Abstract
Merozoite invasion of red blood cells is crucial to the development of the parasite that causes malaria. Merozoite surface proteins (MSPs) mediate the first interaction between parasite and erythrocyte. In Plasmodium falciparum, they include a complex of products from at least 3 genes (msp1, msp6, and msp7), one of which, msp7, is part of a gene family containing 3 and 6 adjacent members in Plasmodium yoelii and Plasmodium falciparum, respectively. We have identified and disrupted msp7 in the Plasmodium berghei gene family. The protein is expressed in schizonts and colocalizes with MSP1. The synthesis and processing of MSP1 was unaffected in the parasite with the disrupted gene (MSP7ko). Disruption of msp7 was not lethal but affected blood-stage parasite growth. MSP7ko parasites initially grew more slowly than wild-type parasites. However, when reticulocytes were prevalent, the rate of increase in parasitemia was similar, suggesting that MSP7ko parasites prefer to invade and grow within reticulocytes. (Blood. 2005;105:394-396)
Introduction
The merozoite form of the malaria parasite attaches to and invades red blood cells (RBCs). Merozoite surface proteins (MSPs) mediate the first interaction between parasite and erythrocyte and are exposed to humoral antibody; therefore, they are vaccine candidates. Ten MSPs have been identified1,2 ; of these, MSP1 is the most extensively studied.3,4 Plasmodium falciparum MSP1 is synthesized as an approximately 200-kDa precursor processed into 4 fragments that remain as a complex on the surface of the merozoite.5,6 At the time of erythrocyte invasion, the complex is shed as the result of a cleavage within the C-terminal 42-kDa fragment.7,8 The shed complex contains other polypeptides that are fragments of MSP6 and MSP7.9-12 The role of these associated proteins is unclear, but it has been suggested that they are involved in the structure, processing, and function of the MSP1 complex.
P falciparum MSP7 is the 351-amino acid precursor to a 22-kDa polypeptide associated with the MSP1 complex.12 The msp7 gene is expressed in mature schizonts at the same time as msp1. Additionally, msp7 is part of a gene family containing 3 and 6 adjacent members in Plasmodium yoelii and P falciparum, respectively.12,13 Little is known about the role or function of the MSP7 family in merozoite invasion of RBCs.
We wanted to study the role of MSP7 in merozoite invasion and MSP1-complex biosynthesis and structure. Here we have identified and disrupted msp7 in Plasmodium berghei by double homologous recombination. This msp7 knockout line (MSP7ko) was used to examine the role of MSP7 in MSP1 synthesis and processing and in parasite biology. Deletion of msp7 resulted in a growth phenotype that reflected an effect on parasite invasion of erythrocytes.
Study design
Disruption of msp7 in P berghei
Northern blot analysis
Total RNA was isolated from purified schizonts, blotted and hybridized with a 1-kb DNA fragment derived from msp7.
Immunoprecipitation and IFA analysis
Schizonts from wild-type (WT) and MSP7ko lines were biosynthetically labeled by incubation for 2 hours at 37°C in [35S]-methionine- and cysteine-containing medium. Labeled parasites were lysed, and specific proteins were immunoprecipitated.16
For immunofluorescence assay (IFA) analysis, thin smears of schizonts were incubated with rabbit antiserum raised against recombinant P yoelii MSP7 (diluted 1:300) and mAb 25.1 (diluted 1:500) against MSP1. Images were captured using a Leica TCS SP2 microscope and software with a 63×/1.32 oil immersion PH3CS objective (Leica Microsystems, Bucks Milton Keynes, United Kingdom), then processed for presentation with Adobe Photoshop software (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA).
Parasite growth and infectivity in mice
To ascertain whether the disruption of msp7 had an effect on parasite growth in vivo, challenge inocula (100 and 1000 blood-stage parasites) from WT and MSP7ko P berghei were injected intravenously into groups of Balb/c mice (6-8 weeks of age). Forty-eight hours after injection and daily for another 10 days, a thin smear of blood was prepared and stained with Giemsa reagent. For each sample, at least 2000 RBCs were examined by microscopy, and the percentage of parasitemia was calculated. The ratio of mature RBCs and reticulocytes infected by WT and MSP7ko parasites was also determined during the 6- to 10-day period after infection. Images were captured using a Leica DMR microscope equipped with a 63 × oil immersion objective and Leica IM 1000 software.
Results and discussion
The P berghei msp7 gene was identified (72% identity/83% similarity with P yoelii MSP7 at the protein level) and targeted for disruption to examine its function. In the MSP7ko parasite line obtained, the DHFR gene was correctly integrated into and disrupted the msp7 locus (Figure 1A). Northern blot analysis failed to detect any expression of msp7 in the MSP7ko parasite, though the gene was highly expressed in the WT parasite (Figure 1A).
Disruption of msp7 in P berghei and MSP7 association with MSP1. (A) The msp7-targeting sequence was cut out from the construct pDHΔMSP7 and inserted by double homologous recombination into the msp7 gene. Southern blot analysis of P berghei genomic DNA from WT and MSP7ko parasites, digested with EcoR1 and HindIII, and probed with (lower left) an msp7 probe or (lower center) a Toxoplasma gondii DHFR probe. Northern blot analysis of msp7 expression (lower right) in WT and MSP7ko parasites: RNA was purified from schizonts of WT (left panels) and MSP7ko (right panels) parasites and were hybridized with probes corresponding to msp7 (upper) and a control (lower). (B) Immunoprecipitation analysis detecting MSP7 as a 42-kDa band in extracts of WT parasites, which is absent in the extracts of MSP7ko parasites. In contrast, MSP1 is expressed in both parasite lines. NP-40 extracts of [35S]-biosynthetically labeled WT parasites (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 8) or MSP7ko parasites (lanes 2, 4, and 6) were mixed with rabbit polyclonal anti-P yoelii MSP7 (lanes 1 and 2), monoclonal antibody 25.1 (lanes 3 and 4), mouse polyclonal anti-P yoelii MSP1 (lanes 5 and 6), normal rabbit serum (lane 7), or normal mouse serum (lane 8). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and fluorography. Locations of the 42-kDa MSP7 and the 230-kDa MSP1 bands are indicated by arrows. Mobilities of standard molecular mass markers are indicated. (C) IFA analysis of MSP7 and MSP1 protein expression in WT and MSP7ko parasites. MSP7 was detected by fluorescence in schizonts of the WT parasite but not in schizonts of the MSP7ko parasite. In contrast, MSP1 was detected in WT and MSP7ko parasites.
Disruption of msp7 in P berghei and MSP7 association with MSP1. (A) The msp7-targeting sequence was cut out from the construct pDHΔMSP7 and inserted by double homologous recombination into the msp7 gene. Southern blot analysis of P berghei genomic DNA from WT and MSP7ko parasites, digested with EcoR1 and HindIII, and probed with (lower left) an msp7 probe or (lower center) a Toxoplasma gondii DHFR probe. Northern blot analysis of msp7 expression (lower right) in WT and MSP7ko parasites: RNA was purified from schizonts of WT (left panels) and MSP7ko (right panels) parasites and were hybridized with probes corresponding to msp7 (upper) and a control (lower). (B) Immunoprecipitation analysis detecting MSP7 as a 42-kDa band in extracts of WT parasites, which is absent in the extracts of MSP7ko parasites. In contrast, MSP1 is expressed in both parasite lines. NP-40 extracts of [35S]-biosynthetically labeled WT parasites (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 8) or MSP7ko parasites (lanes 2, 4, and 6) were mixed with rabbit polyclonal anti-P yoelii MSP7 (lanes 1 and 2), monoclonal antibody 25.1 (lanes 3 and 4), mouse polyclonal anti-P yoelii MSP1 (lanes 5 and 6), normal rabbit serum (lane 7), or normal mouse serum (lane 8). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and fluorography. Locations of the 42-kDa MSP7 and the 230-kDa MSP1 bands are indicated by arrows. Mobilities of standard molecular mass markers are indicated. (C) IFA analysis of MSP7 and MSP1 protein expression in WT and MSP7ko parasites. MSP7 was detected by fluorescence in schizonts of the WT parasite but not in schizonts of the MSP7ko parasite. In contrast, MSP1 was detected in WT and MSP7ko parasites.
Antibodies to MSP7 precipitated a 42-kDa band from an extract of WT parasites that was absent in the extract of MSP7ko parasites (Figure 1B, lanes 1 and 2). Despite the absence of MSP7, MSP1 was produced in similar amounts in WT and MSP7ko parasites (Figure 1B, lanes 3 and 4). The spectrum of polypeptides precipitated by MSP1-specific polyclonal serum, but not normal serum, which represents processing fragments of MSP1, was indistinguishable for the 2 parasite lines (Figure 1B, lanes 5 and 6).
According to IFA analysis, antibodies raised against the C-terminus of MSP7 colocalized with antibodies to MSP1, suggesting coexpression during schizogony in WT parasites. No reactivity with MSP7ko parasites was observed (Figure 1C), though MSP1 was still located at the schizont periphery.
Northern blotting, immunoprecipitation, and IFA experiments clearly showed that MSP7 was not expressed in the MSP7ko parasite. However, the synthesis and surface expression of MSP1 was unchanged. This suggests that either MSP7 is not essential for the synthesis and processing of MSP1 or that other members of the family may substitute its function. In P falciparum the complex between MSP1 and MSP7 is stable in the presence of the detergent NP-40.10 Either this is not the case in P berghei or 1 of the 2 MSP7-related proteins (MSRP1 or MSRP2) might form a more stable interaction with MSP1 than MSP7 does. In the yeast 2-hybrid system, the minimal region of P yoelii MSP7 interacting with MSP1 was mapped to residues 113-324,13 and both MSRP1 and MSRP2 could interact with MSP1. Although this region of MSP7 is not present in the knockout parasite, the processing of MSP1 was unaffected. The expression of MSRP1 and MSRP2 was largely unaffected in the MSP7ko parasite when compared with the WT parasite (data not shown). This clearly suggests that the 3 genes are independently regulated.
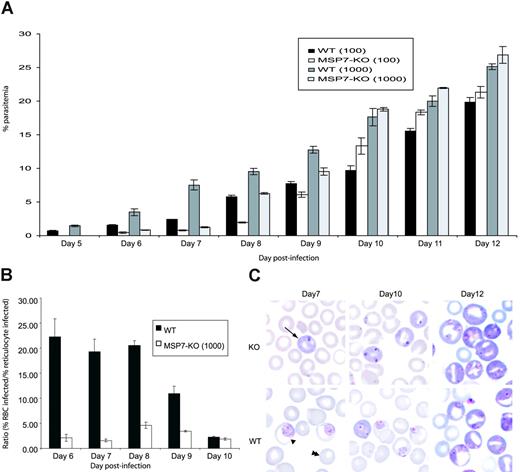
Transgenic parasites were viable, and they invaded and multiplied within erythrocytes. However, the overall growth of these parasites was delayed compared with that of WT parasites in first few days (Figure 2A). This might have been attributed to a reduced ability to invade RBCs. However, by day 9 or 10, after an influx of reticulocytes into the peripheral circulation, the growth rate of the 2 parasites was similar, suggesting that the MSP7ko parasites can invade reticulocytes as efficiently as do WT parasites. This was confirmed by calculating the ratio of the percentage parasitemia in mature RBCs and in reticulocytes for WT and MSP7ko parasites during the course of infection (Figure 2B) and was illustrated by the blood smears (Figure 2C). It is possible, therefore, that the MSP7ko phenotype is an impairment of invasion of the mature RBCs. Infectivity of reticulocytes may be the default pathway because WT and MSP7ko parasites invade reticulocytes equally well, consistent with the previous finding showing preferential invasion of reticulocytes by P berghei.17,18 This preference for reticulocyte invasion will be investigated more thoroughly, for example, by examining whether there are certain molecules on the reticulocyte surface that facilitate parasite invasion.
Parasite invasion of erythrocytes in vivo. (A) Parasite growth in vivo. Parasitemia in groups of 6 mice infected on day 0 with 1000 or 100 WT or MSP7ko parasites. The course of parasitemia was observed for 12 days. (B) Ratio of the percentage parasitemia in normocytes and reticulocytes for WT and MSP-7Ko parasites during the course of an infection initiated with 1000 parasites. (C) Giemsa-stained blood smear from infections with WT or MSP7ko parasites at days 7, 10, and 12 after infection. Infected reticulocyte, infected normocyte (mature RBC), and uninfected normocyte are indicated by arrow, single arrowhead, and double arrowheads, respectively.
Parasite invasion of erythrocytes in vivo. (A) Parasite growth in vivo. Parasitemia in groups of 6 mice infected on day 0 with 1000 or 100 WT or MSP7ko parasites. The course of parasitemia was observed for 12 days. (B) Ratio of the percentage parasitemia in normocytes and reticulocytes for WT and MSP-7Ko parasites during the course of an infection initiated with 1000 parasites. (C) Giemsa-stained blood smear from infections with WT or MSP7ko parasites at days 7, 10, and 12 after infection. Infected reticulocyte, infected normocyte (mature RBC), and uninfected normocyte are indicated by arrow, single arrowhead, and double arrowheads, respectively.
It will be of interest in the future to disrupt other members of the msp7 family, either alone or in various combinations, to see whether any of them is essential for an interaction with MSP1 and parasite invasion.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, August 31, 2004; DOI 10.1182/blood-2004-06-2106.
Supported by the United Kingdom Medical Research Council (MRC), the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) and a Wellcome Trust VIP Award (R.T.).
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 U.S.C. section 1734.
We thank David Bacon and Dale Raine for the illustrations.

![Figure 1. Disruption of msp7 in P berghei and MSP7 association with MSP1. (A) The msp7-targeting sequence was cut out from the construct pDHΔMSP7 and inserted by double homologous recombination into the msp7 gene. Southern blot analysis of P berghei genomic DNA from WT and MSP7ko parasites, digested with EcoR1 and HindIII, and probed with (lower left) an msp7 probe or (lower center) a Toxoplasma gondii DHFR probe. Northern blot analysis of msp7 expression (lower right) in WT and MSP7ko parasites: RNA was purified from schizonts of WT (left panels) and MSP7ko (right panels) parasites and were hybridized with probes corresponding to msp7 (upper) and a control (lower). (B) Immunoprecipitation analysis detecting MSP7 as a 42-kDa band in extracts of WT parasites, which is absent in the extracts of MSP7ko parasites. In contrast, MSP1 is expressed in both parasite lines. NP-40 extracts of [35S]-biosynthetically labeled WT parasites (lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 8) or MSP7ko parasites (lanes 2, 4, and 6) were mixed with rabbit polyclonal anti-P yoelii MSP7 (lanes 1 and 2), monoclonal antibody 25.1 (lanes 3 and 4), mouse polyclonal anti-P yoelii MSP1 (lanes 5 and 6), normal rabbit serum (lane 7), or normal mouse serum (lane 8). Immunoprecipitates were analyzed using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and fluorography. Locations of the 42-kDa MSP7 and the 230-kDa MSP1 bands are indicated by arrows. Mobilities of standard molecular mass markers are indicated. (C) IFA analysis of MSP7 and MSP1 protein expression in WT and MSP7ko parasites. MSP7 was detected by fluorescence in schizonts of the WT parasite but not in schizonts of the MSP7ko parasite. In contrast, MSP1 was detected in WT and MSP7ko parasites.](https://ash.silverchair-cdn.com/ash/content_public/journal/blood/105/1/10.1182_blood-2004-06-2106/6/m_zh80010571710001.jpeg?Expires=1769092476&Signature=KthY5NGTUWhj094IMyG2FVrVacIWWh2XKY3vDJYWvSQs9q2NNVz2-sAZCYWmb7IN0nlXIfhKa0pJ6zpaV~yc87yNFG9VAuay9YShcyTMpTO2qBKpWKWlvy64GD2gUvz2Ici9h0ZzrCu3rsZHgfzblQUy-qtipSYaGAXqEtZYXzGI2ECI6KAeSduh2D6q3UCCqhL2gJxYkij8S-0vDu35P73dzdBI0Uov29r~GhdiGCombU-yTPTHQ5Z5TT0cWVSbsmOVzOqV69XXi6rIZdP43t4kGpxF98eGH0QpZtnzeDR-7aeQpgySi0x9jlAJMQmdAkCbthxaZWSXJKDooiAkbw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal