Abstract
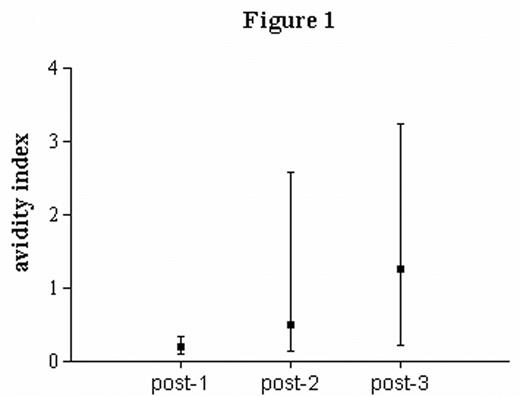
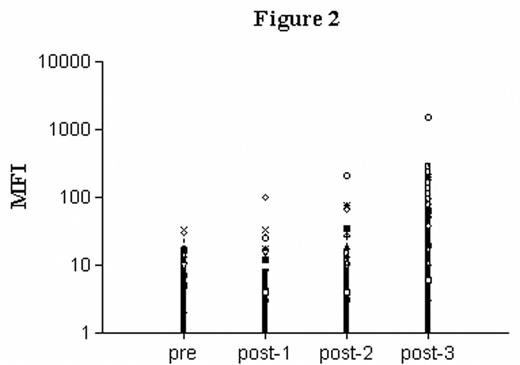
The conditioning regiments for autologous stem cell transplantation (aSCT) lead to impairment of the immune system and susceptibility to infections. Although infectious complications are more prominent in allogeneic transplantation, it is also a major source of morbidity in patients undergoing aSCT. Therefore, vaccination of patients after stem cell transplantation has been recommended. We conducted a prospective follow-up study to determine quantitative and qualitative aspects of the humoral immune response to multiple vaccinations with conjugated Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine in autologous stem cell transplant recipients. Sixteen patients (twelve with multiple myeloma and four with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma) received a conjugated Hib vaccine at 6, 8 and 14 months after transplantation. Antibody titres were determined by ELISA, 21 days after each vaccination. Adequate anti-Hib antibody responses (i.e. a four fold or greater increase in antibody levels in addition to a minimal titre of 50 U/ml corresponding to 18.8 μg/ml) were achieved in 7 (44%) of the patients after one vaccination. A second and third vaccination resulted in an adequate anti-Hib antibody response in 12 (75%) and 14 (88%) patients, respectively. Functionality of anti-Hib antibodies was assessed by measurement of antibody avidity. Repeated vaccination induced maturation of antibody avidity as demonstrated by increased resistance to sodium thiocyanate (NaSCN) treatment (Figure 1; the avidity index (AI) is defined as the molarity of NaSCN at which 50% of the amount of IgG antibodies bound to the coated antigen in the absence of NaSCN has been eluded. Mean AI plus range are shown after one, two and three vaccinations.). Subsequently, opsonizing activity of antibodies was determined by a phagocytosis assay. FITC-labelled Hib was incubated with serum and added to fresh polymorphonuclear cells (PMN). Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was measured by flowcytometry. Anti-Hib antibodies supported phagocytosis by PMN’s after multiple vaccinations (Figure 2; MFI at different time points is shown). In conclusion, multiple vaccinations with Hib-conjugate vaccine in autologous stem cell recipients result in high antibody response rates and functional maturation of antibodies.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal