Abstract
Drug resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has been linked to BCR/ABL gene amplification or mutations in its tyrosine kinase domain of BCR/ABL gene (Phi). However the role of the ABC-transporters in the multidrug resistant phenotype still remains to be clarified.
Objective: to study the functional expression of multidrug resistance gene-1 (MDR-1) and breast cancer resistant protein (BCRP), in imatinib pharmacoresistant K562 Phi+ cells.
Materials and methods: K562 Phi+ cultured cells (ATCC catN°:CCL-2439) were immunophenotyped by flow cytometry, mRNA transcripts of BCR/ABL and MDR-1 were amplified by RT-PCR and P-glycoprotein (P-gp), the product of MDR-1 gene and BCRP, were investigated by inmunocytochemistry, using specific monoclonal antibodies (P-gp: clones C494 and C219; BCRP: clone BXP-21). Total efflux activity of Rhodamine-123 (Rho-123) and its inhibition by Cyclosporin A (CyA) or 4°C, were evaluated using flow cytometry. The apoptotic effect in K-562 cells after 24hs and 72hs of treatment with imatinib (2μmol.L−1) with or without CyA (3ugm.L−1), was evaluated by staining the cells with 1 mL of a mixture of acridine orange (100 mg.mL−1) and ethidium bromide (100 mg.mL−1) in PBS.
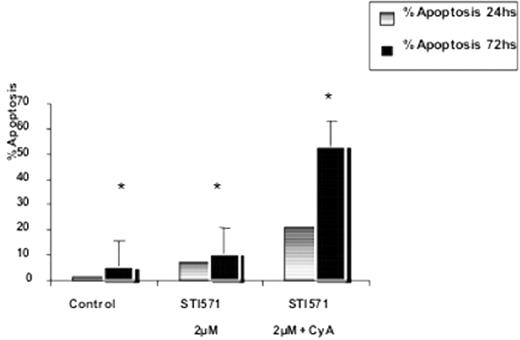
Results: The immunophenotype was: HLA-DR-,CD45++,CD11c−/+,CD13+,CD14−,CD15−/+,CD16−,CD33+,CD34−CD117−/+; CD56−, CD61−/+; CD2−, CD3−, CD4−, CD7−, CD8−, CD10+, CD19−, glyA+ . MDR-1 and BCR/ABL transcripts were highly expressed, and P-gp and BCRP immunostaining were also positive. Rho-123 efflux was inhibited by CyA (3ugm.L−1) or 4°C. Increased apoptotic effect (from 7, 21% to 20, 79%) at 24hs and (11% to 53%) at 72hs was observed with combined imatinib+CyA treatment compared with imatinib alone.(p<0.01*)
Conclusions. Our results suggest that P-gp and BCRP might play an active role in the pharmacoresistance to imatinib treatment in K562Phi+ cells. Combined treatment with Imatinib+CyA (or other more specific inhibitors of P-gp and BCRP) could increase the apoptotic effect in BCR/ABL over-expressing refractory cells.
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal