Abstract
Aim: ASCT has improved survival in patients with multiple myeloma although most patients develop progressive disease. Absolute lymphocyte count recovery at day 15 (ALC-15) following ASCT has been reported as an independent prognostic indicator of overall survival (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) for patients with multiple myeloma. It is not only a good prognostic marker but may also have therapeutic significance.
We evaluated absolute lymphocyte recovery on day 15 (ALC-15), day 30 (ALC-30), day 60 (ALC-60) as a prognostic marker following ASCT in patients with multiple myeloma.
Method: Between 1992 and 2004, 119 consecutive patients underwent ASCT. ALC-15, ALC-30, ALC-60 were evaluated for impact on OS and PFS following ASCT. Information on known prognostic factors for multiple myeloma including age, BM plasma cells (PC), paraprotein (PP), international staging system (ISS staging) and disease response following stem cell transplant were also evaluated.
Result: There were 119 (M/F, 79/43) patients and median age was 57 (30–70) years. Most patients (N=100) received melphalan 200 mg/m2 as conditioning chemotherapy. The median CD34 dose infused was 3.95 x 106/kg (1.30–33.7). Median ALC-15 was 190 (0–254) cells/ul, median ALC-30 was 1000 (60 to 5590) cells/ul and ALC-60 was 1290 (50–6570). There were 28% of patients in complete remission (CR) & 67% in partial remission (PR) following ASCT.
On Multivariate analysis: ALC-30 was significantly associated with OS. Although there was higher PFS with higher lymphocyte count, the difference was not statistically significant. Other known prognostic factors such as ISS staging, PC at diagnosis, age at transplant and CR response following ASCT were also significantly correlated with OS & PFS.
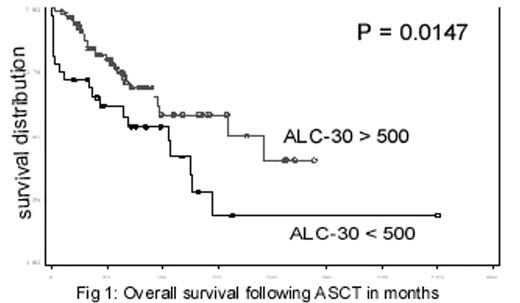
Survival analysis: Median OS was 64 (0.2 to 175) months and PFS 32 (1.7 to 175) months following PBSCT. In patients with ALC-30 >500 cells/ul median OS was 80 months and 53 months in patients with ALC-30 < 500 cells/ul (P= 0.0147).
PFS was 43 months in patients with ALC-30 > 500 cells/ul and 31 months in patients with ALC-30 < 500 cells/ul (P=0.39). Median ALC-30 was 1309 cells/ul in patients who were alive at last follow up while median ALC-30 was 879 cells/ul in patients who were deceased (P=0.0072) and in most of the patients (35/45, 77%) progressive disease was responsible for their demise. There was no significant correlation between CD34+ stem cells dose and lymphocyte dose in autograft with ALC-30 recovery (P=0.26).
Conclusions:
ALC-30 was an independent prognostic indicator of OS following ASCT in patients with multiple myeloma.
There was trend for longer PFS in patients with ALC-30 >500 cells/ul, although the difference was not statistically significant. This may be due small sample size and needs to be evaluated further in prospective study.
We could not find a correlation between lymphocyte dose or CD34 dose in autograft with ALC-30 recovery.
Lower ISS stage, less extensive marrow infiltration at diagnosis and complete response following PBSCT positively influences OS & PFS.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal