Abstract
The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway is an essential regulator of cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, migration, and cell survival. During hematopoiesis, the TGF-β signaling pathway is a potent negative regulator of proliferation while stimulating differentiation and apoptosis when appropriate. In hematologic malignancies, including leukemias, myeloproliferative disorders, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma, resistance to these homeostatic effects of TGF-β develops. Mechanisms for this resistance include mutation or deletion of members of the TGF-β signaling pathway and disruption of the pathway by oncoproteins. These alterations define a tumor suppressor role for the TGF-β pathway in human hematologic malignancies. On the other hand, elevated levels of TGF-β can promote myelofibrosis and the pathogenesis of some hematologic malignancies through their effects on the stroma and immune system. Advances in the TGF-β signaling field should enable targeting of the TGF-β signaling pathway for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.
Introduction
Human cancers arise from the stepwise accumulation of genetic and epigenetic alterations. However, because hematologic malignancies arise from cells that readily circulate and migrate through the body and are readily accessible to therapeutic agents, the pathogenesis and treatment of hematologic malignancies differ from those of epithelial-derived solid tumors in several respects. First, hematologic malignancies occur more readily than solid tumors, requiring as few as one hit (exemplified by the single chromosomal translocation resulting in chronic myelogenous leukemia) and resulting in an increased frequency of hematologic malignancies in children, with leukemia being both the most common cause of cancer death in children and the most common cause of death due to disease in children. In contrast, solid tumors require 4 to 6 hits and are largely a disease associated with aging. Second, in hematologic malignancies the pathogenic events more often involve balanced, simple, and disease-specific chromosomal rearrangements, which occur in 30% of acute leukemias and lymphomas but in less than 5% of epithelial-derived solid tumors. In lymphoid malignancies these chromosomal rearrangements frequently result in activation of a normally silent gene. Third, hematologic malignancies can arise quite rapidly and are not amenable to screening, as opposed to solid tumors, which have a long natural history and arise from preinvasive lesions (ie, adenomatous polyps and ductal carcinoma in situ [DCIS]), allowing for their detection and surgical resection prior to transformation into an invasive cancer. Fourth, hematologic malignancies respond more readily to dose-intensive chemotherapy than solid tumors.
Despite these differences, human cancers arising from hematopoietic cells and from epithelial cells do share many common alterations, including the ability to (1) develop resistance to growth-inhibitory and differentiation factors, (2) proliferate in the absence of exogenous growth signals, (3) evade apoptosis, and (4) evade immunosurveillance. These cellular functions are regulated by signal transduction pathways that normally control homeostasis but are disrupted during the pathogenesis of hematologic malignancies. The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling pathway is one such pathway that has a defined role in regulating normal hematopoiesis and is frequently dysregulated in hematologic malignancies. We have previously reviewed the role of the TGF-β signaling pathway in regulating the underlying hallmarks of cancer and its specific role in epithelial-derived solid tumors.1 Here we review the role of the TGF-β pathway in regulating hematopoiesis, the role of this pathway in hematologic malignancies, including leukemias, myeloproliferative disorders, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma, and conclude with a discussion of potential strategies for targeting the pathway for the treatment of hematologic malignancies.
TGF-β signaling pathway
While the mechanisms for TGF-β signaling have been delineated in several recent reviews,2-4 here we summarize the pathway and focus on aspects of specific relevance to the hematopoietic system. TGF-β exists as 3 isoforms in mammals, TGF-β1, -β2, and -β3, with TGF-β1 being the most abundant, universally expressed, and widely studied isoform. Platelets are an abundant source of TGF-β1 in humans.5 TGF-β is secreted as a latent protein complex that requires activation for biologic activity. Once activated, the TGF-β ligands regulate cellular processes by binding to 2 ubiquitously expressed, high-affinity cell-surface receptors, the type I receptor (TβRI) and type II receptor (TβRII), both of which contain a serine/threonine protein kinase in their intracellular domains. Once bound to TGF-β, TβRII recruits, binds, and transphosphorylates TβRI, thereby stimulating its protein kinase activity.6 The activated TβRI then recruits and phosphorylates the receptor-activated transcription factors, Smad2/3, which then bind to the common Smad4, translocate into the nucleus, and interact in a cell-specific manner with transcription factors (eg, Runx1, E2F), coactivators (eg, CBP, p300), and corepressors (eg, c-Ski, SnoN, TGIF) to regulate the transcription of TGF-β–responsive genes.7,8
On hematopoietic cells, TGF-β ligands also bind to 2 coreceptors, the type III TGF-β receptor (TβRIII or betaglycan) and endoglin.9,10 TβRIII is a ubiquitously expressed coreceptor for TGF-β superfamily ligands that binds all 3 TGF-β isoforms with high affinity and functions to concentrate ligand on the cell surface and facilitate binding to and signaling through TβRI and TβRII.11 However, TβRIII is not expressed at high levels in hematopoietic cells.12,13 Instead, endoglin, a coreceptor expressed more specifically in endothelial and hematopoietic cells, may be the predominant coreceptor in hematopoietic cells, as endoglin does not bind TGF-β2 and hematopoietic cells do not respond well to TGF-β2in terms of inhibition of proliferation.14
Regulation of the TGF-β signaling pathway
Because the TGF-β signaling pathway has essential roles in cellular homeostasis, the pathway is regulated at multiple levels. First, the level of ligand able to bind cell-surface receptors is regulated through the poorly understood process of ligand activation.3 Second, the level of cell-surface receptors, which appears to be an important determinant of cellular responsiveness to TGF-β, is regulated at the transcriptional, translational, and posttranslational levels. Specifically, TGF-β signaling is modulated by the level and duration of TGF-β receptor activation, with continuous nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of Smads permitting them to continuously monitor the levels of activated receptors.15 Third, TGF-β signaling is regulated by internalization of the receptors, which is either required for signaling16-18 or results in down-regulation of signaling.18,19 Fourth, inhibitory Smads, Smad6 and Smad7, are able to inhibit TGF-β responses through multiple mechanisms, including (1) blocking the phosphorylation of Smad2 or Smad3,3 (2) recruiting the ubiquitin ligases Smurf1/Smurf2 to cell-surface receptors, resulting in their ubiquitination and degradation,20 and (3) recruiting GADD34 and the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 1 to TβRI, resulting in its dephosphorylation and inactivation.21 Finally, TGF-β signaling is regulated in the nucleus by the interaction of Smads with numerous transcriptional coactivators and corepressors.3
Regulation of hematopoiesis by TGF-β
Hematopoiesis is regulated by the balance of cellular proliferation (self-renewal), differentiation, and apoptosis of hematopoietic progenitor cells. The effects of TGF-β on hematopoietic cells and hematopoiesis are both cell and context specific. In many cases opposing effects of TGF-β on the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of hematopoietic progenitor cells have been reported in vitro and in vivo.22-24 Here we focus on results obtained on human cells in vitro and in murine models in vivo.
The TGF-β signaling pathway represents a major antiproliferative and differentiation signal for hematopoietic progenitor cells, effectively preventing progression through the cell cycle and promoting differentiation. Exogenous TGF-β1 has been demonstrated to directly arrest growth and inhibit colony formation of CD34+ human stem/progenitor cells in vitro.22,24 Because hematopoietic progenitors are capable of producing and responding to TGF-β1, the effects of autocrine TGF-β1 signaling have been examined using neutralizing TGF-β1 antibodies or antisense to TGF-β1. These studies confirmed a role for endogenous TGF-β1in regulating the quiescence of early hematopoietic progenitors.22 These studies also established that TGF-β preferentially maintains the quiescence of early hematopoietic progenitors while having a less potent effect on later hematopoietic progenitors.22
The antiproliferative and prodifferentiation effects of TGF-β have also been established in vivo, with exogenous TGF-β1 significantly inhibiting proliferation of granulocyte, erythroid, megakaryocyte, and macrophage progenitor cells25 and delaying hematologic recovery after treatment of mice with 5-fluorouracil.26 In a reciprocal fashion, TGF-β1 knockout mice are either embryonic lethal due to defects in hematopoietic- and endothelial-cell differentiation27 or develop a severe autoimmune phenotype leading to death by 3 weeks with increased cellular proliferation in the spleen and lymph nodes and increased numbers of lymphocytes and neutrophils.28,29 However, more recent studies have countered these studies and challenged the role of TGF-β as a regulator of hematopoiesis in vivo. TβRI knockout mice are embryonic lethal due to severe defects in yolk sac and placental vascular development but continue to develop hematopoietic progenitors capable of functional hematopoiesis,30 and conditional knockout of TβRI in adult mice reveals that TGF-β signaling through TβRI is not required for hematopoiesis in vivo, because these mice have normal numbers of fully functional hematopoietic progenitor cells in terms of differentiation potential, cell-cycle status, apoptosis, and repopulation kinetics.31
One potential explanation for these discrepant results is that TGF-β may signal through other receptors to regulate hematopoiesis. Indeed, TGF-β has been demonstrated to signal through another type I TGF-β superfamily receptor, ALK-1, in endothelial and neuronal cells.32,33 In addition, the TGF-β coreceptor, endoglin, which is known to be expressed on hematopoietic stem cells9 and proerythroblasts,10 was shown to be important for the myelopoiesis and definitive erythropoiesis from Flk1+ precursors in vitro.34 Alternatively, other cytokine or growth factor signaling pathways may be able to compensate for loss of TGF-β signaling through TβRI, including the activins, which are also able to signal to Smad2/3. Finally, given that most studies done on human hematopoietic cells in vitro support an important role for TGF-β in regulating human hematopoietic-cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, TGF-β may have fundamentally different effects on murine versus human hematopoiesis.
Regulation of the immune system by TGF-β
In addition to regulating hematopoiesis, the TGF-β signaling pathway is a potent regulator of the immune system.35 In general, TGF-β has an immunosuppressor role mediated predominantly by its effects on T cells and antigen-presenting cells (APCs). In terms of T cells, TGF-β inhibits IL-2–dependent proliferation of T cells by blocking IL-2 production,36 inhibits the maturation of T cells, and prevents naive T cells from acquiring effector functions.37 TGF-β may also mediate its immunosuppressive effects on T cells through CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells, which secrete TGF-β1 and express cell-surface–bound TGF-β1.38 These in vitro effects of TGF-β on T cells have been validated in murine models as T-cell–specific abrogation of TGF-β signaling in mice results in spontaneous T-cell activation and the development of an autoimmune disease of the lung and colon.39 TGF-β also has potent effects on professional APCs, with autocrine TGF-β inhibiting tissue macrophage activation40 and promoting differentiation of dendritic cells from precursors.41 In vivo, TGF-β1–deficient mice lack Langerhans cells in the epidermis despite expressing functional precursors, suggesting that TGF-β is required for normal Langerhans-cell development and/or migration to the epidermis.42
Role of TGF-β in hematopoietic malignancies
As discussed under “Regulation of hematopoiesis by TGF-β,” the TGF-β signaling pathway has a controversial role in regulating normal hematopoiesis. During the pathogenesis of hematologic malignancies, normal homeostatic mechanisms regulating cellular proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis become disrupted. Although there are many alterations in hematologic malignancies, one common theme is the development of resistance to homeostatic functions of TGF-β on proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. However, as opposed to solid tumors, which frequently harbor mutations in members of the TGF-β signaling pathway, including in Smad4 and TβRII,1 hematologic cancers generally become TGF-β resistant through decreased expression of TGF-β receptors on the cell surface or repression of TGF-β signaling by oncoproteins including Evi-143 and Tax.44 We now turn attention the particular role of the TGF-β signaling pathway in leukemias, myeloproliferative disorders, lymphomas, and multiple myeloma.
TGF-β signaling in leukemia
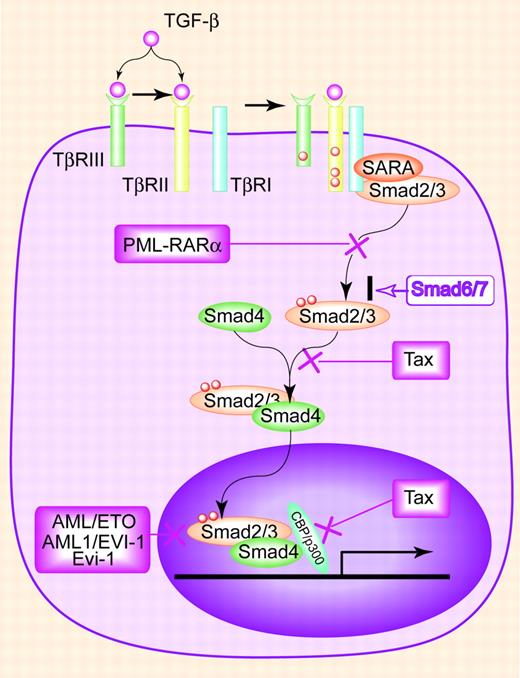
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) arises from the abnormal differentiation of hematopoietic precursors resulting in a paucity of functional, mature hematopoietic cells. AML is classified by cytomorphology, cytochemistry, and distinct cytogenetic abnormalities that provide prognostic information, including t(8;21), inv(16), and t(15;17). For example, t(8;21), which is found in AML-M2 (myeloid with differentiation), is associated with a favorable prognosis.45 The t(8;21) results in the fusion protein AML1(Runx1)/ETO that functions as a dominant negative inhibitor of AML1, which normally functions in partnership with Smad3 to mediate megakaryocyte maturation and T- and B-cell differentiation.46 While the AML1/ETO fusion protein can still bind to Smad3, instead of activating TGF-β signaling, it represses TGF-β–induced transcriptional activity and blocks TGF-β signaling47 (Figure 1).
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL, AML-M3) is an acute myeloid leukemia in which promyelocytes predominate. APL is characterized by t(15;17), in which the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα) gene on 17q12 fuses with a nuclear regulatory factor PML on 15q22 to form the resulting fusion protein PML-RARα. PML normally exists in 2 isoforms, a nuclear isoform that functions as a tumor suppressor gene by regulating the transcriptional activity of p53 and Rb48 and a cytoplasmic isoform that is required for association of Smad2/3 with SARA (Smad anchor for receptor activation) and for the accumulation of SARA and TGF-β receptors into the early endosome, resulting in Smad phosphorylation.49 In APL, PML-RARα functions as a dominant negative of both PML isoforms. First, it physically interacts with the nuclear PML isoform, forcing relocalization from the PML nuclear body to aberrant nuclear structures.48 Second, it antagonizes cytoplasmic PML function by sequestering cytoplasmic PML from the Smad/SARA/TβRI/TβRII complex, thereby abolishing TGF-β signaling.49 Treatment with all-trans retinoid acid (ATRA) induces degradation of PML-RARα and resensitizes leukemic cells to TGF-β–induced growth inhibition, supporting abrogation of TGF-β signaling as an important cellular effect of PML-RARα.49 In addition to the disruption by AML1/ETO and PML-RARα oncoproteins, AML cells have also been found to harbor dominant negative mutations in Smad4 with the identification of a missense mutation in the MH1 (MAD-homology 1) domain and a frameshift mutation in the MH2 (MAD-homology 2) domain of Smad4 in AML specimens.50 Finally, patients with AML express TβRI with a polymorphism in the signal sequence (TβRI(6A)) at a higher frequency than the healthy population.51 The TβRI(6A) receptor is unable to fully mediate TGF-β's antiproliferative signals,51 suggesting that this polymorphism may contribute to the pathogenesis of AML. Taken together, these studies suggest that disruption of the TGF-β signaling pathway plays a critical role in leukemogenesis of AML.
The TGF-β signaling pathway and mechanisms of inhibition during leukemogenesis. TGF-β binds TβRII, directly or through TβRIII, inducing association of TβRII with TβRI. TβRII then phosphorylates and activates TβRI, which then phosphorylates Smad2 or Smad3. SARA acts to concentrate Smad2/3 near the cell surface, facilitating their phosphorylation by TβRI. Phosphorylated Smad2/3 associate with Smad4 and translocate into the nucleus, where they activate transcription of target genes. Smad7 inhibits TGF-β signaling by preventing TβRI's activation of Smad2/3. In leukemias, disease-specific oncoproteins disrupt this pathway through different mechanisms. PML-RARα prevents the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 by interrupting the formation of TGF-β receptor/SARA/Smad complexes. AML/ETO, AML/EVI-1, and Evi-1 inhibit Smad3 DNA binding and recruit the transcription repressor, CtBP. Tax disrupts the interaction of Smads with the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300 and blocks the formation of Smad2/3/4 complexes.
The TGF-β signaling pathway and mechanisms of inhibition during leukemogenesis. TGF-β binds TβRII, directly or through TβRIII, inducing association of TβRII with TβRI. TβRII then phosphorylates and activates TβRI, which then phosphorylates Smad2 or Smad3. SARA acts to concentrate Smad2/3 near the cell surface, facilitating their phosphorylation by TβRI. Phosphorylated Smad2/3 associate with Smad4 and translocate into the nucleus, where they activate transcription of target genes. Smad7 inhibits TGF-β signaling by preventing TβRI's activation of Smad2/3. In leukemias, disease-specific oncoproteins disrupt this pathway through different mechanisms. PML-RARα prevents the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 by interrupting the formation of TGF-β receptor/SARA/Smad complexes. AML/ETO, AML/EVI-1, and Evi-1 inhibit Smad3 DNA binding and recruit the transcription repressor, CtBP. Tax disrupts the interaction of Smads with the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300 and blocks the formation of Smad2/3/4 complexes.
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a chronic myeproliferative disorder characterized by the massive overproduction of myeloid cells and defined by the pathopneumonic cytogenetic abnormality, a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22 (the Philadelphia chromosome). This translocation results in a fused BCR-ABL protein with abnormal tyrosine kinase activity that causes the disordered myelopoiesis. During the blast crisis of CML, expression of Evi-1, a zinc finger protooncogene that is expressed at very low levels in normal hematopoietic cells, is increased.52 Evi-1 functions to attenuate TGF-β signaling by associating with the MH2 domain of Smad3 and repressing its DNA-binding ability and transcriptional activity43 and by binding and recruiting the corepressor, CtBP, to repress the expression of TGF-β target genes.53 Apart from altered expression, the t(3;21) chromosomal translocation, which is also associated with the blast crisis of CML, results in the formation of AML1(Runx1)/EVI-1 chimeric protein, in which the N-terminal half of AML1 is fused to the entire Evi-1 oncoprotein. AML/EVI-1 functions by both diminishing the effect of AML1 on Smad3-mediated transcription and directly binding to Smad3 to antagonize Smad3-mediated transcription54 (Figure 1). These studies suggest that while BCR-ABL initiates leukemogenesis of CML, resistance to TGF-β signaling facilitates entry into blast crisis.
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) can be divided into adult and childhood ALL and further categorized as either a preB-cell, B-cell, or T-cell phenotype. ALL is the most common cancer occurring in children, representing 23% of cancer diagnoses among children younger than 15 years. In childhood T-cell ALL, Smad3 protein is absent or markedly decreased despite normal levels of Smad3 mRNA.55 In Smad3-deficient mice, loss of Smad3 alone is insufficient to induce leukemia, but when combined with the loss of the p27kip1 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, which is also frequently altered in human T-cell ALL, T-cell leukemia develops.55 Inactivation of TGF-β signaling has also been demonstrated in HTLV-1–induced adult acute T-cell leukemia, through the action of the viral oncoprotein Tax. Several models for Tax function in disrupting TGF-β signaling have been proposed, including (1) directly interacting with the transcriptional coactivator CBP/p300 to disrupt its interaction with Smads,44 (2) directly interacting with the MH2 domains of Smads 2, 3, and 4 to inhibit Smad3/4 complex formation and disrupt the interaction of the Smads with CBP/p300 (Figure 1),56 and (3) activating JNK to increase phosphorylation of c-Jun followed by the formation of Smad3/c-Jun complexes, which abrogate Smad3 DNA-binding activity.57 Taken together, these results suggest that the TGF-β signaling pathway is a critical tumor suppressor in T-cell leukemia. Indeed, disruption of TGF-β signaling in T cells does result in hyperproliferation of the CD8+ T-cell compartment and subsequent development of T-cell leukemia in murine models.58
TGF-β signaling in BCR-ABL–negative myeloproliferative diseases
In addition to CML, there are BCR-ABL–negative myeloproliferative disorders, which are all clonal disorders of hematopoietic stem cells, including polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET), and myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. These diseases share a number of features including impaired hematopoieses, uncontrolled proliferation of a distinct myeloid stem cell, which appears to be due to an activating JAK2 mutation (JAK2V617F),59 and a reactive myelofibrosis characterized by abnormal deposition of collagen in the bone marrow. The TGF-β signaling pathway has complex roles in regulating both the proliferation of the distinct myeloid stem cells and the reactive myelofibrosis in these diseases.
ET is characterized by the sustained proliferation of megakaryocytes, which normally produce and are negatively regulated by TGF-β1. However, in ET the megakaryocyte colony-forming units are less sensitive to TGF-β1 due to a decrease in Smad4 expression.60 Importantly, reexpression of Smad4 is able to restore sensitivity to TGF-β1, establishing the important role for loss of Smad4 expression in the pathogenesis of ET.60 Decreased expression of TβRII has also been demonstrated in ET specimens,61 suggesting that loss of sensitivity to TGF-β1 may be a common feature in this myeloproliferative disease.
PV is characterized by panhyperplasia of the marrow with increased numbers of circulating erythrocytes predominating. Although an activating JAK2 mutation appears to drive the clonal proliferation, decreased expression of TβRII has been reported in PV specimens,61 which may play a role in the clonal expansion in PV.
Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia is a chronic myeloproliferative disease characterized by clonal myeloproliferation and prominent reactive myelofibrosis. While the expression of TGF-β1 and TβRI is not decreased in CD34+ progenitors from these patients, there is a specific decrease in TβRII expression at both the message and protein levels compared with normal CD34+ progenitors, suggesting that decreased TβRII expression confers TGF-β resistance in this disease.62
The reactive myelofibrosis associated with myeloproliferative diseases occurs in the latter stages of CML and PV, while occurring early in myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. The pathogenesis of this myelofibrosis is thought to involve the action of cytokines secreted by megakaryocytes, platelets, and monocytes that directly increase collagen synthesis. Because megakaryocytes and platelets are a major source of TGF-β and TGF-β is able to increase collagen synthesis, TGF-β is thought to be one of the major cytokines involved in this reactive myelofibrosis. In a mouse model of a thrombopoietin-induced myeloproliferative disorder, lethally irradiated wild-type host animals receiving grafts with TGF-β1–null and wild-type bone marrow stem cells both developed a myeloproliferative syndrome. However, while the wild-type cells induced myelofibrosis in all animals, the TGF-β1–null cells never induced myelofibrosis, supporting TGF-β1 as the critical cytokine mediating this myelofobrosis.63 In addition, in 2 separate models of myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia (induced by forced thrombopoietin expression or decreased GATA-1 expression) the development of myelofibrosis was associated with high levels of TGF-β1 in the bone marrow and the spleen, suggesting that both of these models converge on the TGF-β signaling pathway to mediate myelofibrosis.64
TGF-β signaling in lymphoma/lymphoproliferative diseases
Lymphomas are lymphoproliferative malignancies that arise from lymphoid tissues and can spread to other organs. Lymphomas can be classified into Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads in a predictable manner, and non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs), a heterogeneous group of diseases that spread in a less predictable manner and are more likely to disseminate to extranodal sites. NHLs can be further classified by the World Health Organization/Revised European-American Lymphoma (WHO/REAL) classification based on morphologic, genetic, immunotypic, and genetic features. As lymphomas arise from B cells, T cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, all of which are potently growth inhibited by TGF-β, uncontrolled proliferation of these cells during the pathogenesis of lymphomas would be expected to be accompanied by alterations in the TGF-β signaling pathway resulting in resistance to the growth-inhibitory effects of TGF-β. Surprisingly, whether this occurs in Hodgkin lymphoma has not been addressed, perhaps due in part to the difficulty in isolating primary Hodgkin lymphoma cells. In certain types of NHL, however, specific alterations in the TGF-β signaling pathway have been documented.
In cutaneous T-cell lymphoma specimens as well as in Sézary syndrome, the leukemic form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, reduced cell-surface levels of TβRI and TβRII have been reported.65,66 In these cases, TβRI and TβRII mRNA and intracellular TβRII protein can be detected; however, TβRII contains a specific mutation (D404G), with the mutant acting in a dominant negative manner to prevent cell-surface expression of wild-type TβRII.66,67 Mutation of TβRII has been linked to malignant progression in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas, because indolent clones from the same patients do not have mutations in TβRII and respond to TGF-β.65,67 In cell lines from low-grade NHL, the bone morphogenetic protein Smad, Smad1, is overexpressed and phosphorylated in response to TGF-β1, suggesting a role for Smad1 in mediating the effects of TGF-β in low-grade NHL.68 In addition, in one anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, a 5-kb deletion of the TβRI gene, which results in loss of TβRI expression on the cell surface, has been described.69
In small lymphocytic lymphoma/chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), characterized by the progressive accumulation of histologically small, mature clonal CD5+ B lymphocytes in the blood, bone marrow, and lymphatic tissues due to the absence of apoptosis, the B-CLL cells become resistant to the growth-inhibitory and proapoptotic effects of TGF-β 70,71 despite expressing high levels of TGF-β.72 The lack of response of CLL cells to TGF-β has been attributed to decreased cell-surface expression of TGF-β receptors, especially TβRI.73 Indeed, CLL cells resistant to TGF-β have either loss of cell-surface expression of TβRI, despite normal message levels of TβRI,74 or mutations in the signal sequence for TβRI (L12Q substitution with a single in-frame A deletion), resulting in attenuated TGF-β signaling.75 In contrast, 2 separate studies have determined that CLL cells have increased expression of the TGF-β coreceptor, TβRIII, which is normally not expressed abundantly in hematopoietic cells.12,13 The relevance of this observation remains to be established. TGF-β is also secreted at higher levels from CLL cells and stromal cells, resulting in suppression of normal bone marrow and selective expansion of the clonal CLL cells.72
In hairy-cell leukemia, a chronic lymphoproliferative disorder involving the circulation of hairy cells in the blood, infiltration of hairy cells in the bone marrow and spleen, and associated with bone marrow fibrosis, patients have higher circulating levels of TGF-β1 in the blood, with the hairy cells being the main source of this TGF-β1.76 Elevated TGF-β1 levels significantly enhance the extent of bone marrow fibrosis, and bone marrow plasma from these patients is able to induce bone marrow fibrosis in vitro, with this effect abolished by neutralizing TGF-β1 antibodies, supporting elevated levels of circulating TGF-β1 as the major cause of bone marrow fibrosis in patients with hairy-cell leukemia.76 These studies establish resistance to the antiproliferative and antiapoptotic actions of TGF-β as an important factor in the pathogenesis of some lymphoproliferative disorders. Further studies are necessary to determine whether mutation and loss of TGF-β receptors is a common phenomenon in lymphoproliferative disorders and whether this occurs in Hodgkin lymphoma as well.
TGF-β signaling in multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is an incurable plasma-cell malignancy arising from germinal center B cells. Disease progression occurs through several stages, including monoclonal gammopathy of uncertain significance and smoldering myeloma, and is associated with immunoglobulin gene translocations, dysregulation of cyclins D1, D-2, and D-3 and myc, and activating mutations in N-ras, K-ras, or fibroblast growth factor receptor3 (FGFR3). Once developed, multiple myeloma cells home to the bone marrow, where multiple cytokines, including IL-6, VEGF, and TGF-β, regulate their proliferation and migration. TGF-β is a potent suppressor of normal B-cell proliferation and immunoglobulin production.77 In multiple myeloma, TGF-β is secreted at higher levels from both myeloma cells and from bone marrow stromal cells.78,79 Increased production of TGF-β correlates with increased IL-6 and VEGF secretion by stromal cells, and neutralizing antibodies to TGF-β or a small molecule inhibitor to TβRI (SD-208) are able to block increased IL-6 and VEGF secretion, supporting TGF-β as the major inducer of IL-6 and VEGF secretion by bone marrow stromal cells.79,80 Higher serum levels of TGF-β also correlate with lower levels of normal immunoglobulins in patients with myeloma81 and appear to result in the functional immune impairment in multiple myeloma.78 While producing excess amounts of TGF-β, multiple myeloma cells from human patients and myeloma cell lines from humans and mice are resistant to TGF-β–mediated inhibition of Rb phosphorylation,79 cell growth, and induction of apoptosis.82 Multiple myeloma cells contain no mutations in the TβRI or TβRII genes and express TβRI and TβRII proteins in the cytoplasm.83 However, these receptors do not traffic to the cell surface due to the formation of intracellular TGF-β receptor complexes.82,83 These studies establish resistance of multiple myeloma cells to the antiproliferative actions of TGF-β and the effects of TGF-β on the bone marrow stroma as important factors in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma.
The TGF-β signaling pathway as a therapeutic target in hematologic malignancies
In human hematologic malignancies, multiple mechanisms are used to decrease cellular responsiveness to TGF-β, including mutations in the TGF-β receptors and negative regulation by specific oncoproteins (Table 1). These studies establish a clear tumor suppressor role for the TGF-β signaling pathway in hematologic malignancies. However, in contrast to epithelial-derived solid tumors, the TGF-β signaling pathway does not appear to have a general dichotomous tumor suppressor/tumor promoter role in hematologic malignancies, as evidence that elevated levels of TGF-β result in more aggressive disease or that a poorer prognosis for patients with hematologic malignancies is lacking. Thus, while the complex role of TGF-β in other human diseases including cardiovascular disease still needs to be considered,85 targeting the TGF-β pathway may be a more straightforward task in many hematologic malignancies.
Altered TGF-β signaling in hematalogic malignancies
Disease and alterations in the TGF-β signaling pathway . | Reference . |
|---|---|
| AML-M2 | |
| AML1/ETO blocks Smad3 DNA binding | Jakubowiak et al47 |
| AML-M3 | |
| PML-RARα blocks phosphorylation of Smad2/3 | Lin et al49 |
| AML | |
| Dominant negative mutations in Smad4 | Imai et al50 |
| Hypomorphic TβRI polymorphism, TβRI(6A) | Pasche et al51 |
| CML | |
| Evi-1 overexpression blocks Smad3 DNA binding, recruits corepressor | Kurokawa et al43 |
| AML1/EVI-1 blocks Smad3 DNA binding, recruits corepressor | Kurokawa et al54 |
| Childhood T-cell ALL | |
| Decreased Smad3 protein expression | Wolfraim et al55 |
| Adult T-cell ALL | |
| HTLV-1 Tax inhibits coactivator CBP/p300, blocks Smad2/3/4 formation, inhibits Smad3 DNA binding | Mori et al44 , Lee et al56 , Arnulf et al57 |
| CLL | |
| Decreased TβRI expression | DeCoteau et al74 , Lagneaux et al84 |
| TβRI mutation (Leu12Gln with single in-frame Ala deletion) | Schiemann et al75 |
| Increased TβRIII expression | Klein et al12 , Jelinkek et al13 |
| Hairy-cell leukemia | |
| Increased TGF-β production enhances bone marrow fibrosis | Shehata et al76 |
| Polycythemia vera | |
| Decreased TβRII expression | Rooke et al61 |
| Essential thrombocythemia | |
| Decreased Smad4 expression | Kuroda et al60 |
| Decreased TβRII expression | Rooke et al61 |
| NHL | |
| Reduced TβRI and TβRII expression | Capocasale et al66 , Schiemann et al69 |
| Dominant negative mutation of TβRII (D404G) | Knaus et al67 |
| Multiple myeloma | |
| Deficient trafficking of TGF-β receptors to the cell surface | Fernandez et al83 |
Disease and alterations in the TGF-β signaling pathway . | Reference . |
|---|---|
| AML-M2 | |
| AML1/ETO blocks Smad3 DNA binding | Jakubowiak et al47 |
| AML-M3 | |
| PML-RARα blocks phosphorylation of Smad2/3 | Lin et al49 |
| AML | |
| Dominant negative mutations in Smad4 | Imai et al50 |
| Hypomorphic TβRI polymorphism, TβRI(6A) | Pasche et al51 |
| CML | |
| Evi-1 overexpression blocks Smad3 DNA binding, recruits corepressor | Kurokawa et al43 |
| AML1/EVI-1 blocks Smad3 DNA binding, recruits corepressor | Kurokawa et al54 |
| Childhood T-cell ALL | |
| Decreased Smad3 protein expression | Wolfraim et al55 |
| Adult T-cell ALL | |
| HTLV-1 Tax inhibits coactivator CBP/p300, blocks Smad2/3/4 formation, inhibits Smad3 DNA binding | Mori et al44 , Lee et al56 , Arnulf et al57 |
| CLL | |
| Decreased TβRI expression | DeCoteau et al74 , Lagneaux et al84 |
| TβRI mutation (Leu12Gln with single in-frame Ala deletion) | Schiemann et al75 |
| Increased TβRIII expression | Klein et al12 , Jelinkek et al13 |
| Hairy-cell leukemia | |
| Increased TGF-β production enhances bone marrow fibrosis | Shehata et al76 |
| Polycythemia vera | |
| Decreased TβRII expression | Rooke et al61 |
| Essential thrombocythemia | |
| Decreased Smad4 expression | Kuroda et al60 |
| Decreased TβRII expression | Rooke et al61 |
| NHL | |
| Reduced TβRI and TβRII expression | Capocasale et al66 , Schiemann et al69 |
| Dominant negative mutation of TβRII (D404G) | Knaus et al67 |
| Multiple myeloma | |
| Deficient trafficking of TGF-β receptors to the cell surface | Fernandez et al83 |
TGF-β indicates transforming growth factor-β.
Because the TGF-β signaling pathway is often disrupted by disease-specific oncoproteins, including AML1/ETO, AML-1/EVI1, and PML-RARα, directly targeting these proteins should not only relieve the resistance to TGF-β but also target the other pathways disrupted by these oncoproteins. Indeed, as mentioned above, treatment with ATRA induces degradation of PML-RARα and resensitizes leukemic cells to TGF-β–induced growth inhibition, providing proof of principle for this approach.49 With the advent of RNA interference (RNAi), which has the potential to specifically target and decrease expression of disease-causing mutants, and improving methods for delivery of RNAi constructs, such treatments may soon become a clinical reality.86
In hematologic malignancies in which decreased receptor expression is a mechanism for TGF-β resistance, including CLL, BCR-ABL–negative myeloproliferative disorders, and lymphomas, increasing expression of these receptors may be a reasonable therapeutic target. There are 2 agents approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in hematologic malignancies: 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (decitabine; MGI Pharma, Bloomington, MN), a DNA methyl transferase inhibitor being used in myelodysplastic syndrome and in clinical trials for acute and chronic leukemia,87 and bortezomib (Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Cambridge, MA), a proteasome inhibitor being used in multiple myeloma that may be useful in increasing TGF-β receptor expression. When incorporated into the genome, 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine prevents promoter hypermethylation and induces expression of proteins that normally would have been silenced by promoter hypermethylation, including TGF-β receptors. In addition, because the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway has a role in regulating TGF-β receptor expression,20 inhibiting the proteasome may increase their expression. These agents could potentially be used in conjunction with standard therapy for hematologic malignancies or combined with other targeted approaches.
In certain hematologic malignancies, including multiple myeloma and myeloproliferative disorders, TGF-β functions to regulate stromal elements to enhance their pathogenesis. In multiple myeloma, TGF-β acts on the bone marrow microenvironment to both directly and indirectly enhance myeloma-cell activity in the bone, while in myeloproliferative disorders TGF-β enhances myelofibrosis. In addition, many hematologic malignancies secrete TGF-β, which may be essential for the circulating cancer cells or cancer cells in lymphoid organs to evade immunosurveillance. Accordingly, in these diseases, decreasing TGF-β activity may be appropriate. There are several strategies for decreasing TGF-β activity; however, the strategies that are currently in clinical trials for the treatment of human diseases are neutralizing TGF-β antibodies, which bind ligand and prevent ligand binding to its cell-surface receptors, antisense to individual TGF-β ligand isoforms, and small molecule inhibitors of TβRI kinase activity.88-90 Indeed, as mentioned in the discussion of TGF-β signaling in MM, in multiple myeloma, neutralizing antibodies to TGF-β or a small molecule inhibitor to TβRI (SD-208) are able to block increased IL-6 and VEGF secretion,79,80 providing preclinical support for this therapeutic strategy in these patients.
Conclusions and future directions
Although hematologic malignancies represent a broad spectrum of disease, the involvement of the TGF-β signaling pathway in hematologic malignancies can be characterized by several themes. In many hematologic malignancies, resistance to the growth-inhibitory and apoptotic effects of TGF-β allows clonal expansion and suggests an early role for the TGF-β signaling pathway in disease pathogenesis. This resistance can occur through distinct mechanisms, with loss of TGF-β cell-surface receptors occurring in CLL, ET, PV, NHL, and multiple myeloma; interference with TGF-β signaling by disease-specific oncoproteins occurring in AML and ALL; and decreased Smad expression and/or Smad mutation mediating TGF-β resistance in childhood T-cell ALL, AML, and ET. On the other hand, in CML, disease-specific oncoproteins interfere with TGF-β signaling after disease initiation and are associated with disease progression, suggesting a role for disrupted TGF-β signaling in disease progression. Finally, elevated levels of TGF-β ligand appear to be an essential mediator of myelofibrosis in myeloproliferative diseases and hairy-cell leukemia.
Although these studies establish clear roles for the TGF-β signaling pathway in aspects of the pathogenesis of hematologic malignancies, major challenges in the TGF-β signaling field remain in defining specific pathways involved in mediating the cell- and context-dependent effects of TGF-β, the contributions of other signaling pathways that TGF-β both signals through and crosstalks with (ie, MAP kinase, Rho, and Akt/PI-3 kinase pathways), and the mechanisms for signaling through these pathways. Once these questions are addressed, defining alterations occurring in the TGF-β signaling pathways at a molecular level in an individual patient will allow matching of targeted therapies with these alterations to make treatment of hematologic malignancies both more effective and less toxic.
Prepublished online as Blood First Edition Paper, February 16, 2006; DOI 10.1182/blood-2005-10-4169.
Supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute (grant nos. CA100065, CA105255, and CA106307); The V Foundation for Cancer Research; the American Association for Cancer Research; and the Susan G. Komen Foundation (M.D.).

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal