerted reaction to multiple stimulants, we investigated the effects of cell activation by bacterial chemotactic peptide on the expression and function of CCR5. This study shows that CCR5 in monocytes can be rapidly phosphorylated and subsequently desensitized by stimulation of the cells with the bacterial chemotactic peptide fMLF, causing reduced cell susceptibility to HIV-1 entry and infection.
Materials and methods
CCR5 phosphorylation
Monocytes were isolated from the peripheral blood of normal donors (Transfusion Medicine Department, National Institutes of Health [NIH] Clinical Center, Bethesda, MD) and enriched for mononuclear cells by means of counterflow elutriation. The purity of the cell preparations was examined by morphology after cytospin and exceeded 90%. The cells were stimulated with different concentrations of chemokines for indicated time periods at 37°C and lysed for 20 minutes on ice with periodic mixing in lysis buffer (1% Triton X-100; 20 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 137 mmol/L NaCl; 15% glycerol; 5 mmol/L EDTA) containing phosphotase and protease inhibitors (1 mmol/L phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride [PMSF], 5 μg/mL aprotinin, 5 μg/mL leupeptin, 1 mmol/L sodium orthovanadate, 1 mmol/L egtazic acid [EGTA]). Cell lysates were precleared with 30 μL washed protein-A sepharose beads (Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ); 1 μg polyclonal antiphospho-serine antibody (Zymed Laboratory, South San Francisco, CA) was added to 200 μg cell lysates diluted with 2 × immunoprecipitation (IP) buffer (1 × buffer contains 1% Triton X-100; 10 mmol/L Tris-HCl, pH 7.4; 137 mmol/L NaCl; 1 mmol/L EDTA; 1 mmol/L EGTA; 0.2 mmol/L sodium orthovanadate; 0.2 mmol/L PMSF; 0.5% Nonidet P-40 [NP-40]). The reaction mixture was incubated at 4°C overnight under constant rocking. The immune complex was captured by adding 50 μL of washed protein-A sepharose beads (25 μL packed beads) and incubating the reaction mixture at 4°C for 2 additional hours. The beads were spun down (10 seconds at 14 000 rpm), and the pellets were washed 3 times with ice-cold IP buffer, resuspended in 30 μL of 2 × Laemmli sample buffer (126 mmol/L Tris-HCl, 20% glycerol, 4% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS], 0.005% bromophenol blue with or without addition of 1% 2-mercaptoethanol; Novex, San Diego, CA), and boiled for 5 minutes to elute the immune complex. After electrophoresis on 4% to 12% SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) precast gel (Novex), the proteins were transferred to Immobilon P membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA). The membranes were blocked in freshly prepared phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 3% dry milk overnight, then were incubated with 1 μg/mL of polyclonal anti-CCR5 antibody (Millenium Biotechnology, Ramona, CA) overnight at 4°C followed by washing 3 times with PBS containing 0.05% Tween 20. The membranes were incubated with a horseradish-peroxidase–conjugated goat antirabbit immunoglobulin (Ig)–G (1:5000) (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) in PBS containing 3% dry milk for 1 hour at room temperature with agitation. After washing 3 times with PBS–0.05% Tween 20, the membranes were incubated with Super Signal Chemiluminescent Substrate Stable Peroxide Solution (Pierce, Rockford, IL) for 1 minute and exposed to Biomax-MR film (Eastman Kodak, Rochester, NY). The phosphorylation of CCR5 was also measured in 293 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged CCR5 complementary DNA (cDNA) (CCR5/293 cells, a gift from Dr P. Gray, ICDS, Seattle, WA). CCR5/293 cells in 10-mm dishes were washed once with phosphate-free Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM) (BioWhittaker, Walkersville, MD) and incubated at 37°C for 90 minutes in the same medium containing32phosphorus (150 μCi/mL; Amersham, Piscataway, NJ). After treatment with macrophage inflammatory protein 1β (MIP-1β) (1 μg/mL) for 5 minutes, cells were washed twice with ice-cold Dulbecco (D)PBS and lysed in lysis buffer. Insoluble material was removed by centrifugation at 15 000g for 20 minutes. Precleared cell lysates were incubated with anti-FLAG M2 monoclonal antibody agarose (Sigma) at 4°C for 2 hours. After 3 washes with ice-cold IP buffer, immune complexes were dissociated from agarose by boiling in SDS sample buffer for 5 minutes. After electrophoresis on 10% SDS-PAGE precast gel, the proteins were transferred to Immobilon membranes. The phosphorylated proteins were visualized by autoradiography with the use of Biomax-MR film and an intensifying screen at −80°C for 3 days.
Binding assays
Binding assays were performed by preincubating duplicate samples of monocytes (2 × 106) with 10−6mol/L of fMLF at 37°C for different time periods in a volume of 200 μL per sample of binding medium (RPMI 1640 with 1% bovine serum albumin [BSA], 25 mmol/L Hepes, and 0.05% NaN3). After washing, the cells were incubated with 0.2 ng of 125I-labeled MIP-1β (specific activity: 2200 Ci/mmol; Dupont NEN, Boston, MA) for 40 minutes at room temperature to measure total cell binding. The nonspecific binding was determined by parallel incubation of cells in the presence of 1000-fold excess of unlabeled MIP-1β (Pepro Tech, Rocky Hill, NJ). After incubation, the cells were washed with DPBS and centrifuged through a 10% sucrose/DPBS cushion. The tips of tubes containing cell pellets were cut, and the cell-associated radioactivity was determined in a gamma counter. The results were presented as counts per minute (cpm) on 2 × 106monocytes and were representative of at least 3 experiments performed. The binding assays with 125I-MIP-1β were also performed at 4°C for 90 minutes and yielded the same results.
Chemotaxis assays
Monocyte migration was assessed by a 48-well microchemotaxis-chamber technique. In the lower compartment of the chemotaxis chamber, we placed 25 μL MIP-1β diluted in assay medium (RPMI 1640 with 1% BSA and 25 mmol/L Hepes). We placed 50 μL cell suspension (1 × 106 cell per milliliter) in the upper compartment of the chamber. The upper and lower compartments were separated by a polycarbonate filter (5 μm pore-size; Neuroprobe, Cabin John, MD). The chamber was incubated at 37°C for 90 minutes in humidified air with 5% CO2. At the end of the incubation, the filter was removed and fixed and stained with Diff-Quik (Harlew, Gibbstown, NJ). The migrated cells in 3 high-powered fields (HPFs) obtained in triplicate (400 ×) were counted by light microscopy after coding the samples. The results are expressed as the net mean (± SD) number of migrated cells in 3 HPFs after subtraction of spontaneous migration. At least 3 experiments were performed with the same results.
Calcium mobilization
Calcium mobilization was measured by incubating monocytes (2 × 107/mL) in loading medium (DMEM, 10% fetal calf serum) with 5 μmol/L Fura-2 am (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR) for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark. The dye-loaded cells were washed 3 times and resuspended in saline buffer (138 mmol/L NaCl; 6 mmol/L KCl; 1 mmol/L CaCl2; 10 mmol/L Hepes, pH 7.4; 5 mmol/L glucose; 0.1% BSA). The cells were then transferred into quartz cuvettes (2 × 106 cells in 2 mL), which were placed in a luminescence spectrometer (LS-50B; PerkinElmer, Beaconsfield, UK). Stimulants at different concentrations were added in a volume of 20 μL to each cuvette at the indicated time points. The ratio of fluorescence at 340 and 380 nm was calculated by means of an FL-WinLab program (PerkinElmer). To examine the effect of fMLF, monocytes were preincubated with 10−6 mol/L fMLF or with medium alone for 60 minutes at 37°C. The cells were thoroughly washed and then were stained with Fura-2 for the calcium mobilization desensitization. The results are representative of at least 3 experiments performed.
CCR5 expression
The change of surface expression of CCR5 on monocytes was monitored by fluorescence-activated cell sorter analyses (courtesy of L. Finch, SAIC Frederick, National Cancer Institute, Frederick, MD). We pretreated 1 × 106 monocytes with medium or 10−6 mol/L fMLF (Sigma) for 60 minutes at 37°C. After incubation, the cells were washed and stained with a fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated monoclonal anti-CCR5 antibody 2D7 (20 μL per test) (PharMingen, San Diego, CA) on ice for 60 minutes. For protein kinase C inhibitor treatment, cells suspended in binding medium were incubated with 1.4 ng/mL staurosporine (Sigma) for 30 minutes at 37°C or 50 ng/mL calphostin C (Sigma) for 2.5 hours at 37°C with an 8-W fluorescent light source, followed by incubation with fMLF and anti-CCR5 antibodies. The cells were then washed twice with DPBS containing 2% BSA and fixed with 1% paraformaldehyde (Sigma). The fluorescence was measured by flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA). Results are presented as the percentage of cells stained with anti-CCR5 antibody.
HIV-1-envelope-glycoprotein–mediated fusion and viral infection
HIV-1-envelope-glycoprotein (env)–mediated fusion assays were performed as previously described.14 Briefly, human osteosarcoma (HOS) cells transfected to express CD4 and CCR5 (HOS/CCR5/CD4 cells, a kind gift from the NIH AIDS Research and Reference Reagents Program) were further transfected to coexpress formyl peptide receptor (FPR), a high-affinity receptor for the bacterial chemotactic peptide fMLF. Control cells were transfected with plasmic vector pcDNA3 alone (mock/CCR5/CD4). HeLa cells (ATCC, Rockville, MD) were first infected with a recombinant vaccinia virus vBC43 expressing monocyte-tropic HIV-1-env (BAL 31) and vBC21R containing a T7 promoter linked to the LacZ reporter gene. HOS cells expressing CCR5/CD4 in the absence or presence of FPR were infected with recombinant vaccinia virus vTF7-3 encoding the bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase under the control of the natural P7.5 early-late vaccinia promoter. After infection overnight at 31°C, 1 × 105 infected HeLa cells were mixed with 1 × 105 infected HOS cells and seeded in triplicate in the wells of 96-well tissue-culture plates. Chemokines or fMLF were added simultaneously when 2 cell types were mixed. After incubation at 37°C for 12 hours, the cells were lysed with 0.05% NP-40 and spun at 2500 rpm for 5 minutes. We mixed 50 μL cell lysate with 50 μL of 16 mmol/L chlorophenol red-β-galactopyranoside (CPRG; Boehringer Mannheim, Piscataway, NJ) dissolved in 2 × phosphate buffer (0.12 mol/L Na2HPO4, 0.08 mol/L NaH2PO4, 0.02 mol/L KCl, 0.002 mol/L MgSO4, 0.01 mol/L β-mercaptoethanol). The reactions were kept at room temperature for 2 to 4 hours before the color was measured with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) reader for absorbance at 570 nm. The same procedure was used in assays with human monocytes. For studies of viral infection of macrophages, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were allowed to adhere to plastic for 2 hours, and the nonadherent cells were removed. The adherent cells were cultured in monocyte-colony stimulating factor (rhM-CSF) (100 ng/mL) for 7 days to induce macrophage differentiation. The monocyte-derived macrophages were then treated with fMLF at the designated concentrations, and after 1 hour, the treated cells were infected with HIVJRFL at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1.0. At 4 hours after HIV infection, the cells were washed with PBS and fresh medium was added. HIV p24 antigen levels were then measured on day 6 by means of an ELISA. The fMLF treatment did not affect the viability of macrophages as compared with cells treated with medium alone.
Results
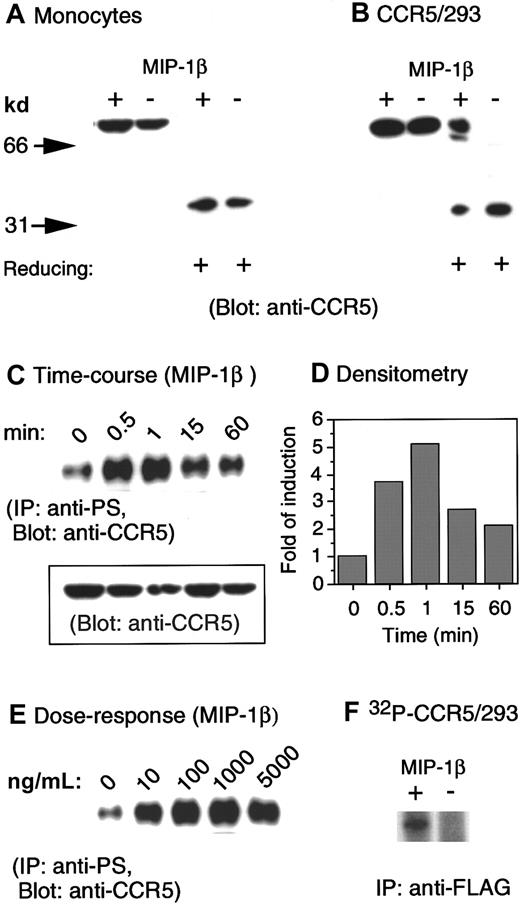
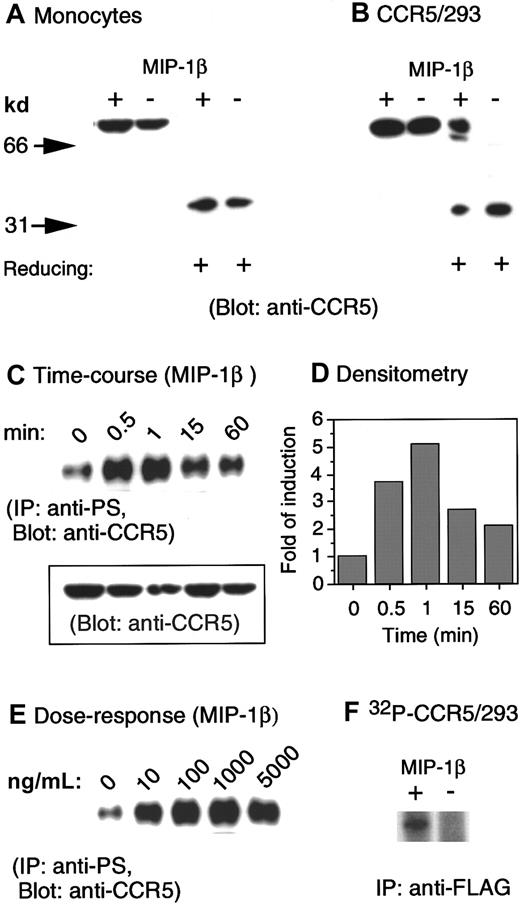
Several studies have previously shown that CCR5 can be rapidly phosphorylated upon binding of its native ligands, such as RANTES and MIP-1β.15-18 Since these studies were performed in cell lines transfected to express CCR5, but not in native cells in which the signaling molecules coupled to CCR5 may differ, we investigated the effect of CCR5 ligands on the phosphorylation patterns of CCR5 in peripheral blood monocytes. A polyclonal anti-CCR5 antibody was tested for its ability to detect CCR5 in lysates prepared from monocytes and human embryonic kidney (HEK) 293 cells transfected with a FLAG-tagged CCR5 cDNA (CCR5/293). CCR5 was detected by immunoblotting as a single protein species of about 75 kd under nonreducing conditions and as a 40-kd species under reducing conditions, in both monocytes (Figure1A) and CCR5/293 cells (Figure1B). In addition, stimulation of CCR5/293 cells, but not monocytes, with specific chemokines further promoted the resolution of CCR5 as a higher molecular protein species that was detectable even under reducing conditions (Figure 1B). These results may support the observation of other studies17 18 that in receptor-transfected cells CCR5 formed homodimers after ligand stimulation. However, such a hypothesis requires further investigation to fully exclude possible association of nonreceptor protein species with CCR5.
Phosphorylation of CCR5 induced by chemokine MIP-1β.
(A) Human monocytes were incubated in the presence or absence of MIP-1β (1 μg/mL) for 1 minute at 37°C. Cell lysates (20 μg) were electrophoresed in the presence (reducing +) or absence of 2-mercaptoethanol, transferred to IP membranes, and then immunoblotted with a polyclonal anti-CCR5 antibody. (B) CCR5-transfected human kidney embryonic 293 cells (CCR5/293) received the same treatment described in panel A. (C) Human monocytes incubated at designated times with MIP-1β (1 μg/mL) were lysed, and 200 μg cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antiphosphoserine antibody. The immunocomplexes were electrophoresed followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody. The inset shows the detection by immunoblot of CCR5 in 20 μg cell lysates prior to immunoprecipitation. (D) Densitometric measurement of the levels of phosphorylated CCR5 shown in panel C normalized to the receptor contents (inset in panel C). (E) Induction of CCR5 phosphorylation by different concentrations of MIP-1β. (F) An increased phosphorylation of CCR5 was detected by an anti-FLAG antibody in32phosphorus-labeled 293 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged CCR5 cDNA.
Phosphorylation of CCR5 induced by chemokine MIP-1β.
(A) Human monocytes were incubated in the presence or absence of MIP-1β (1 μg/mL) for 1 minute at 37°C. Cell lysates (20 μg) were electrophoresed in the presence (reducing +) or absence of 2-mercaptoethanol, transferred to IP membranes, and then immunoblotted with a polyclonal anti-CCR5 antibody. (B) CCR5-transfected human kidney embryonic 293 cells (CCR5/293) received the same treatment described in panel A. (C) Human monocytes incubated at designated times with MIP-1β (1 μg/mL) were lysed, and 200 μg cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antiphosphoserine antibody. The immunocomplexes were electrophoresed followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody. The inset shows the detection by immunoblot of CCR5 in 20 μg cell lysates prior to immunoprecipitation. (D) Densitometric measurement of the levels of phosphorylated CCR5 shown in panel C normalized to the receptor contents (inset in panel C). (E) Induction of CCR5 phosphorylation by different concentrations of MIP-1β. (F) An increased phosphorylation of CCR5 was detected by an anti-FLAG antibody in32phosphorus-labeled 293 cells transfected with FLAG-tagged CCR5 cDNA.
We next examined the phosphorylation of CCR5 in monocytes by using immunoprecipitation with an antiphosphoserine antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody, since CCR5 phosphorylation has been reported to occur exclusively on serine residues at the C-terminus of the receptor.15,16 As shown in Figure 1C, although in resting monocytes low and variable levels of serine phosphorylation of CCR5 could be consistently observed among cells from different donors, there was a rapid (within 1 minute) (Figure 1C) increase in CCR5 phosphorylation upon cell stimulation with CCR5 chemokine agonist MIP-1β. Densitometry measurement of phosphorylated CCR5 signals normalized to the receptor content (Figure 1C, inset) revealed a 3.8-fold increase in the level of CCR5 phosphorylation after 30-second cell stimulation with MIP-1β (Figure 1D). The maximal CCR5 physphorylation induced by MIP-1β was observed at 1 minute after stimulation (5-fold versus baseline, Figure 1D). The phosphorylation of CCR5 induced by MIP-1β was also dose-dependent with maximal effect at 1 μg/mL of the chemokine (Figure 1E). The detection of an increased level of CCR5 phosphorylation was corroborated by immunoprecipitation with an anti-FLAG antibody in CCR5/293 cells labeled with32phosphorus (Figure 1F). Use of antiphosphotheorine antibody failed to detect CCR5 phosphorylation in our studies (data not shown), supporting the notion that CCR5 is phosphorylated mainly at the serine sites after activation.15 16
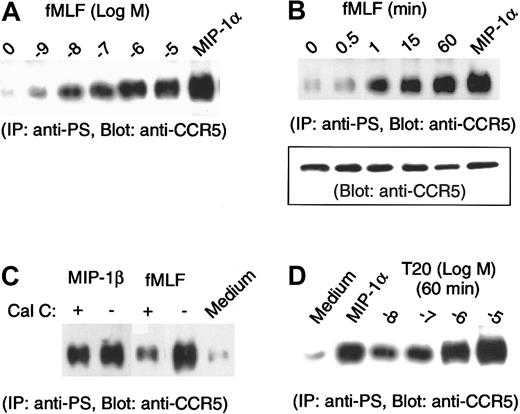
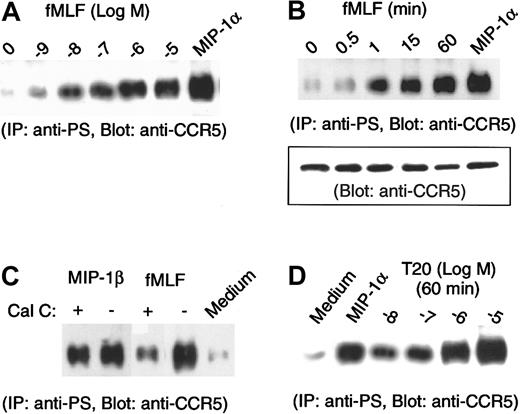
The agonist-induced phosphorylation of STM receptors such as CCR5 can result in homologous desensitization and internalization of the receptors.15-18 STM receptors may also be subjected to “heterologous desensitization” if the cells are activated by agonists by means of certain unrelated STM receptors. Since monocytes express a variety of STM chemoattractant receptors, including the high-affinity fMLF receptor FPR, we next determined whether activation of monocytes by the classical chemoattractant fMLF could affect the phosphorylation and expression of CCR5. As shown in Figure2A, incubation of monocytes with fMLF resulted in an increased level of CCR5 phosphorylation, which became detectable at low nanomolar concentrations of fMLF. Furthermore, an increase in phosphorylation of CCR5 in monocytes was observed 1 minute (5-fold of baseline) after stimulation with fMLF (Figure 2B), and a maximal phosphorylation was observed at 60 minutes (10-fold of baseline). By comparison, treatment of cells from the same donor with the CCR5 ligand MIP-1α for 1 minute induced an 11-fold increase in CCR5 phosphorylation (Figure 2B). These results suggest that the mechanisms of chemokine-induced and fMLF-induced phosphorylation of CCR5 in monocytes may be distinct. While phosphorylation of CCR5 induced by native chemokine ligands is dependent on the coupling of G-protein receptor kinases,15-18 fMLF is likely to exert its effect on CCR5 through a receptor “cross-desensitization” pathway that may involve the activation of protein kinase C (PKC).19-21 We tested this possibility by incubating monocytes with the specific PKC inhibitors staurosporine or calphostin C, followed by fMLF stimulation. Figure 2C shows that the level of CCR5 phosphorylation induced by fMLF was markedly reduced in monocytes preincubated with calphostin C. In contrast, calphostin C had little effect on MIP-1β–induced CCR5 phosphorylation, suggesting that fMLF-induced CCR5 phosphorylation is dependent on the activation of PKC. We previously showed that the high-affinity receptor for fMLF, FPR, is also a functional receptor for a synthetic peptide T20/DP178, which is derived from the C-terminal domain of the HIV-1-envelope protein gp41.22 Since T20/DP178 is a potent chemoattractant and activator for human monocytes in addition to being an extremely efficacious anti–HIV-1 agent,23-27 we examined the effect of T20/DP178 on CCR5 phosphorylation. As shown in Figure 2D, T20/DP178 induced a significant and dose-dependent phosphorylation of CCR5 in monocytes, supporting the hypothesis that activation of FPR in monocytes transduces signals leading to CCR5 phosphorylation.
Phosphorylation of CCR5 in monocytes treated with fMLF.
(A, B) Monocytes preincubated with the designated concentrations of fMLF (1 hour at 37°C) (panel A) or with 10−6 mol/L fMLF (panel B) for designated time intervals were lysed, and lysates (200 μg) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an antiphosphoserine antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody. Chemokine MIP-1α at 1 μg/mL (37°C, 1 minute) was used as a positive control. Inset in panel B shows the detection by immunoblotting of CCR5 in 20 μg cell lysates prior to immunoprecipitation. Relative fold increase in levels of phosphorylated CCR5 normalized to receptor contents were as follows: for fMLF, 1.2 (0.5 minutes), 5 (1 minute), 7 (15 minutes), and 10 (60 minutes); for MIP-1α, 11 (1 minute). (C) Monocytes preincubated with or without calphostin C (Cal C; 50 ng/mL, 2.5 hour at 37°C) were stimulated with MIP-1β (1 μg/mL, 37°C, 1 minute) or fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes), and the cell lysates were examined for serine phosphorylation of CCR5. (D) Monocytes were treated with different concentrations of synthetic T20 peptide derived from HIV-1 gp41 and were then measured for CCR5 phosphorylation. MIP-1α treatment at 1 μg/mL (37°C, 1 minute) was used as a positive control.
Phosphorylation of CCR5 in monocytes treated with fMLF.
(A, B) Monocytes preincubated with the designated concentrations of fMLF (1 hour at 37°C) (panel A) or with 10−6 mol/L fMLF (panel B) for designated time intervals were lysed, and lysates (200 μg) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an antiphosphoserine antibody followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody. Chemokine MIP-1α at 1 μg/mL (37°C, 1 minute) was used as a positive control. Inset in panel B shows the detection by immunoblotting of CCR5 in 20 μg cell lysates prior to immunoprecipitation. Relative fold increase in levels of phosphorylated CCR5 normalized to receptor contents were as follows: for fMLF, 1.2 (0.5 minutes), 5 (1 minute), 7 (15 minutes), and 10 (60 minutes); for MIP-1α, 11 (1 minute). (C) Monocytes preincubated with or without calphostin C (Cal C; 50 ng/mL, 2.5 hour at 37°C) were stimulated with MIP-1β (1 μg/mL, 37°C, 1 minute) or fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes), and the cell lysates were examined for serine phosphorylation of CCR5. (D) Monocytes were treated with different concentrations of synthetic T20 peptide derived from HIV-1 gp41 and were then measured for CCR5 phosphorylation. MIP-1α treatment at 1 μg/mL (37°C, 1 minute) was used as a positive control.
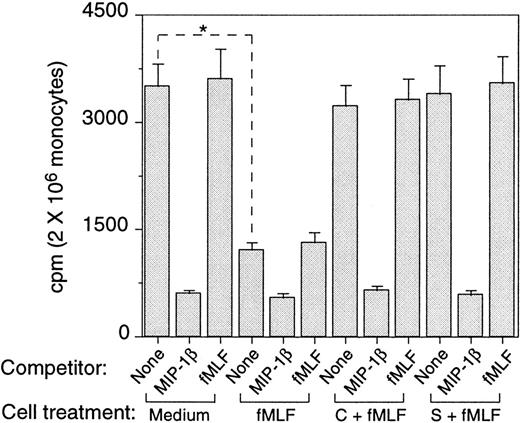
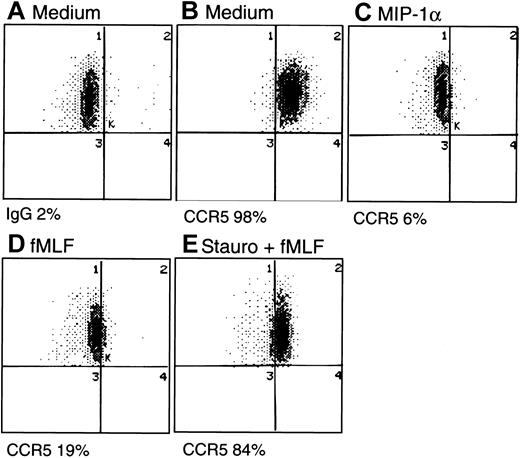
The consequences of fMLF-induced phosphorylation of CCR5 were studied by assaying the expression of CCR5 by monocytes. Freshly isolated human monocytes expressed specific binding sites for radio-iodinated MIP-1β, as most of the cell-associated 125I-MIP-1β could be displaced by a 1000-fold excess of unlabeled ligand (Figure3). In contrast, high concentrations of fMLF did not displace any 125I-MIP-1β binding, indicating that these 2 ligands use distinct cell-surface receptors. Monocytes treated with fMLF for 30 minutes at 37°C showed a significantly reduced (by 30%) specific binding for 125I-MIP-1β. Treatment with fMLF for 1 hour further reduced (by 75%) the level of specific binding for 125I-MIP-1β, and this reduction of binding was reversed if the cells were pretreated with PKC inhibitors calphostin C or staurosporine (Figure 3). Additionally, we examined the monocyte surface expression of CCR5 by using specific anti-CCR5 antibody and flow cytometry. A substantial proportion of freshly isolated human monocytes expressed CCR5 on the cell surface (Figure4A-B), which was down-regulated by the chemokine ligands MIP-1α, MIP-1β, or RANTES (Figure 4C and data not shown). The expression of CCR5 on monocytes was also markedly down-regulated by prior treatment of the cells with fMLF (Figure 4D) whereas cells preincubated with PKC inhibitors showed a level of CCR5 on the surface comparable to that on the native monocytes (Figure 4E). These results indicate that phosphorylation of CCR5 induced by fMLF in monocytes resulted in the down-regulation of CCR5 from the cell surface.
Effect of preincubation with fMLF on the capacity of monocytes to bind CCR5 chemokine ligand MIP-1β.
The binding of 125I-MIP-1β to monocytes preincubated with medium or fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes) was measured at room temperature or at 4°C (not shown). Unlabeled MIP-1β (1 μg/mL) and fMLF (10−6 mol/L) were used to compete with 125I-MIP-1β for binding. Aliquots of monocytes were preincubated with calphostin C (50 ng/mL, 2.5 hours at 37°C, C + fMLF) or staurosporine (1.4 ng/mL, 60 minutes, 37°C, S + fMLF) before treatment with fMLF. * Indicates significantly reduced binding of 125I-MIP-1β on cells treated with fMLF compared with untreated cells (P < .01).
Effect of preincubation with fMLF on the capacity of monocytes to bind CCR5 chemokine ligand MIP-1β.
The binding of 125I-MIP-1β to monocytes preincubated with medium or fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes) was measured at room temperature or at 4°C (not shown). Unlabeled MIP-1β (1 μg/mL) and fMLF (10−6 mol/L) were used to compete with 125I-MIP-1β for binding. Aliquots of monocytes were preincubated with calphostin C (50 ng/mL, 2.5 hours at 37°C, C + fMLF) or staurosporine (1.4 ng/mL, 60 minutes, 37°C, S + fMLF) before treatment with fMLF. * Indicates significantly reduced binding of 125I-MIP-1β on cells treated with fMLF compared with untreated cells (P < .01).
Cell surface expression of CCR5 by monocytes.
Monocytes incubated with different reagents were stained with an FITC-conjugated anti-CCR5 monoclonal antibody (2D7) and analyzed for the percentage of positively stained populations by flow cytometry. (A) Cells incubated with medium and stained with FITC-conjugated mouse IgG. (B) Cells incubated with medium and stained with FITC–anti-CCR5. (C) Cells treated with MIP-1α (1 μg/mL, 15 minutes, 37°C) and stained with FITC–anti-CCR5. (D) Cells treated with fMLF (10−6mol/L, 60 minutes, 37°C), then stained with FITC–anti-CCR5. (E) Cells pretreated with staurosporine (Stauro; 1.4 ng/mL, 30 minutes, 37°C) followed by fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 60 minutes, 37°C) and then stained with FITC–anti-CCR5.
Cell surface expression of CCR5 by monocytes.
Monocytes incubated with different reagents were stained with an FITC-conjugated anti-CCR5 monoclonal antibody (2D7) and analyzed for the percentage of positively stained populations by flow cytometry. (A) Cells incubated with medium and stained with FITC-conjugated mouse IgG. (B) Cells incubated with medium and stained with FITC–anti-CCR5. (C) Cells treated with MIP-1α (1 μg/mL, 15 minutes, 37°C) and stained with FITC–anti-CCR5. (D) Cells treated with fMLF (10−6mol/L, 60 minutes, 37°C), then stained with FITC–anti-CCR5. (E) Cells pretreated with staurosporine (Stauro; 1.4 ng/mL, 30 minutes, 37°C) followed by fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 60 minutes, 37°C) and then stained with FITC–anti-CCR5.
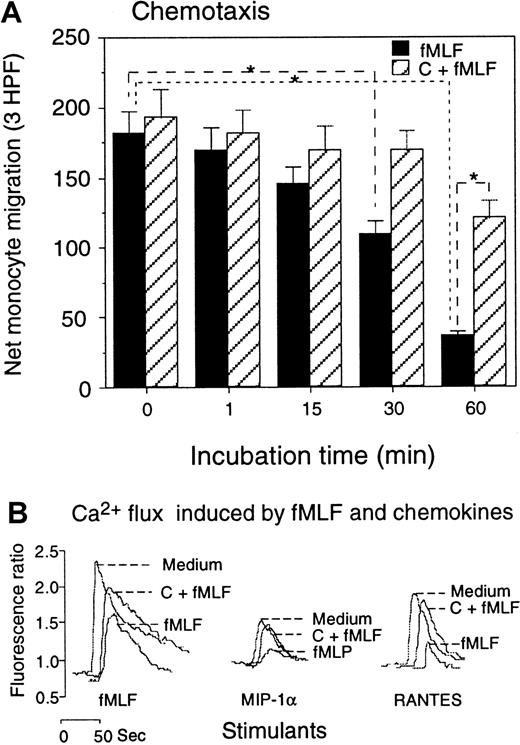
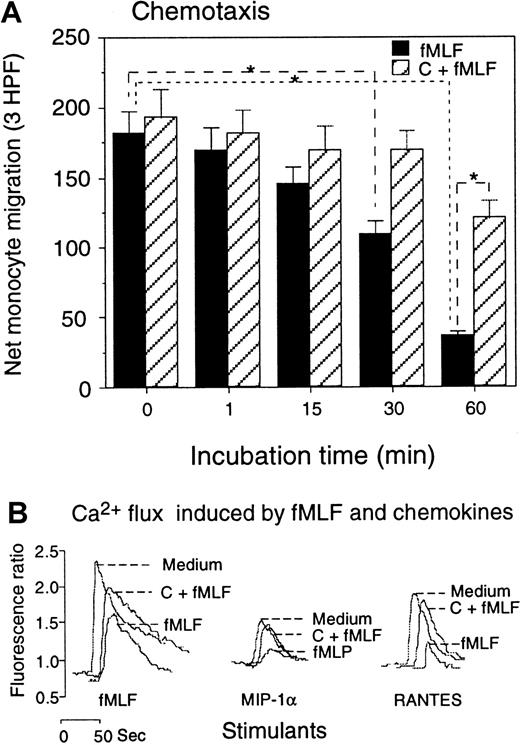
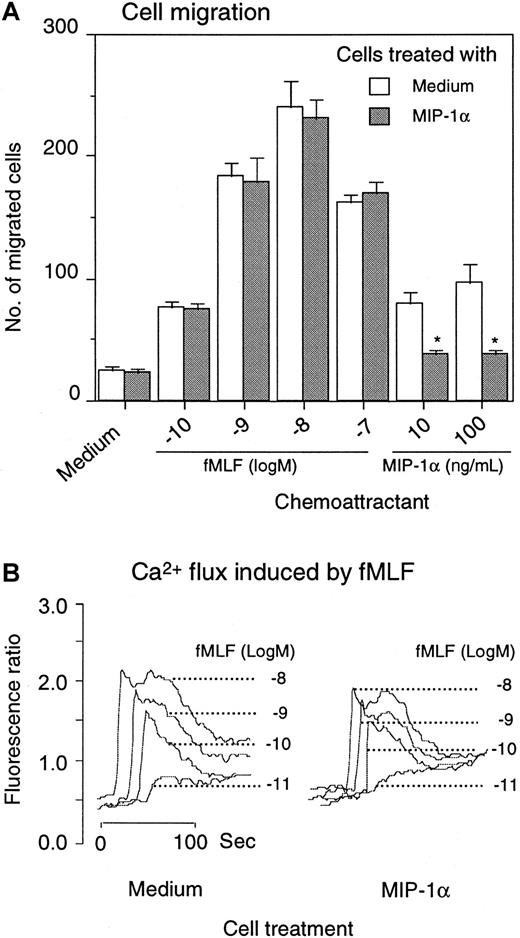
In agreement with the down-regulation of the surface expression, the biological function of CCR5 in monocytes treated with fMLF was also reduced. Monocytes pretreated with fMLF showed a progressively diminished chemotactic response to the CCR5 agonist MIP-1β (Figure5A), and the effect of fMLF was significantly reduced by pretreatment of the cells with the PKC inhibitors. The functional capacity of monocytes in response to CCR5 ligands after treatment with fMLF was further examined by calcium (Ca++) mobilization experiments. Since MIP-1β is a poor inducer of Ca++ flux in monocytes, we used MIP-1α and RANTES, 2 chemokines that activate multiple receptors including CCR5 and are potent inducers of phosphorylation of CCR5 (refer to Figure2A-B as controls) (also data not shown). Both RANTES and MIP-1α induced a transient rise in Ca++ in monocytes (Figure 5B). However, cells pretreated with fMLF had reduced Ca++ flux in response to these chemokines. Similarly to the results obtained from chemotaxis experiments, monocytes pretreated with PKC inhibitors showed a virtually normal Ca++ flux response to CCR5 ligands (Figure 5B). In contrast to the effect of fMLF on CCR5 function, monocytes pretreated with the chemokine MIP-1α (Figure6) or MIP-1β (data not shown) showed a normal chemotactic response to fMLF, although the Ca++ flux is marginally reduced (Figure 6A-B). These results suggest that the fMLF receptor in monocytes is more resistant to the cross-desensitization effect by chemokines that use CCR5.
Effect of fMLF on monocyte response to CCR5 ligands.
(A) Monocytes preincubated with fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C) for the designated time intervals were tested for migration in response to MIP-1β (100 ng/mL). Cells preincubated with calphostin C (50 ng/mL, 2.5 hours, 37°C) followed by fMLF treatment were tested in parallel. Results are expressed as the net number of migrated monocytes in 3 high-powered fields (HPFs) after subtraction of spontaneous migration in response to medium (55 ± 7 cells) (P < .01). (B) Calcium mobilization of monocytes in response to fMLF and chemokines. Monocytes were preincubated with medium (Medium), calphostin C (50 ng/mL, 2.5 hours), followed by fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes) (C + fMLF), or fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes) (fMLF); the Ca++ mobilization in response to fMLF (10−6 mol/L) or the chemokines MIP-1α or RANTES (1 ng/mL) was then measured.
Effect of fMLF on monocyte response to CCR5 ligands.
(A) Monocytes preincubated with fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C) for the designated time intervals were tested for migration in response to MIP-1β (100 ng/mL). Cells preincubated with calphostin C (50 ng/mL, 2.5 hours, 37°C) followed by fMLF treatment were tested in parallel. Results are expressed as the net number of migrated monocytes in 3 high-powered fields (HPFs) after subtraction of spontaneous migration in response to medium (55 ± 7 cells) (P < .01). (B) Calcium mobilization of monocytes in response to fMLF and chemokines. Monocytes were preincubated with medium (Medium), calphostin C (50 ng/mL, 2.5 hours), followed by fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes) (C + fMLF), or fMLF (10−6 mol/L, 37°C, 60 minutes) (fMLF); the Ca++ mobilization in response to fMLF (10−6 mol/L) or the chemokines MIP-1α or RANTES (1 ng/mL) was then measured.
Effect of MIP-1α on monocyte response to fMLF.
Monocytes were preincubated for 1 hour at 37°C with 1 μg/mL MIP-1α. After washing 3 times with PBS, the cells were examined for migration in response to fMLF and MIP-1α (A). *P < .01 compared with response of cells pretreated with medium alone. For calcium mobilization, monocytes were first loaded with Fura-2 and then treated with MIP-1α for 1 hour at 37°C. After washing, the cells were measured for Ca++ flux induced by fMLF (B).
Effect of MIP-1α on monocyte response to fMLF.
Monocytes were preincubated for 1 hour at 37°C with 1 μg/mL MIP-1α. After washing 3 times with PBS, the cells were examined for migration in response to fMLF and MIP-1α (A). *P < .01 compared with response of cells pretreated with medium alone. For calcium mobilization, monocytes were first loaded with Fura-2 and then treated with MIP-1α for 1 hour at 37°C. After washing, the cells were measured for Ca++ flux induced by fMLF (B).
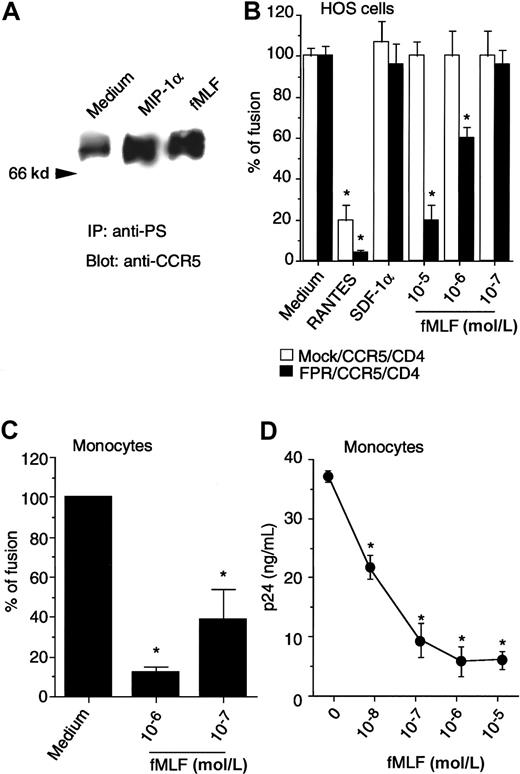
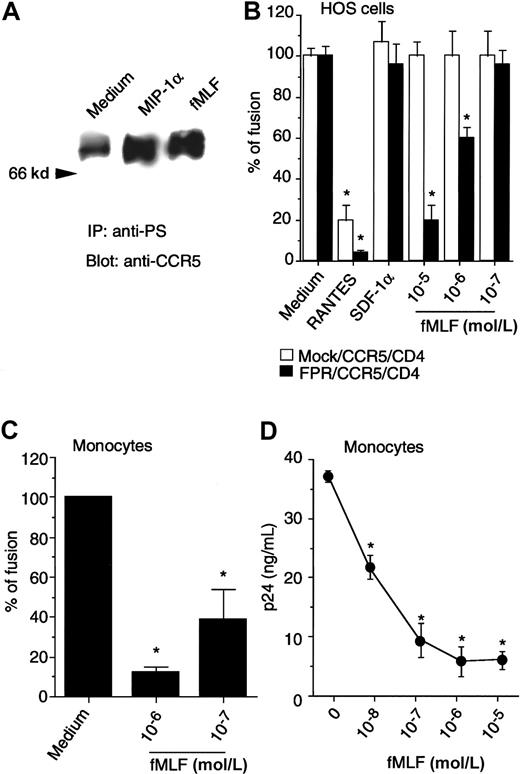
Since CCR5 is a major fusion coreceptor for monocytotropic HIV-1 strains, we investigated whether the activation of the high-affinity fMLF receptor, FPR, might have any impact on HIV-1-envelope fusion and viral infection when FPR is co-expressed with CCR5 and CD4 in human cells. FPR was stably transfected into the HOS cell line expressing both CD4 and CCR5. After transfection with FPR, the cells migrated and mobilized Ca++ in response to both fMLF and CCR5 agonists (data not shown). In addition, treatment of HOS/CD4/CCR5 cells co-expressing FPR with fMLF or MIP-1α induced increased phosphorylation of CCR5 (Figure 7A), indicating that both CCR5 and FPR were functionally expressed in these cells. The HOS/CD4/CCR5 cells in the presence or absence of FPR supported HIV-1BAL-env–mediated fusion equally well (Figure 7B), as assessed by a quantitative β-galactosidase gene activation assay system using recombinant-vaccinia-virus–expressing monocyte-tropic HIV-1BAL-env or the reporter gene. While the HIV-1-env fusion was inhibitable only by CCR5-specific chemokines, the addition of fMLF markedly inhibited HIV-1BAL-env–mediated fusion in cells coexpressing FPR, but not in the cells expressing CD4 and CCR5 only. The effect of fMLF on HIV-1-env–mediated fusion with FPR-expressing cells was rapid, since simultaneous addition of fMLF into the fusion assay system with env-expressing cells significantly inhibited fusion (Figure 7B). HOS cells transfected to express only CD4 and FPR did not support HIV-1BAL-env–mediated fusion, suggesting FPR is not a coreceptor for this HIV-1 strain (data not shown). The inhibition of HIV-1-env–mediated fusion by fMLF was also observed with blood monocytes, which express HIV-1 coreceptors as well as FPR (Figure 7C). We further confirmed that in both FPR-transfected HOS cells and peripheral blood monocyte/macrophages, treatment with fMLF significantly reduced the fusion and infection of the cells by monocyte-tropic strains of HIV-1, as measured by syncytia formation (data not shown) and p24 production (Figure 7D). These results suggest that the rapidly increased phosphorylation of CCR5 induced by fMLF could effectively impair the capacity of CCR5 to act as an HIV-1 fusion coreceptor, although a longer period of stimulation with fMLF was needed to eventually down-regulate CCR5 from the cell surface in association with reduced chemotactic and Ca++ mobilizing activity.
Effect of activation of FPR on monocytotropic HIV-1–envelope fusion and viral infection.
(A) HOS/CD4/CCR5 cells stably contransfected with FPR cDNA, treated with MIP-1α (1 μg/mL, 1 minute, 37°C) or fMLF (10−6mol/L, 60 minutes, 37°C) were examined for CCR5 phosphorylation with the use of antiphosphoserine antibody for immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody. (B) HeLa cells infected with recombinant vaccinia encoding the envelope protein from HIV-1BAL 31 were fused with HOS/CD4/CCR5 cells with (FPR/CCR5/CD4) or without FPR (mock/CCR5/CD4). Chemokines (10 μg/mL) or fMLF were added when env-expressing HeLa cells and target cells were mixed. (C) Human monocytes cultivated for 48 hours in the absence of fetal bovine serum were also fused with HeLa cells expressing the HIV-1BAL 31 env in the presence or absence of fMLF. Results are the mean (± SD) from 2 separate experiments. *Denotes significantly reduced β-galactosidase. (D) Expression of HIV-1 p24 protein following HIV-1 infection of macrophages. rhM-CSF–induced peripheral blood macrophages were exposed to fMLF for 1 hour followed by infection with HIVJRFL. Four hours later, the cells were washed and placed in culture for 6 days; the supernatants were then collected for analysis of p24 by ELISA. * Significantly reduced p24 production. Similar results were obtained with HOS cells transfected with CD4, CCR5, as well as the fMLF receptor FPR (data not shown).
Effect of activation of FPR on monocytotropic HIV-1–envelope fusion and viral infection.
(A) HOS/CD4/CCR5 cells stably contransfected with FPR cDNA, treated with MIP-1α (1 μg/mL, 1 minute, 37°C) or fMLF (10−6mol/L, 60 minutes, 37°C) were examined for CCR5 phosphorylation with the use of antiphosphoserine antibody for immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting with anti-CCR5 antibody. (B) HeLa cells infected with recombinant vaccinia encoding the envelope protein from HIV-1BAL 31 were fused with HOS/CD4/CCR5 cells with (FPR/CCR5/CD4) or without FPR (mock/CCR5/CD4). Chemokines (10 μg/mL) or fMLF were added when env-expressing HeLa cells and target cells were mixed. (C) Human monocytes cultivated for 48 hours in the absence of fetal bovine serum were also fused with HeLa cells expressing the HIV-1BAL 31 env in the presence or absence of fMLF. Results are the mean (± SD) from 2 separate experiments. *Denotes significantly reduced β-galactosidase. (D) Expression of HIV-1 p24 protein following HIV-1 infection of macrophages. rhM-CSF–induced peripheral blood macrophages were exposed to fMLF for 1 hour followed by infection with HIVJRFL. Four hours later, the cells were washed and placed in culture for 6 days; the supernatants were then collected for analysis of p24 by ELISA. * Significantly reduced p24 production. Similar results were obtained with HOS cells transfected with CD4, CCR5, as well as the fMLF receptor FPR (data not shown).
Discussion
We have shown in this study that the expression and critical functions of the chemokine receptor CCR5 can be suppressed by a classical chemotactic peptide fMLF via the activation of an unrelated STM receptor, FPR. Leukocyte recruitment at the sites of inflammation and infection is an early host response to invading pathogens. A number of leukocyte chemotactic factors have been identified that specifically induce migration of leukocyte subpopulations. The discovery of synthetic fMLF as a phagocyte chemoattractant has been considered a major advance in the study of leukocyte chemotaxis.28Several natural N-formyl peptide chemoattractants, including the prototype fMLF, have been purified from bacterial supernatants, providing evidence that they are biologically relevant ligands for the receptor used by chemotactic formyl peptides. The prototype receptor for formyl peptides designated FPR is expressed by neutrophils and monocytes and was cloned a decade ago.11-13 FPR can be activated by a diverse array of agonists, including the bacterial fMLF, and many synthetic small peptides with or without N-terminal modifications.11-13,29,30 We recently found that the anti–HIV-1 peptide derived from HIV-1 gp41 C-terminal domain, T20/DP178, which does not bear any sequence identity to the reported FPR agonists, induces migration and Ca++mobilization in monocytes and neutrophils through the use of FPR.22 Although mitochondrial proteins are N-formylated and chemotactic for neutrophils,31 whether these proteins represent a source of human cell-derived agonist(s) for FPR is not clear. Therefore, FPR is unique among numerous STM chemoattractant receptors because, unlike the receptors for most endogenously produced chemoattractants such as C5a, LTB4, or chemokines, FPR recognizes mainly exogenous signals and thus may play a major role in phagocytic cell recognition and activation in response to bacteria. This hypothesis is supported by the fact that mice depleted of FPR gene are more susceptible to microbacterial infection although these mice maintain an apparently normal phenotype.32
Cell responses to chemotactic factors is subjected to up-regulation through priming or down-regulation by desensitization. Two forms of desensitization have been described for G-protein–coupled STM receptors that are used by most chemoattractants. Homologous desensitization occurs when the receptor is occupied by its cognate ligands and phosphorylated by G-protein–coupled receptor kinases. The phosphorylated receptor associates with arrestin-family proteins and undergoes internalization. Heterologous desensitization is characterized by a decrease in receptor responsiveness to its ligands following phosphorylation induced by second-messenger–triggered kinases such as protein kinase A or PKC, which have been activated by different receptors or signaling cascade.19Unlike homologous desensitization, heterologous desensitization does not require agonist occupancy of the receptor and may not result in arrestin-mediated receptor internalization. Both homologous and heterologous desensitization of G-protein–coupled receptors may participate in the fine tuning of cell responses when multiple chemoattractants are present.19
As a classical G-protein–coupled chemoattractant receptor, FPR has been extensively studied for its property of signal transduction and cross-talk with other receptors. The binding of FPR by agonists, including fMLF, results in a cascade of G-protein–mediated signaling events leading to phagocytic cell adhesion, chemotaxis, release of oxygen intermediates, enhanced phagocytosis, and bacterial killing, as well as mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and gene transcription.33 Activation through FPR can also lead to heterologous desensitization of a subsequent cell response to other G-protein receptor ligands, such as the chemokine interleukin 8, presumably by protein-kinase–mediated receptor phosphorylation.19-21 In contrast, FPR by itself is relatively resistant to PKC-mediated phosphorylation and therefore less sensitive to heterologous desensitization by other unrelated chemotactic agonists.19 Our present study provides novel evidence that CCR5 in monocytes is also a target of FPR-activation–induced phosphorylation. This rapid and progressively increased level of CCR5 phosphorylation is accompanied by down-regulation of the surface expression and function of CCR5 in monocytes. However, treatment of monocytes with CCR5 ligands did not substantially compromise the cell response to fMLF. These results support the “hierrachy” phenomenon observed in cross-desensitization of G-protein–coupled chemoattractant receptors19 and suggest an important role of FPR in orchestration of host responses in the presence of multiple leukocyte chemoattractants at sites of local inflammation. Moreover, in the in vitro HIV-1 fusion model using target cells expressing CD4 and CCR5 as well as FPR, treatment of the target cells with fMLF potently reduced the capacity of CCR5 to serve as a viral envelope fusion coreceptor. Interestingly, simultaneous addition of fMLF in the assay was sufficient to significantly inhibit HIV-1-envelope–mediated fusion. This may support the notion that HIV-1 fusion and viral infectivity are progressive phenomena that require many minutes (probably hours) to evolve. The presence of fMLF interaction with the receptor FPR during such a process could effectively result in desensitization of CCR5 and reduce its HIV-1 fusion receptor activity. On the other hand, in a recent study, Alfano et al34 reported that a cellular binding subunit of pertussis toxin, termed B-oligomer, could rapidly desensitize CCR5 without down-regulating its surface expression, yet abolished HIV-1 fusion and infection via CCR5 in activated human mononuclear cells. These results suggest that disruption of the signaling capacity of CCR5 may be sufficient to compromise its role as an HIV-1 coreceptor.34 35 It is therefore plausible that CCR5 desensitization, with or without its surface down-regulation, may be used as a novel approach to the design of anti-inflammatory and anti-HIV agents.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr P. M. Murphy for critical review of the manuscript, Dr P. Gray for providing the CCR5/293 cells, N. M. Dunlop and Y. Feng for technical support, and C. Fogle for secretarial assistance.
Supported in part with funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health (NIH), under Contract NO1-CO-56000. W.S. has been supported in part by a fellowship from the Office of International Affairs, National Cancer Institute, NIH. This work was partially supported by NIH grants DA06650 and DA11130 (T.J.R.); DA05894 and T32DA07237 (M.A.W.); and DA12113 (E.E.H.).
W.S. and B.L. contributed equally to this study.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
References
Author notes
Ji Ming Wang, LMI, DBS, NCI-FCRDC, Bldg 560, Rm 31-40, Frederick, MD 21702-1201; e-mail: wangji@mail.ncifcrf.gov.