Abstract
Ex vivo modification of donor lymphocytes with purine analogs (mDL) may help to minimize graft versus host disease (GvHD) while providing beneficial graft versus leukemia (GvL) effects. In a murine model system, we have shown that allogeneic donor splenocytes, treated with fludarabine ex vivo have significantly reduced GvHD activity when transferred to irradiated recipient mice, and retain anti-viral and GvL activities (Giver, 2003). This effect appears to be mediated by relative depletion of donor CD4 CD44low, “naive” T-cells. As a first step toward developing mDL for use in patients, we sought to evaluate the effects of ex vivo fludarabine exposure on human T-cell subsets, and to determine the minimum dose of fludarabine required to achieve this effect.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cell samples from 6 healthy volunteers were evaluated at 0, 24, 48, and 72 hour time points after ex vivo incubation in varying dosages of fludarabine: 2, 5, and 10(n=3) mcg/ml. Fludarabine incubated samples were compared to samples that received no fludarabine (untreated). The total viable cell number was determined and the fractions and absolute numbers of viable CD4 and CD8 naïve and memory T-cells were determined using flow cytometry after incubation with 7-AAD (dead cell stain), CD4, CD8, CD45RA, CD62L, and CCR7 antibodies, and measuring the total viable cells/ml.
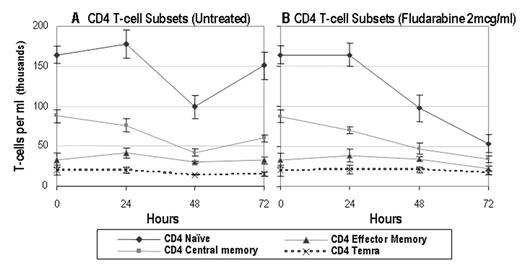
Results: The numbers of viable CD4 and CD8 T-cells remained relatively stable in control cultures. Without fludarabine, the average viability at 72 hr of naive and memory T-cells were 92% and 77% for CD4 and 86% and 63% for CD 8 (Fig. 1A). Naive CD4 T-cells were more sensitive to fludarabine-induced death than memory CD4 cells. At 72 hr, the average viability of fludarabine-treated naive CD4 T-cells was 33% at 2 mcg/ml (8.2X the reduction observed in untreated cells) and 30% at 5 mcg/ml, while memory CD4 T-cells averaged 47% viability at 2 mcg/ml (2.3X the reduction observed in untreated cells) (Fig. 1B) and 38% at 5 mcg/ml. The average viability of naive CD8 T-cells at 72 hr was 27% at 2 mcg/ml and 20% at 5 mcg/ml, while memory CD8 T-cell viability was 22% at 2 mcg/ml and 17% at 5 mcg/ml. Analyses on central memory, effector memory, and Temra T-cells, and B-cell and dendritic cell subsets are ongoing. The 5 and 10 mcg/ml doses also yielded similar results in 3 initial subjects, suggesting that 2 mcg/ml or a lower dose of fludarabine is sufficient to achieve relative depletion of the naive T-cell subset.
Conclusions: Future work will determine the minimal dose of fludarabine to achieve this effect, test the feasibility of using ex vivo nucleoside analog incubation to reduce alloreactivity in samples from patient/donor pairs, and determine the maximum tolerated dose of mDL in a phase 1 clinical trial with patients at high risk for relapse and infectious complications following allogeneic transplantation.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal