Abstract
Introduction: Immunotherapy with Natural Killer (NK) cells may eradicate residual chemotherapy-resistant myeloma (MM) after a state of minimal residual disease has been achieved by autologous stem cell supported high-dose chemotherapy. NK cell activity is regulated by Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors (KIRs). The principal inhibitory ligands of KIRs are HLA Class I molecules (-C and -Bw4) expressed by target cells. NK cells lyse tumor cells that do not display such inhibitory KIR-ligands (KIR-L), such as the K562 cell line. The proteasome is responsible for the generation of peptides that bind to and stabilize Class I molecules at the cell surface. We hypothesized that treatment of MM cells with the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib results in the down-regulation of Class I and thereby sensitizes MM to NK cell mediated lysis.
Methods: MM cell lines and primary MM cells were treated with concentrations of bortezomib easily achievable in vivo. The objectives were to determine a) the optimal concentration of bortezomib to down-regulate Class I, b) the time to maximum down-regulation of Class I, and c) a bortezomib concentration that increases NK-mediated MM killing without affecting NK cell function.
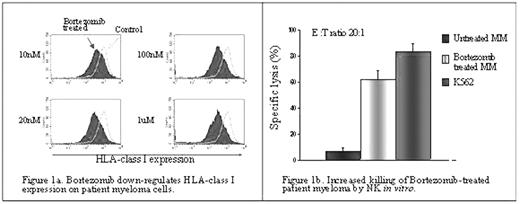
Results: We found that down-regulation of Class I post-bortezomib treatment of the MM cell line, JJN3, and primary MM cells was dose and time dependent. Bortezomib at 10–20nM down-regulated HLA-class I by 63% compared to untreated control cells with maximal down-regulation at 24hrs (Fig.1a). Bortezomib treatment of primary MM cells greatly increased sensitivity to NK cell-mediated lysis, compared to controls (6% vs. 61%) at an E:T ratio of 20:1 (Fig.1b). These bortezomib concentrations did not affect NK cell function.
Conclusions: We observed that bortezomib down-regulates Class I and enhances the sensitivity of MM to NK cell-mediated lysis. Our findings have clear therapeutic implications for MM and other NK cell-sensitive malignancies.
Bortezomib down-regulates HLA-class I expression on patient myeloma cells.
Bortezomib down-regulates HLA-class I expression on patient myeloma cells.
Increased killing of bortezomib-treated patient myeloma by NKin vitro.
Increased killing of bortezomib-treated patient myeloma by NKin vitro.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal