Abstract
Local bone marrow (BM) renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is an autocrine-paracrine system affecting hematopoiesis [Haznedaroglu IC, et al. A local RAS in the bone marrow.
MedHypotheses. 1996;46:507–10.
, Haznedaroglu IC. A local RAS in the bone marrow still awaits its Christopher Columbus. ExpHematol. 1998;26:279.
, Haznedaroglu IC, et al.Towards the understanding of the local hematopoietic bone marrow RAS. IntJBiochemCellBiol. 2003;35:867–80
.] Angiotensin II type 1a (AT1a) receptors are present on the CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells from the BM or cord blood (CB) [Goker H, et al. Local umbilical cord blood renin-angiotensin system. AnnHematol. 2005;84:277–81
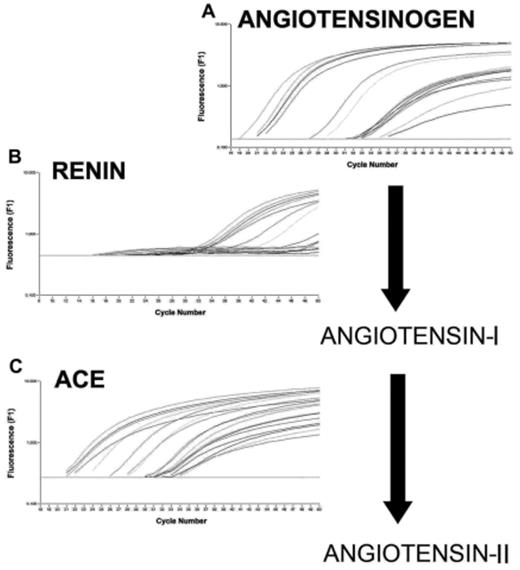
]. Angiotensin II stimulates the proliferation of BM and umbilical CB hematopoietic progenitors. Local RAS may also be involved in leukemogenesis and polycythemia vera [Aksu S, et. al. Enhanced Expression of the Local Haematopoietic Bone Marrow Renin-Angiotensin System in Polycythemia Rubra Vera J Int Med Res (in press), Aksu S, et. al. Over-expression of angiotensin converting enzyme (CD143) on leukemic blasts as a clue for the activated local bone marrow RAS in AML. Leukemia and Lymphoma (in press)]. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) hyperfunction may lead to the acceleration of negative hematopoietic regulator peptide, AcSDKP, metabolism, which in turn lowers its level in the bone marrow microenvironment, finally removing the anti-proliferative effect of AcSDKP on the hematopoietic cells and blasts. Renin expression could have a role in leukemia development and angiotensin may act as an autocrine growth factor for AML cells. In this study, the expression of the mRNAs of the major RAS components, namely ACE, renin, and angiotensinogen in human BM samples were quantified by RT-PCR to confirm the presence of the local BM RAS. Furthermore, we assessed quantitative alterations of the ACE, renin, and angiotensinogen mRNAs in leukemic BM samples. The aim of this study was to search those major RAS components in the leukemic blast cells taken from the BM of the patients with AML. BM aspirations were obtained from 10 patients with AML and 8 patients with non-malignant hematological disorders. All of three gene expressions were found to be significantly higher in the BM samples of AML patients compared to the BM samples of the control group (Figure 1). Pathological activity of the local RAS-mediated regulation may be important, since the angiotensin peptides represent a molecular target in the disease management.Author notes
Corresponding author
2005, The American Society of Hematology
2005

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal