Abstract
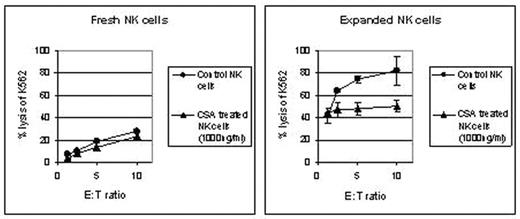
The ability to expand NK cells in vitro has led to the recent initiation of protocols incorporating adoptive NK cell infusions after HCT. Calcineurin inhibitors such as CSA are commonly used to prevent graft versus host disease (GVHD) in HCT recipients. Recently, Hong et al found the phenotype and function of fresh NK cells cultured in vitro with CSA was altered, with CSA treated NK cell cultures having enhanced cytotoxicity against tumor targets. However, the impact of CSA on in vitro expanded NK cell function and phenotype has not been explored. We analyzed cell proliferation, IFN-gamma production, cell surface immunofluorescent staining and cytotoxicity against K562 and renal cell carcinoma cell lines by in vitro expanded vs freshly isolated NK cells cultured in physiological doses of CSA (40ng/ml, 200ng/ml, 1000ng/ml for 18hrs). Fresh NK cells were obtained from the PBMC of healthy donors using immunomagnetic beads to isolate CD56+/ CD3− cells. NK cells were expanded in vitro using irradiated EBV transformed B cells as feeder cells in media containing IL-2 [500U/ml] for 12–14 days. Comparing CSA containing cultures to controls, there was a significant reduction in IL-2 stimulated fresh NK cell proliferation (stimulation index 0.51± 0.1) and TRAIL expression (MFI 10.4 vs 3.01). Furthermore, an ELISA assay showed fresh NK cells treated with CSA had a significant reduction in IL-2 induced IFN-g production compared to controls (median 231 vs 57 pg/ml, p=0.025). In contrast, in vitro expanded NK cells cultured in CSA showed no significant reduction of proliferation or TRAIL expression. At the highest doses of CSA (1000ng/ml), minimal inhibition of K562 killing of freshly isolated NK cells was observed. In contrast, expanded NK cells cultured in CSA for 18 hours compared to controls had a significant reduction in the killing of K562 cells (E:T=10:1, median 66 vs 43% lysis, p=0.011) and RCC tumor cells (E:T=20:1, 14.8 vs 8.8%, p=0.043).
These data confirm CSA alters the phenotype and function of CD3−/CD56 + NK cells. Importantly, CSA appears to have a deleterious effect on expanded NK cell tumor cytotoxicity that was not observed with fresh NK cells. These finding suggest the anti-tumor effects of in vitro expanded NK cells could be hindered when adoptively infused in HCT patients receiving CSA.
Author notes
Disclosure: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal