Abstract
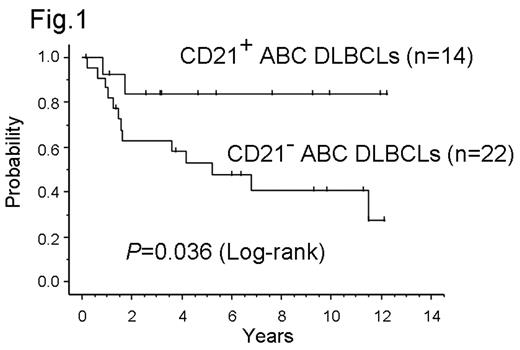
We have reported that CD21 expression in tumor cells is a favorable prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs)(
Signature genes to distinguish between CD21-positive and CD21-negative DLBCLs were as follows; IgM (P=0.00017), CCR6 (P=0.0011), IL7 (P=0.0017), IgK (P=0.0037), EBI2 (P=0.0066), CD24 (P=0.0099) etc. were overexpressed in CD21-negative DLBCLs, and CR2 (CD21) (P=0.0010), MKNK2 (P=0.0028), LMO2 (P=0.00478), CDKN2A (P=0.0059), PDE8B (P=0.0066) etc. were overexpressed in CD21-positive DLBCLs. In 40 cases of DLBCLs, overall survival of patients with sIgM-positive DLBCL was significantly worse than that of patients with sIgM-negative DLBCL (P=0.023). Furthermore, in 216 consecutive cases of DLBCLs analyzed by immunohistochemistry using frozen sections from 1987 to 2004, overall survival according to sIgM expression was significantly different (P=0.013).
In conclusion,
CD21 expression was a favorable prognostic factor in ABC DLBCLs.
A top feature gene to distinguish between CD21-positive and CD21-negative DLBCLs was IgM. CD21 expression seemed to be related to the differentiation level of lymphoma cells.
sIgM expression itself was a poor prognostic factor in ABC DLBCLs and in whole DLBCLs.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal