Abstract
Recently, the JAK2V617F mutation was found in patients with myeloproliferative disorders (MPDs), including most with polycythemia vera (PV). The mutant JAK2 has increased kinase activity, and it was shown to be pathogenic in mouse models. Herein, we analyzed blood samples randomly collected from a clinical laboratory. Surprisingly, as many as 37 samples from a total of 3935 were found positive for the JAK2 mutation. However, only one of these samples had blood test results indicative for probable PV, but several had nonhematologic diseases. On average, samples with the mutation had normal red cell counts but significantly higher white blood cell and platelet counts, although most were within the normal range. The data suggest that the JAK2V617F mutation is apparently much more common than MPDs. Its occurrence may be a prelude to full blood cell abnormalities and other diseases, but it cannot by itself diagnose MPDs.
Introduction
Protein tyrosine kinases are central regulators of signaling pathways and are attractive therapeutic targets.1-3 Recently, several groups identified a recurrent somatic activating mutation in the JAK2 tyrosine kinase in polycythemia vera (PV), essential thrombocythemia (ET), and idiopathic myelofibrosis.4-8 Infrequent occurrence of this mutation has been also reported in chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, atypical myeloproliferative disorders (MPDs), myelodysplastic syndrome, systemic mastocytosis, chronic neutrophilic leukemia, and acute myeloid leukemia.9-13 This mutation results in a valine to phenylalanine substitution within the pseudokinase domain of JAK2. The mutant JAK2 possesses enhanced tyrosine kinase activity and causes a PV-like phenotype in mouse bone marrow transplantation models.6,14,15 However, it remains unclear whether the JAK2V617F mutation is solely responsible for these diseases and why it is associated with such a wide spectrum of phenotypes. Previous investigations were carried out to identify JAK2V617F in samples from specific diseases. In this study, we analyzed blood samples randomly collected from a clinical laboratory.
Materials and methods
Blood samples
Deidentified, consecutive peripheral blood samples from donors (all Chinese) of any age, sex, and disease were randomly collected from the clinical laboratory of China Japan Union Hospital, Changchun, China, over a period of about 6 months. Institutional Review Board approvals were obtained from both Jilin University and the University of Oklahoma Health Science Center.
PCR amplification
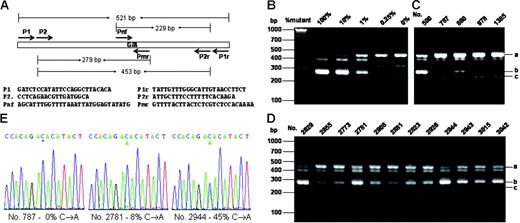
Genomic DNA was extracted from the whole blood. A genomic DNA fragment containing the exon 14 of the JAK2 gene which bears the V617F mutation site was amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with primers P1 and P1r (Figure 1A). The PCR was run with Taq DNA polymerase or Phusion polymerase (for confirmation of the positive samples) for 35 cycles with 94°C for 20 seconds, 60°C for 20 seconds, and 72°C for 30 seconds. For allele-specific PCR, 0.2 μL of the initial PCR product was used for further PCR amplification with nested primers P2 and P2r, mutation-specific primer Pmr, and non–mutation-specific primer Pnf (Figure 1A). The PCR was performed as above except for only 30 cycles. For BsaX116,17 and sequencing analyses, the initial PCR product of 521 bp (base pair) was gel-purified. After 3 hours of digestion with BsaX1, the products were amplified by allele-specific PCR with primers P2 and Pmr as described above (Figure S1). DNA sequencing was performed with an ABI3730 capillary sequencer (ABI Instruments, Foster City, CA). Throughout the experiments, purified plasmid DNAs carrying 521 bp JAK2 genomic DNA with or without the V617F mutation were used as controls.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed by using the Excel program (Microsoft, Redmond, WA). Differences between 2 groups of samples were accessed by using t tests assuming unequal variances. P values of less than .05 (2 tailed) are considered significantly different.
Results and discussion
For initial screening of JAK2V617F, we relied on the nested allele-specific PCR method with primers shown in Figure 1A The specificity and sensitivity of the method was verified by using DNA plasmids carrying the mutant and wild-type DNA as shown in Figure 1B. The method could unambiguously detect as low as 0.25% of the mutation. Figure 1C-D shows allele-specific PCR analyses of several positive and negative samples. With this method, we detected a total of 38 JAK2V617F-positive samples. All but one of these positive samples were further confirmed by using the BsaX1 restriction enzyme digestion methods (for detail see Figure S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Figure link at the top of the online article). We thus identified 37 positive samples from a total of 3935, corresponding to 0.94%. By performing DNA sequencing of the 521-bp PCR product obtained with primer P1 and P1r, we verified 12 positive samples that contained at least 7% of the mutant DNA (Figure 1E). The remaining 25 samples contained less than 5% of the mutation and could not be unambiguously confirmed by DNA sequencing.
Allele-specific PCR assays and DNA sequencing of the JAK2V617F mutation. (A) PCR design and primer sequences. (B) Verification of allele-specific PCR analysis by using standard DNA plasmids. A 521-bp DNA fragment from genomic DNAs containing wild-type and JAK2V617F mutation with P1 and P1r primers and cloned into the pBluescript KS vector (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). A total of 4 ng plasmid DNA mixtures containing the indicated amount of JAK2V617F mutant were subjected to PCR analysis with a primer mixture of P2, P2r, Pmr, and Pnf. (C-D) Allele-specific PCR analysis of blood genomic DNA. Genomic DNA was amplified by PCR with primers P1 and P1r and further amplified with allele-specific primer mixture P2, P2r, Pmr, and Pnf. PCR products were analyzed on 3% agarose and visualized with ethedium bromide staining. The expected PCR products were indicated by i (453 bp), ii (279 bp), and iii (229 bp). Among the blood DNA samples (C-D), nos. 787, 978, and 1385 are considered negative, and all the rest are considered positive. (E) Sequencing of PCR products from genomic DNAs amplified by using primers P1 and P1r. Sequencing was performed from the 3′-side with primer P1r. Percentages of the mutant in the total PCR products were determined by measuring the relative peak heights of DNA sequencing data in reference to those obtained with standard DNA mixtures containing known proportions of JAK2V617F and wild-type JAK2.
Allele-specific PCR assays and DNA sequencing of the JAK2V617F mutation. (A) PCR design and primer sequences. (B) Verification of allele-specific PCR analysis by using standard DNA plasmids. A 521-bp DNA fragment from genomic DNAs containing wild-type and JAK2V617F mutation with P1 and P1r primers and cloned into the pBluescript KS vector (Stratagene, La Jolla, CA). A total of 4 ng plasmid DNA mixtures containing the indicated amount of JAK2V617F mutant were subjected to PCR analysis with a primer mixture of P2, P2r, Pmr, and Pnf. (C-D) Allele-specific PCR analysis of blood genomic DNA. Genomic DNA was amplified by PCR with primers P1 and P1r and further amplified with allele-specific primer mixture P2, P2r, Pmr, and Pnf. PCR products were analyzed on 3% agarose and visualized with ethedium bromide staining. The expected PCR products were indicated by i (453 bp), ii (279 bp), and iii (229 bp). Among the blood DNA samples (C-D), nos. 787, 978, and 1385 are considered negative, and all the rest are considered positive. (E) Sequencing of PCR products from genomic DNAs amplified by using primers P1 and P1r. Sequencing was performed from the 3′-side with primer P1r. Percentages of the mutant in the total PCR products were determined by measuring the relative peak heights of DNA sequencing data in reference to those obtained with standard DNA mixtures containing known proportions of JAK2V617F and wild-type JAK2.
The blood test results of the entire group and JAK2V617F-positive samples are shown in Table 1 Of the 37 JAK2V617F-positive samples, 23 had a specific age entry. The average age was 55.6 years (SD = 13.6 years), which is significantly higher than the average of the entire sample (P = .02). The majority of these positive samples had normal red blood cell counts and hemoglobin levels. Only one (no. 1695) had a hemoglobin level slightly above normal, and this patient also had elevated white blood cell and platelet counts, suggesting the presence of probable PV.18 The average white blood cell and platelet counts of JAK2V617F-positive samples were 9.44 × 109/L (SD = 5.07 × 109/L) and 272 × 109/L (SD = 99.6 × 109/L), respectively, which are significantly higher than those of the entire sample (P = .02 and .001, respectively). Ten samples had above-normal platelet counts, but none of these reached a level of diagnosis of ET.19 Eleven samples had above-normal white blood cell counts, among which 4 had high platelet counts, but we do not know whether these represented secondary elevations. Among the 19 samples for which we collected detailed clinical information, 15 had various illnesses, including kidney failure, stomach cancer, pneumonia, thrombosis, coronary heart disease, diabetes, cervical spine injury, arteriosclerosis, cerebral ischemia, cerebral infarction, and fracture. Importantly, none of these 19 donors were diagnosed with a MPD or were under chemotherapies or radiation therapies which are known to affect blood counts.
Results of blood tests
| . | Sex . | Age, y . | WBC count, × 109/L . | RBC count, × 1012/L . | Hemoglobin level,g/L . | Platelet count,× 109/L . | V716F, % . | Diagnosis . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire samples, mean ± SD | — | 48.6 ± 16.6 | 7.39 ± 3.69 | 4.26 ± 1.19 | 128.3 ± 23.4 | 213.4 ± 84 | — | — |
| JAK2V617F positive, mean ± SD | — | 55.6 ± 13.6 | 9.44 ± 5.07 | 4.40 ± 0.58 | 132 ± 19 | 272 ± 99.6 | — | — |
| Sample no. | ||||||||
| 224 | M | NA | 4* | 3.02* | 88* | 92* | 41 | Kidney failure |
| 500 | F | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 86 | NA |
| 548 | M | 37 | 11.1† | 3.69* | 101* | 382† | < 5 | Stomach cancer |
| 832 | M | 58 | 8.8 | 5.44 | 156 | 249 | < 5 | Pneumonia |
| 860 | F | NA | 4.7 | 4.67 | 145 | 202 | < 5 | NA |
| 896 | F | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 57 | NA |
| 1255 | M | NA | 4.6 | 3.74* | 99* | 147 | 48 | NA |
| 1381 | M | NA | 10 | 4.79 | 141 | 432† | < 5 | NA |
| 1591 | M | 41 | 20.1† | 3.74* | 118* | 216 | < 5 | Arterial and venous thrombosis |
| 1644 | M | NA | 4.7 | 4.82 | 130 | 196 | < 5 | NA |
| 1648 | F | NA | 14.3† | 4.27 | 136 | 256 | < 5 | NA |
| 1651 | F | NA | 4* | 5.17 | 105* | 297 | < 5 | NA |
| 1695 | M | NA | 15.2† | 5.39 | 166† | 521† | 7 | NA |
| 1909 | M | 61 | 8.4 | 4.33 | 123* | 275 | < 5 | NA |
| 2026 | M | 45 | 7.3 | 4.58 | 148 | 170 | < 5 | NA |
| 2066 | F | 74 | 8.1 | 4.85 | 157 | 295 | < 5 | NA |
| 2109 | F | 69 | 9 | 4.38 | 129 | 367† | < 5 | NA |
| 2281 | F | 68 | 6.6 | 3.88 | 123 | 206 | < 5 | NA |
| 2304 | F | NA | 6 | 4.46 | 134 | 372 | < 5 | NA |
| 2335 | M | 44 | 3.1* | 4.63 | 145 | 174 | < 5 | Hemangioma |
| 2629 | F | NA | 9.2 | 4.05 | 121 | 387† | 30 | NA |
| 2655 | F | NA | 7.4 | 4.6 | 143 | 279 | < 5 | NA |
| 2773 | M | 53 | 4.5 | 4.77 | 143 | 301† | < 5 | Coronary heart disease |
| 2781 | M | 54 | 15.6† | 4.75 | 141 | 454† | 8 | NA |
| 2823 | M | 43 | 6.1 | 4.94 | 154 | 234 | < 5 | Diabetes |
| 2881 | M | NA | 9.5 | 3.2* | 112* | 197 | < 5 | ND |
| 2908 | M | 38 | 10.7† | 4.41 | 146 | 179 | < 5 | Cervical spine injury |
| 2926 | M | 66 | 9 | 4.04 | 124 | 246 | < 5 | Diabetes |
| 2943 | F | 65 | 5.8 | 4.05 | 132 | 190 | < 5 | Coronary heart disease |
| 2944 | F | 48 | 18.2† | 4.27 | 125 | 464† | 45 | ND |
| 3015 | F | 65 | 10.5† | 3.97 | 117 | 236 | 11 | Arteriosclerosis |
| 3042 | M | 50 | 3.5* | 4.48 | 124 | 145 | < 5 | Pneumonia |
| 3243 | M | 45 | 26.2† | 4.45 | 132 | 273 | < 5 | ND |
| 3714 | M | 73 | 12.6† | 4.9 | 151 | 254 | 8 | Cerebral ischemia |
| 3910 | F | 82 | 9.7 | 5.07 | 163 | 306† | 46 | ND |
| 3981 | M | 34 | 12.2† | 4.99 | 136 | 216 | < 5 | Cerebral infarction |
| 4120 | F | 66 | 9.6 | 3.39 | 105 | 310† | 10 | Fracture |
| . | Sex . | Age, y . | WBC count, × 109/L . | RBC count, × 1012/L . | Hemoglobin level,g/L . | Platelet count,× 109/L . | V716F, % . | Diagnosis . |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entire samples, mean ± SD | — | 48.6 ± 16.6 | 7.39 ± 3.69 | 4.26 ± 1.19 | 128.3 ± 23.4 | 213.4 ± 84 | — | — |
| JAK2V617F positive, mean ± SD | — | 55.6 ± 13.6 | 9.44 ± 5.07 | 4.40 ± 0.58 | 132 ± 19 | 272 ± 99.6 | — | — |
| Sample no. | ||||||||
| 224 | M | NA | 4* | 3.02* | 88* | 92* | 41 | Kidney failure |
| 500 | F | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 86 | NA |
| 548 | M | 37 | 11.1† | 3.69* | 101* | 382† | < 5 | Stomach cancer |
| 832 | M | 58 | 8.8 | 5.44 | 156 | 249 | < 5 | Pneumonia |
| 860 | F | NA | 4.7 | 4.67 | 145 | 202 | < 5 | NA |
| 896 | F | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 57 | NA |
| 1255 | M | NA | 4.6 | 3.74* | 99* | 147 | 48 | NA |
| 1381 | M | NA | 10 | 4.79 | 141 | 432† | < 5 | NA |
| 1591 | M | 41 | 20.1† | 3.74* | 118* | 216 | < 5 | Arterial and venous thrombosis |
| 1644 | M | NA | 4.7 | 4.82 | 130 | 196 | < 5 | NA |
| 1648 | F | NA | 14.3† | 4.27 | 136 | 256 | < 5 | NA |
| 1651 | F | NA | 4* | 5.17 | 105* | 297 | < 5 | NA |
| 1695 | M | NA | 15.2† | 5.39 | 166† | 521† | 7 | NA |
| 1909 | M | 61 | 8.4 | 4.33 | 123* | 275 | < 5 | NA |
| 2026 | M | 45 | 7.3 | 4.58 | 148 | 170 | < 5 | NA |
| 2066 | F | 74 | 8.1 | 4.85 | 157 | 295 | < 5 | NA |
| 2109 | F | 69 | 9 | 4.38 | 129 | 367† | < 5 | NA |
| 2281 | F | 68 | 6.6 | 3.88 | 123 | 206 | < 5 | NA |
| 2304 | F | NA | 6 | 4.46 | 134 | 372 | < 5 | NA |
| 2335 | M | 44 | 3.1* | 4.63 | 145 | 174 | < 5 | Hemangioma |
| 2629 | F | NA | 9.2 | 4.05 | 121 | 387† | 30 | NA |
| 2655 | F | NA | 7.4 | 4.6 | 143 | 279 | < 5 | NA |
| 2773 | M | 53 | 4.5 | 4.77 | 143 | 301† | < 5 | Coronary heart disease |
| 2781 | M | 54 | 15.6† | 4.75 | 141 | 454† | 8 | NA |
| 2823 | M | 43 | 6.1 | 4.94 | 154 | 234 | < 5 | Diabetes |
| 2881 | M | NA | 9.5 | 3.2* | 112* | 197 | < 5 | ND |
| 2908 | M | 38 | 10.7† | 4.41 | 146 | 179 | < 5 | Cervical spine injury |
| 2926 | M | 66 | 9 | 4.04 | 124 | 246 | < 5 | Diabetes |
| 2943 | F | 65 | 5.8 | 4.05 | 132 | 190 | < 5 | Coronary heart disease |
| 2944 | F | 48 | 18.2† | 4.27 | 125 | 464† | 45 | ND |
| 3015 | F | 65 | 10.5† | 3.97 | 117 | 236 | 11 | Arteriosclerosis |
| 3042 | M | 50 | 3.5* | 4.48 | 124 | 145 | < 5 | Pneumonia |
| 3243 | M | 45 | 26.2† | 4.45 | 132 | 273 | < 5 | ND |
| 3714 | M | 73 | 12.6† | 4.9 | 151 | 254 | 8 | Cerebral ischemia |
| 3910 | F | 82 | 9.7 | 5.07 | 163 | 306† | 46 | ND |
| 3981 | M | 34 | 12.2† | 4.99 | 136 | 216 | < 5 | Cerebral infarction |
| 4120 | F | 66 | 9.6 | 3.39 | 105 | 310† | 10 | Fracture |
Normal ranges: WBC count, 4.5 × 109/L-10 × 109/L; RBC count, 4 × 1012/L-5.5 × 1012/L (male) or 3.5 × 1012/L-5.5 × 1012/L (female); hemoglobin level, 126-160 g/L (male) or 110–150 g/L (female); platelet count, 100 × 109/L-300 × 109/L.
WBC indicates white blood cell; RBC, red blood cell; —, not applicable; NA, not available; ND, not determined or no diagnosis to make.
Samples with blood level below normal.
Samples with blood level above normal.
Collectively, by using nested allele-specific PCR and BsaX1 digestion analyses we identified 37 JAK2V617F-positive samples from a total of 3935, corresponding to near 1%. Twelve of these samples, corresponding to 0.3%, contained enough of the mutation to be firmly detected by using DNA-sequencing analyses. Either number with a positive mutation is unexpectedly high. JAK2V617F was mainly found in PV, ET, and idiopathic myelofibrosis but was uncommon in myeloid malignancies.4-8,9-13 The classic MPDs are relatively rare. Among them, PV has the highest incidence, but its occurrence is only 0.002% in the United States and is considerably lower in Asia.18 Our study thus demonstrates that the JAK2V617F mutation is more common than the anticipated number of MPDs, and that it can occur with nonhematologic diseases. Nonetheless, the data do not show that the mutation is irrelevant to hematologic diseases. It may be an early manifestation of a broad spectrum of blood disorders, particularly MPDs, which are yet to be fully manifested.
JAK2 is a tyrosine kinase involved in signaling pathways regulating cell growth.20,21 Chromosomal translocations resulting in fusions deregulating JAK2 activity are implicated in leukemias.22-24 Studies have demonstrated that JAK2V617F causes a PV-like phenotype in mouse models.6,14,15 Our data demonstrate that the mutation is much more common than MPDs and is present in patients with many other conditions that have not manifested MPDs. Interestingly, many of the JAK2V617F carriers had elevated white blood cell or platelet counts. These elevations may be sufficient to indicate forthcoming clinical problems before development of a full blood disorder. Considering its greatly enhanced kinase activity, the mutant JAK2 should have pathogenic implications. JAK2V617F may not be used exclusively for the diagnosis of MPDs, but it may be useful for the early identification of MPDs and other diseases, for the prognosis of these diseases, and for designing proper prevention and treatment methods. The relatively high incidence of the JAK2V617F mutation further suggests its importance to human health. Therefore, further studies to define its pathologic role and the correlation of its occurrence with environmental factors are warranted.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Contribution: X.X., Q.Z., J.L., and S.X. performed the research; Q.L. and S.B.K. analyzed data; X.F. and Z.J.Z. designed, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 30470391) (X.F.) and the National Institutes of Health (grants HL076309 and HL079441) (Z.J.Z.).

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal