We have previously shown that coculture of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) for 14 days with immortalized fetal hepatocytes yields CD34+ cells that can be expanded in serum-free liquid culture into large numbers of megaloblastic nucleated erythroblasts resembling yolk sac–derived cells. We show here that these primitive erythroblasts undergo a switch in hemoglobin (Hb) composition during late terminal erythroid maturation with the basophilic erythroblasts expressing predominantly Hb Gower I (ζ2ϵ2) and the orthochromatic erythroblasts hemoglobin Gower II (α2ϵ2). This suggests that the switch from Hb Gower I to Hb Gower II, the first hemoglobin switch in humans is a maturation switch not a lineage switch. We also show that extending the coculture of the hESCs with immortalized fetal hepatocytes to 35 days yields CD34+ cells that differentiate into more developmentally mature, fetal liver–like erythroblasts, that are smaller, express mostly fetal hemoglobin, and can enucleate. We conclude that hESC-derived erythropoiesis closely mimics early human development because the first 2 human hemoglobin switches are recapitulated, and because yolk sac–like and fetal liver–like cells are sequentially produced. Development of a method that yields erythroid cells with an adult phenotype remains necessary, because the most mature cells that can be produced with current systems express less than 2% adult β-globin mRNA.
Introduction
In humans, primitive erythropoiesis originates from the extra-embryonic mesoderm, is first detectable in the yolk sac 14 to 19 days after conception, and persists in this organ until the ninth week of gestation. It has long been known that yolk sac–derived primitive erythrocytes undergo a partial hemoglobin (Hb) switch: At week 5, yolk sac erythroblasts synthesize primarily Hb Gower I (ζ2ϵ2), but at weeks 6 to 8, they also synthesize large amounts of Hb Gower II (α2ϵ2).1
Definitive erythropoiesis, which originates from the aorta-gonado-mesonephros region of the embryo proper,2 is first detectable in the fetal liver during the sixth week of development. Erythroblasts produced in this organ express ζ, ϵ, α, γ, and small amounts of β-globin but the ϵ and ζ-globin genes are rapidly silenced while the α and γ-globin genes remain expressed at high level until around birth. At that point, bone marrow erythropoiesis, which is first detectable around the eleventh week of gestation, becomes the major site of erythropoiesis and expression of the β-globin gene, which had slowly risen during gestation almost completely replaces γ-globin expression. In addition to these differences in globin-expression patterns, yolk sac, fetal liver, and bone marrow erythrocytes differ in morphology because yolk sac erythroblasts are nucleated and megaloblastic, while both fetal liver and bone marrow erythrocytes are enucleated. Fetal and adult erythrocytes differ by size, with the fetal cells bigger than the adult ones.
Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) can self-renew indefinitely in culture while retaining the capacity to differentiate into derivatives of the 3 germ layers.3 Several laboratories including ours have reported that hESCs could be induced to differentiate into hematopoietic cells using either coculture with various stromal cells or through the formation of embryoid bodies.4,,,,,–10 In previous studies, we observed that H1 hESCs cocultured with FH-B-hTERT, a human fetal liver hepatocyte cell line,11 differentiated into CD34+ hematopoietic cells which, when seeded on methylcellulose, developed into colonies representing the major myeloid blood cell lineages.5 Importantly, increasing the length of the coculture of the hESCs on FH-B-hTERT cells from 14 days to 21 days led to an increase in γ-globin expression in colony forming units–erythroid (CFU-E) colonies, recapitulating one of the globin switches that occur during development. Other investigators working with either human, primate, or mouse cells have also reported that the production of hematopoietic cells seems to spontaneously progress through the early stages of human development after removal of the hESCs cells from self-renewal condition.8,12,13
We have also recently developed a method for the large-scale production of erythroid cells from hESCs.14 In this method, hESCs are cocultured for 14 days with FH-B-hTERT to produce CD34+ cells that are then sorted and seeded in a 4-step culture system. In steps 1 and 2 cocktails of cytokines are used to promote first the proliferation and then the maturation of erythroid precursors. In steps 3 and 4, terminal maturation of the erythrocytes is facilitated by transfer to plates containing a feeder layer composed of MS-5 mouse bone marrow stromal cells (Figure 1A). This method of culture routinely produces 5 × 106 to 5 × 107 fully differentiated erythroid cells that morphologically resemble primitive yolk sac–derived erythroblasts. We report here that extending to 35 days the length of the coculture of the hESCs with immortalized fetal hepatocytes yielded CD34+ cells that gave rise to erythroblasts that had a more developmentally mature phenotype, because they were of smaller size, express predominantly fetal hemoglobin, and can enucleate.
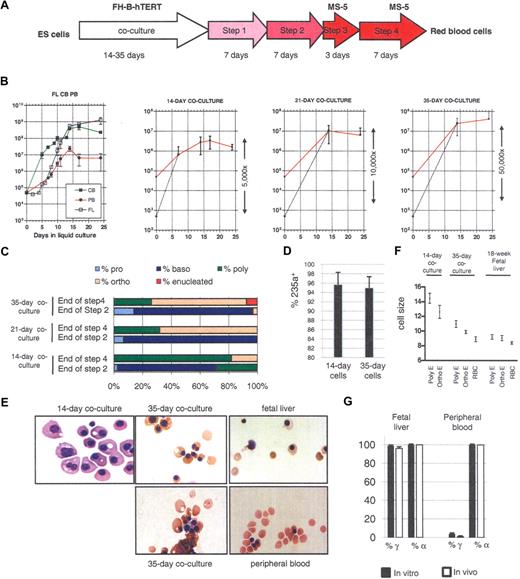
Production of enucleated RBCs from hESCs. (A) Protocol to produce RBCs from hESCs. Embryonic stem (ES) cells were cocultured with irradiated FH-B-hTERT cells for 14 to 35 days. The cells were then dissociated and CD34+ cells were sorted and seeded in liquid culture in the presence of Flt-3L, stem cell factor (SCF), erythropoietin (EPO), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-4, and interleukin (IL)-3 (amplification 1, 7 days) and then of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-)1, SCF, EPO, BMP-4, and IL3 (amplification 2, 7 days). Terminal maturation was induced by culture on an MS-5 feeder layer for 10 days (first 3 days in the presence of EPO, then without any cytokines). (B) Proliferation rate of CD34+ cells from fetal liver (FL), cord blood (CB), and peripheral blood (PB; first panel) and of hESC-derived CD34+ cells from 14-, 21-, and 35-day coculture (panels 2-4) placed in condition described in panel A. The red curves represent the actual amplification. The dotted lines represent the calculated amplification assuming 1% survival of the seeded cells (see “Lengthening the coculture time leads to the production of red blood cells that can enucleate”). (C) Morphologic characterization and enumeration of the erythroblasts demonstrated that differentiation was relatively synchronous during the liquid culture period. (D) Flow cytometric analysis with anti-CD 235a (glycophorin A) antibodies of erythrocytes obtained after 14 or 35 days of coculture and 24 days of liquid culture. The bar graph summarizes the results of 3 experiments. (E) Micrographs of red cells obtained at the end of step 4 of our culture system. The total length of the 4-step culture varied between 24 and 29 days because steps 1 and 2 were occasionally lengthened for practical reasons (see “Amplification and differentiation of CD34+ cells”). Fourteen-day cocultures yielded large nucleated RBCs similar to cells produced in the yolk sac. Thirty-five-day cocultures yielded orthochromatic and enucleated RBCs similar to cells produced in the FL. (F) Size of the erythroblasts produced in culture. Sizes were estimated microscopically after 21 or 24 days of liquid culture. Poly-E, polychromatic erythroblasts; Ortho-E, orthochromatic erythroblasts; RBC, enucleated red blood cells. The cells from 35-day culture were closer in size to FL-derived cells than to the 14-day cells. (G) Bar graph summarizing globin expression (determined by HPLC) in erythroblasts produced either in culture from FL- or PB-derived CD34+ cells, or circulating at the time of harvest of the CD34+ cells. Globin levels observed in vitro closely matched the levels observed in vivo. Black bars, expression in in vitro–produced cells; white bars, expression in in vivo–produced cells. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + β-globin). Error bars represent SD.
Production of enucleated RBCs from hESCs. (A) Protocol to produce RBCs from hESCs. Embryonic stem (ES) cells were cocultured with irradiated FH-B-hTERT cells for 14 to 35 days. The cells were then dissociated and CD34+ cells were sorted and seeded in liquid culture in the presence of Flt-3L, stem cell factor (SCF), erythropoietin (EPO), bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-4, and interleukin (IL)-3 (amplification 1, 7 days) and then of insulin-like growth factor (IGF-)1, SCF, EPO, BMP-4, and IL3 (amplification 2, 7 days). Terminal maturation was induced by culture on an MS-5 feeder layer for 10 days (first 3 days in the presence of EPO, then without any cytokines). (B) Proliferation rate of CD34+ cells from fetal liver (FL), cord blood (CB), and peripheral blood (PB; first panel) and of hESC-derived CD34+ cells from 14-, 21-, and 35-day coculture (panels 2-4) placed in condition described in panel A. The red curves represent the actual amplification. The dotted lines represent the calculated amplification assuming 1% survival of the seeded cells (see “Lengthening the coculture time leads to the production of red blood cells that can enucleate”). (C) Morphologic characterization and enumeration of the erythroblasts demonstrated that differentiation was relatively synchronous during the liquid culture period. (D) Flow cytometric analysis with anti-CD 235a (glycophorin A) antibodies of erythrocytes obtained after 14 or 35 days of coculture and 24 days of liquid culture. The bar graph summarizes the results of 3 experiments. (E) Micrographs of red cells obtained at the end of step 4 of our culture system. The total length of the 4-step culture varied between 24 and 29 days because steps 1 and 2 were occasionally lengthened for practical reasons (see “Amplification and differentiation of CD34+ cells”). Fourteen-day cocultures yielded large nucleated RBCs similar to cells produced in the yolk sac. Thirty-five-day cocultures yielded orthochromatic and enucleated RBCs similar to cells produced in the FL. (F) Size of the erythroblasts produced in culture. Sizes were estimated microscopically after 21 or 24 days of liquid culture. Poly-E, polychromatic erythroblasts; Ortho-E, orthochromatic erythroblasts; RBC, enucleated red blood cells. The cells from 35-day culture were closer in size to FL-derived cells than to the 14-day cells. (G) Bar graph summarizing globin expression (determined by HPLC) in erythroblasts produced either in culture from FL- or PB-derived CD34+ cells, or circulating at the time of harvest of the CD34+ cells. Globin levels observed in vitro closely matched the levels observed in vivo. Black bars, expression in in vitro–produced cells; white bars, expression in in vivo–produced cells. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + β-globin). Error bars represent SD.
Using quantitative high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, we characterized in detail globin expression in erythrocytes obtained from the 14-day and the 35-day cocultures.
The first switch in globin expression that we observed was caused by the down-regulation of the ζ-globin gene and the up-regulation of the α-globin genes during late terminal erythroid maturation of the primitive erythroblasts obtained from the 14-day cocultures. In these cultures, the basophilic erythroblasts expressed primarily Gower I and mature to orthochromatophilic erythroblasts that expressed mostly hemoglobin Gower II. By contrast both the basophilic and the orthochromatophilic erythroblasts obtained from the 35-day coculture expressed primarily Hb F (α2γ2). A maturation switch similar to the one described for the primitive cells, but of smaller amplitude, could nevertheless be detected in these cells too. The switch from expression of Hb Gower II to Hb F therefore resulted from the production of a second wave of erythrocytes more similar to cells found in early human fetal liver.
Methods
ES cell culture
Human ES cell line H1 was maintained as undifferentiated cells by coculture with irradiated mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells (80 cGy) in Dulbecco modified Eagle medium (DMEM)/F12 media (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 20% Knockout Serum Replacer (Invitrogen), 1% MEM-nonessential amino acids (Invitrogen), 1mM l-glutamine, 4 ng/mL basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF; ProSpecTany, Rehovot, Israel) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin (P/S) as described by Thomson et al.3 Media was changed daily. H1 cells were passaged weekly by dissociation with 1 mg/mL collagenase IV (Invitrogen). MEF, MS-5, and FH-B-hTERT cells were grown in DMEM (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% P/S. FH-B-hTERT cells and MEF cells were irradiated with 80 Gy before attachment onto gelatin-coated 6-well plates. The hESCs used were between passages 30 and 70.
Red blood cell production in liquid culture
Differentiation of hESCs into CD34+ cells.
Undifferentiated H1 cells were passaged onto irradiated FH-B-hTERT feeder layers, and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 20% FBS (Invitrogen), 2 mM l-glutamine, 1% MEM-nonessential amino acids, 100 u/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin. The medium was changed every 2 to 3 days.
Extended cocultures of hESCs and FH-B hTERT for up to 35 days were performed by passaging the differentiating hESCs on fresh FH-B-hTERT cells every 2 weeks as described in the preceding paragraph.
On day 14, 21, or 35 of coculture, differentiated H1 cells on FH-B-hTERT were dissociated into single cell suspensions by using collagenase IV followed by trypsin/EDTA or Tryple Express (Invitrogen) supplemented with 5% chick serum. CD34 cell separations were performed using EasySep CD34 magnetic beads according to the manufacturer's instructions (StemCell Technologies, Vancouver, BC). Briefly, dissociated cells were labeled with CD34 antibodies (clone Qbend10) conjugated to dextran for 15 minutes. Magnetic nanoparticles conjugated to antidextran antibodies were then added for 10 minutes and labeled cells were recovered using a magnet. The H1 hESCs line is listed in the NIH hESC registry under the name WA01.15
Purification of CD34+ from fetal liver, cord blood, and peripheral blood was performed using EasySep CD34 magnetic beads. All samples were obtained using protocols approved by the institutional review board of Albert Einstein College of Medicine.
Amplification and differentiation of CD34+ cells.
CD34+ cells obtained either from hESCS or from fetal liver, cord blood, or peripheral blood were then seeded in the following 4-step system: In the first step (amplification of progenitors), sorted CD34+ cells were placed on a 6-well plate at a density of 50 000 cells/mL with serum-free basal medium StemSpan (StemCell Technologies) supplemented with Hydrocortisone (10−6 M), IL3 (13 ng/mL), BMP4 (13 ng/mL), Flt3L (33 ng/mL), SCF (100 ng/mL), and EPO (2.7 U/mL) for 7 days. In the second step (differentiation of progenitors to erythroid lineage), the cells were transferred to StemSpan medium supplemented with hydrocortisone (10−6 M), IL3 (13 ng/mL), BMP4 (13 ng/mL), SCF (40 ng/mL), EPO (3.3 U/mL) and IGF-1 (40 ng/mL) for 7 days. Cell density was kept below one million cells per mL at all time by adding fresh medium every 2 or 3 days as needed. In the third step (final maturation of the erythroid cells), the cells were plated on flasks containing confluent MS-5 cells and basal medium supplemented with EPO (3 U/mL) and hemin (5 μM) for 3 days. Finally, in the fourth step, the medium was replaced with the same medium but without EPO and the cells were incubated for 7 more days. Cells were rinsed with PBS between each step. This protocol was adapted from procedures developed by the Douay laboratory in Paris.16,17 Steps 1 and 2 were occasionally extended by up to 3 days if the cells did not expand rapidly enough.
Experiments with hESCs were repeated 3 to 6 times. Experiments with in vivo–derived CD34+ cells were repeated 2 to 3 times.
Flow cytometry.
Single-cell suspensions were washed with Ca2+- and Mg2+-free PBS supplemented with 2% serum replacer and labeled with CD34-PE, CD45-FITC, CD71-FITC or CD235a-PE antibodies (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN) and their corresponding IgG1 controls. Dead cells were gated out based on 7-AAD exclusion. For experiments described in Figure 3B, single cells were directly sorted into 96-well plates.
HPLC.
Cells were collected at different timepoints, washed twice with PBS, and lysed in water by 3 rapid freeze-thaw cycles. Debris was eliminated by centrifugation at 16 000g and the lysates stored in liquid nitrogen before HPLC analysis. HPLC were performed as described.18 Sufficient material to perform quantitative HPLC analysis could only be obtained reliably after 12 or more days of liquid culture.
Cytospin and Giemsa staining.
Cells were spun onto poly-lysine–coated slides using a cytospin apparatus (Cytospin 2; Thermo Shandon, Pittsburgh, PA). After drying for a minute, slides were stained with Wright-Giemsa reagents (Hema 3 stain; Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA) following the manufacturer's instructions. Cell size was estimated microscopically using ACT-2U version 1.6 software (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The results are expressed in arbitrary unit (u).
Globin expression analysis by quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
Total RNA from cells at different timepoints in liquid culture were isolated with Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) following manufacturer's instructions. For small scale analysis, frozen cell pellets stored at −80°C were thawed rapidly in water, divided into multiple aliquots and directly used for quantitative real-time (Qrt)-PCR. Real-time reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR was performed with a one-step SYBR-Green RT-PCR kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) on a LightCycler3 (Roche, Nutley, NY). Standard curves were established using cloned cDNA for each globin. Concentrations of standard were carefully quantified using a NanoDrop ND-1000 micro-spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE). The detection limit for all primers was under 100 copies of mRNA. Samples with fewer than 1000 copies of mRNA were excluded from the analysis.
The primers for each globin mRNA were: α-globin forward: CGGTCAACTTCAAGCTCCTAAG; α-globin reverse: CCGCCCACTCAGACTTTATT; β-globin forward: TACATTTGCTTCTGACACAAC; β-globin reverse: ACAGATCCCCAAAGGAC; γ-globin forward: CTTCAAGCTCCTGGGAAATGT; γ-globin reverse: GCAGAATAAAGCCTACCTTGAAAG; ϵ-globin forward: GCCTGTGGAGCAAGATGAAT; ϵ-globin reverse: GCGGGCTTGAGGTTGT; ζ-globin forward: CGGTGAAGAGCATCGACG; ζ-globin reverse: GGATACGACC-GATAGGAACTTGT.
Results
Lengthening the coculture time leads to the production of red blood cells that can enucleate
Because we have previously reported that longer periods of coculture of hESCs with immortalized fetal hepatocytes yielded burst forming units–erythroid (BFU-E) and CFU-E colonies with a more mature globin expression program,5 we hypothesized that large amounts of mature erythroid cells similar to cells produced in the fetal liver could be produced in liquid culture by seeding CD34+ cells obtained after long cocultures of hESCs and FH-B hTERT.
To test this hypothesis, we seeded our 4-step serum-free liquid culture (see “Amplification and differentiation of CD34+ cells” and Figure 1A) with sorted CD34+ cells derived from hESCs that had been cocultured for 14, 21, or 35 days with FH-B-hTERT cells. As controls, CD34+ cells purified from human fetal liver, cord blood, or peripheral blood were differentiated in the same 4-step culture system.
At the end of the fourth step of erythroid differentiation, the absolute cell number had increased 32-fold (± 11.5) in the 14-day cocultures, 129-fold (± 78) in the 21-day cocultures, and 846-fold (± 235) in the 35-day cocultures (Figure 1B), yielding in the latter condition more than 4 × 107 cells from 50 000 initial cells. The amplification of the hematopoietic cells seeded in the culture was actually much larger, because only a small fraction of the CD34+ cells obtained by coculture were hematopoietic.19 In the case of the 14-day cocultures, we previously reported than no more than 1% of the cells survived the first 3 days of culture.
Enumeration of the erythroid progenitors after Wright-Giemsa staining (Figure 1C) and flow cytometric analysis with anti-CD 235a (glycophorin A) antibodies (Figure 1D) revealed that more than 95% of the cells present at the end of the 4-step culture of the 35-day CD34+ cells were erythroid and that differentiation was relatively synchronous in these cultures. Importantly, extended coculture time yielded erythroblasts with a more developmentally mature appearance characterized by a smaller size, more eccentric nuclei, and a different color than the cells obtained after 14 days of coculture. In addition, a fraction of the cells obtained after 35 days of coculture were enucleated (Figure 1E). Enucleation rates in the 35 day cocultures were somewhat variable. They averaged 6.5% plus or minus 6.7% and ranged from 1.5% to 16%. Experiments are in progress to define the causes of this variability. Importantly, no enucleated cells could be detected in the cells derived from the 14-day coculture and only rare enucleated cells could be detected in the 21-day cocultures. Therefore, while, as previously reported, 14-day cocultures yielded erythroblasts morphologically similar to erythroid cells produced in the yolk sac, 35-day cocultures yielded erythroblasts most similar to erythrocytes produced in early fetal livers. Twenty-one-day cocultures were more heterogeneous and were probably a mixture of 14-day and 35-day cells.
As expected, enucleated cells were also obtained when control CD34+ cells from an 18-week fetal liver, cord blood, and peripheral blood were cultured in the same conditions (Figure 1E). Interestingly, the rate of enucleation seemed to increase with the developmental age of the CD34+ cells and ranged from approximately 5% to 15% for fetal liver CD34+ cells, 25% to 35% for the cord blood, and 60% to 70% for peripheral blood CD34+ cells, maybe because our enucleation conditions are optimized for adult cells. Whether erythrocytes derived from 35-day cocultures of hESCs can enucleate at a higher rate in a different set of conditions remains to be determined.
Erythrocyte size
To further characterize the erythrocytes derived from the 14- and 35-day cultures, we estimated their sizes by microscopy and compared them to control erythrocytes derived from an 18-week fetal liver. As summarized in Figure 1F, the 35-day erythrocytes were much closer in size to erythrocytes derived from fetal liver than to the 14-day cells, because the average diameters (± standard error) of the 14-day–, 35-day–, and fetal liver–derived erythrocytes were respectively 12.6 u plus or minus 0.88 u, 9.89 u plus or minus 0.21 u, and 9.07 u plus or minus 0.34 u. The diameters of the 35-day enucleated erythrocytes averaged 8.9 u plus or minus 0.32 u while the diameter of the fetal liver–derived enucleated erythrocytes averaged 8.4 u plus or minus 0.16 u. No enucleated red blood cells were detected in the 14-day cultures.
Globin expression in erythroid cells derived from 14-day cocultures
To ascertain that our culture conditions did not dramatically affect globin expression, we first compared erythroid cells produced in vitro and in vivo: fetal liver and peripheral blood–derived CD34+ cells were placed in the 4-step culture system for 24 days and globin expression levels of the cells thus produced were compared to globin expression levels in the erythrocytes that were circulating in the cord or peripheral blood at the time of harvest of the CD34+ cells.
As expected, none of the cells that were produced expressed ζ because this gene is not expressed in mature erythroid cells from the fetal liver or the peripheral blood (Figure 1G). The percentage of γ-globin expression in in vitro–produced erythrocytes also reflected the source of CD34+ cells, although, as expected,20,,,–24 it was slightly higher in vitro than in vivo (99% ± 1% vs 95% ± 2% in fetal liver CD34+-derived cells; 4% ± 2% vs 1% ± 1% in peripheral blood–derived CD34+ cells). We conclude that despite a small deregulation of the γ-globin gene, these experiments demonstrated a very good correlation between globin expression in erythrocytes produced in vitro and in vivo, and therefore that results obtained in vitro can be extrapolated to globin expression levels that would be produced in vivo.
Quantification of globin expression on hESC-derived erythroblasts at different stages of maturation revealed dramatic differences in the expression of the α-like globin genes during the 4-step liquid culture. As shown in Figure 2A,B, pro- and basophilic erythroblasts harvested after 14 days of liquid culture mainly produced ζ- and ϵ-globin, and small amounts of α- and γ-globin (α/ζ = 0.16 ± 0.05; γ/ϵ = 0.31 ± 0.01), while the polychromatophilic and orthochromatic erythroblasts that are found in the same culture 10 days later expressed large amounts of α-globin and a slightly increased ratio of γ- to ϵ-globin ((α/ζ = 3.77 ± 1.43; γ/ϵ = 0.50 ± 0.09). Thus, during the last 10 days of the culture, most ζ-globin expression was shut down and replaced by α-globin, while in parallel only a small switch from ϵ- to γ-globin occurred.
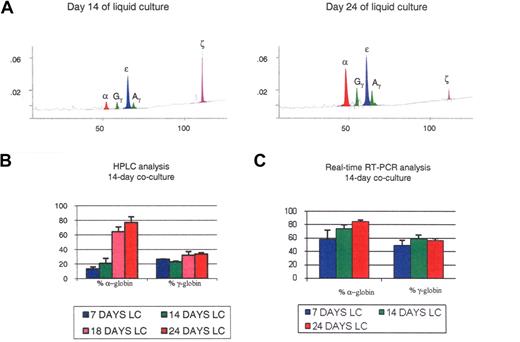
Globin expression in the 14-day cocultures. (A) HPLC chromatograms illustrating globin expression in erythroblasts obtained after 14 days (left panel) or 24 days (right panel) of liquid culture of CD34+ cells that had been obtained after coculture of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT for 2 weeks. Cells in the left panel, which were mostly pro- and basophilic erythroblasts, expressed predominantly ζ- and ϵ-globin. Cells in the right panel, which were mostly poly- and orthochromatic erythroblasts, expressed predominantly α- and ϵ-globin. (B,C) Histograms summarizing the quantification of globin expression by HPLC (B) or real-time PCR (C) in the cells described in panel A. Results demonstrated that the globin expressed in these cells was of the embryonic type and that at least part of the regulation occurred at the transcriptional level. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Error bars represent SD.
Globin expression in the 14-day cocultures. (A) HPLC chromatograms illustrating globin expression in erythroblasts obtained after 14 days (left panel) or 24 days (right panel) of liquid culture of CD34+ cells that had been obtained after coculture of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT for 2 weeks. Cells in the left panel, which were mostly pro- and basophilic erythroblasts, expressed predominantly ζ- and ϵ-globin. Cells in the right panel, which were mostly poly- and orthochromatic erythroblasts, expressed predominantly α- and ϵ-globin. (B,C) Histograms summarizing the quantification of globin expression by HPLC (B) or real-time PCR (C) in the cells described in panel A. Results demonstrated that the globin expressed in these cells was of the embryonic type and that at least part of the regulation occurred at the transcriptional level. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Error bars represent SD.
We then analyzed globin expression at the RNA level by real-time RT-PCR. At day 7 of liquid culture the α/ζ and γ/ϵ mRNA ratios were 2.04 (± 0.69) and 0.82 (± 0.28); at day 14, 3.60 (± 0.48) and 1.10 (± 0.33), and at day 24, 6.47 (± 1.90) and 1.4 (± 0.3). These results support and extend the HPLC data because they confirm the dramatic switch in the α-cluster and a much more modest switch in the β-globin cluster, and becausethey suggest that at least part of the regulation occurs at the transcriptional or posttranscriptional level (Figure 2C). The higher percentage of α-globin mRNAs relative to the protein level might be because HPLC measures globin accumulation, while mRNA levels reflect future globin production, or might indicate that some posttranscriptional regulation is occurring. Importantly, in these 14-day coculture experiments the β-globin protein was undetectable by HPLC, and only traces of β-globin mRNA could be detected by real-time PCR.
The observation of large percentages of ζ- and ϵ-globin chains, the 2 components of hemoglobin Gower I, in the pro- and basophilic erythroblasts derived from these cocultures confirmed that the erythroblasts obtained were primitive. However, the dramatic ζ- to α-globin switch that we detected during the terminal phase of the culture was unexpected and could be explained either by a maturation switch or by a lineage switch model (Figure 3A). In the first model, the globin switch would be due to the fact that cells at different stages of maturation expressed different α-like globin. In the second model, the switch would be due to sequential maturation in the culture of two types of progenitors programmed to express either ζ or α-globin. Because these cultures are relatively synchronous, the maturation switch model seemed the most likely.
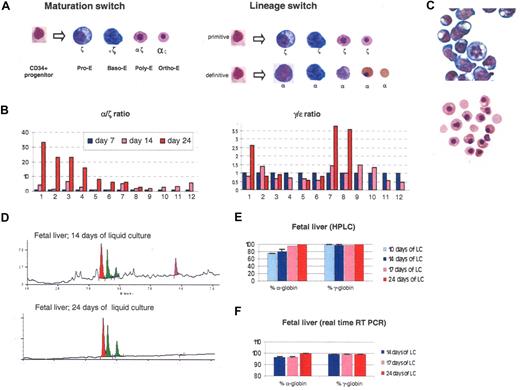
The ζ to α switch occurs during terminal erythroid maturation. (A) Two possible models to explain the switch observed in liquid culture. (B) Histograms illustrating globin expression determined by real-time PCR on 14 clonal populations obtained by liquid culture of sorted individual CD34+ cells produced in 2-week cocultures of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT. (C) Morphology of cells obtained after 14 or 24 days of liquid culture of CD34+ cells from a 20-week-old fetal liver. After 14 days, most cells are pro- or basophilic erythroblasts. After 24 days, most cells are orthochromatic or enucleated red cells. (D) Chromatograms illustrating globin expression in the cells depicted in panel C. The pro- and basophilic erythroblasts express ζ-globin in much larger amounts than the orthochromatic and enucleated red cells. (E) Histograms summarizing the quantification of the results illustrated in panel D. (F) Histograms summarizing a real-time PCR analysis of globin expression performed on the cells described in panel C. The results suggest that at least part of the regulation occurs at the transcriptional level. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Error bars represent SD.
The ζ to α switch occurs during terminal erythroid maturation. (A) Two possible models to explain the switch observed in liquid culture. (B) Histograms illustrating globin expression determined by real-time PCR on 14 clonal populations obtained by liquid culture of sorted individual CD34+ cells produced in 2-week cocultures of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT. (C) Morphology of cells obtained after 14 or 24 days of liquid culture of CD34+ cells from a 20-week-old fetal liver. After 14 days, most cells are pro- or basophilic erythroblasts. After 24 days, most cells are orthochromatic or enucleated red cells. (D) Chromatograms illustrating globin expression in the cells depicted in panel C. The pro- and basophilic erythroblasts express ζ-globin in much larger amounts than the orthochromatic and enucleated red cells. (E) Histograms summarizing the quantification of the results illustrated in panel D. (F) Histograms summarizing a real-time PCR analysis of globin expression performed on the cells described in panel C. The results suggest that at least part of the regulation occurs at the transcriptional level. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Error bars represent SD.
ζ- to α-globin switch is maturation switch.
To differentiate between these models, we cocultured hESCs with FH-B-hTERT cells for 14 days and sorted individual CD34+ cells in 96-well plates that were then cultured as described in Figure 1A. In 14 of the seeded wells, rapid proliferation of erythroid cells was visible after a few days of culture. Globin expression in these clonal mini-4–step cultures was then quantified by real-time RT-PCR at days 7, 14, and 24 (Figure 3B). The size of each colony differed, probably because progenitors with different proliferation potential had been seeded into each well. Reliable expression data could be obtained from 12 of the 14 colonies. In 4 of the colonies, expression data on day 24 of the culture could not be obtained for technical reasons. Eleven of the 12 colonies analyzed exhibited a dramatic switch from ζ- to α-globin expression. An ϵ- to γ-globin switch of much smaller amplitude could also be detected in 3 of the colonies. No colony expressed only α-globins as would be predicted if the lineage switch model was correct. These results therefore strongly support the hypothesis that a maturation switch occurs in these cells and that pro- and basophilic erythroblasts of the primitive lineage express large amounts of ζ-globin while polychromatophilic and orthochromatic erythroblasts express mostly α-globin.
Maturation switch also detectable in culture of fetal liver CD34+ cells.
To determine whether the maturation switch in the α-globin cluster also occurred in hematopoietic cells produced in vivo, we then sorted CD34+ cells from a 19-week-old human fetal liver and placed the cells in the same 4-step culture system.
Wright-Giemsa staining revealed that after 14 days in liquid culture most of the cells were pro- or basophilic erythroblasts (Figure 3C) and HPLC analysis demonstrated that ζ-globin was expressed and represented approximately 20% of the α-like globin chains (Figure 3D,E). Ten days later, the same analyses demonstrated that almost all of the cells had matured to orthochromatic and enucleated erythroblasts and that ζ-globin was no longer detectable. These results were confirmed by Qrt-PCR analyses, which showed that ζ-globin mRNAs represented approximately 5% of total α-like globin mRNAs after 2 weeks of culture but were almost undetectable after 24 days of culture (Figure 3F).
Therefore, the maturation switch that we observed on cells derived from hESCs could also be detected in a more attenuated form in CD34+ cells derived from fetal liver. No ζ-globin expression could be detected by HPLC in erythroid cells derived from peripheral blood CD34+ cells (data not shown).
Globin expression in erythroid cells derived from 21-day and 35-day cocultures.
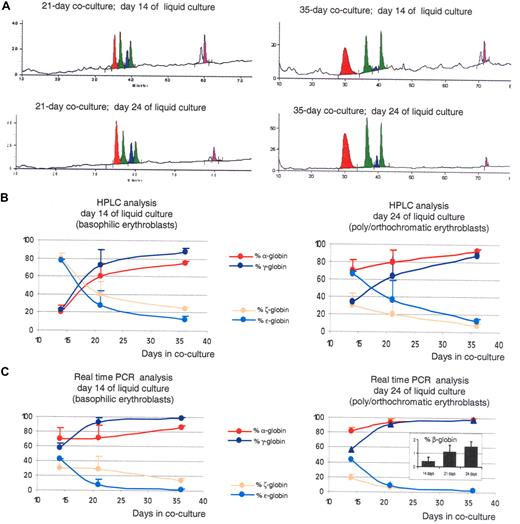
To determine whether lengthening the time in coculture alters globin expression profiles, as predicted by the morphologic analysis, we then measured globin expression levels on cells that had been cocultured with FH-B-hTERT for 21 or 35 days and then placed in liquid culture. HPLC analysis performed after 14 days of liquid culture revealed that the pro- and basophilic erythroblasts expressed mostly α- and γ-globin (α/ζ = 3.1 ± 0.23 and γ/ϵ = 7.1 ± 0.42; Figure 4A,C). Because cells derived from 14-day cocultures expressed ratios of α/ζ = 0.16 and γ/ϵ = 0.31, we conclude that extending the time in coculture has a dramatic effect on globin expression. This globin switch, which can be detected in pro- and basophilic erythroblasts, is different from the maturation switch and conforms to the lineage switch model described in Figure 3A. Cells from the 21-day cocultures exhibited intermediate levels of globin expression (Figure 4A,B).
Increasing the time of coculture leads to the production of RBCs with a more mature globin expression program. (A) HPLC chromatograms illustrating globin expression in erythroblasts obtained after 14 days (top panels) or 24 days (bottom panels) of liquid culture of CD34+ cells that had been obtained after coculture of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT for 21 (left panels) and 35 days (right panels). Cells in the top panels, which were mostly pro- and basophilic erythroblasts, expressed predominantly α- and γ-globin. Cells in the left panel, which were mostly poly- and orthochromatic erythroblasts, expressed even more α-globin because of the maturation switch. The levels of α- and γ-globins are higher in the 35-day cocultures than in the 21-day cocultures. (B) X-Y plots summarizing the quantification of the HPLC results described in Figure 2 and 4. (C) X-Y plots summarizing the results of a real-time RT PCR analysis on the cells described in Figures 2 and 4. Inset: RT-PCR determination of β-globin expression in 35-day CD34+ cells after 14, 21, or 24 days in liquid culture (% β-globin indicates β/β+γ+ϵ). Results show that increasing the length of coculture of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT cells lead to a dramatic switch in the globin produced. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Percent ζ-globin was calculated as 100 × ζ-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent ϵ-globin was calculated as 100 × ϵ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Error bars represent SD.
Increasing the time of coculture leads to the production of RBCs with a more mature globin expression program. (A) HPLC chromatograms illustrating globin expression in erythroblasts obtained after 14 days (top panels) or 24 days (bottom panels) of liquid culture of CD34+ cells that had been obtained after coculture of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT for 21 (left panels) and 35 days (right panels). Cells in the top panels, which were mostly pro- and basophilic erythroblasts, expressed predominantly α- and γ-globin. Cells in the left panel, which were mostly poly- and orthochromatic erythroblasts, expressed even more α-globin because of the maturation switch. The levels of α- and γ-globins are higher in the 35-day cocultures than in the 21-day cocultures. (B) X-Y plots summarizing the quantification of the HPLC results described in Figure 2 and 4. (C) X-Y plots summarizing the results of a real-time RT PCR analysis on the cells described in Figures 2 and 4. Inset: RT-PCR determination of β-globin expression in 35-day CD34+ cells after 14, 21, or 24 days in liquid culture (% β-globin indicates β/β+γ+ϵ). Results show that increasing the length of coculture of hESCs with FH-B-hTERT cells lead to a dramatic switch in the globin produced. Percent α-globin was calculated as 100 × α-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent γ-globin was calculated as 100 × γ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Percent ζ-globin was calculated as 100 × ζ-globin/(α-globin + ζ-globin). Percent ϵ-globin was calculated as 100 × ϵ-globin/(γ-globin + ϵ-globin). Error bars represent SD.
A similar analysis on orthochromatic erythroblasts and enucleated erythrocytes obtained 10 days later at the end of the cultures revealed α/ζ and γ/ϵ ratios equal to 12.3 (± 0.24) and to 7.1 (± 0.42), respectively (Figure 4A,B). This confirmed that these cells expressed a more mature phenotype than the cells obtained after 2 weeks of cocultures and demonstrated that the maturation switch in the α-like cluster also happens in these conditions. However, the amplitude of the maturation switch was smaller because of higher levels of expression of the α-globin gene relative to ζ-globin in the pro- and basophilic erythroblasts. No β-globin gene expression could be detected by HPLC analysis.
Real-time PCR analysis on these cells demonstrated that both globin switches occur at least in part at the transcriptional or posttranscriptional level (Figure 4C). Importantly, β-globin expression could be detected and easily quantified at the mRNA levels in the cells derived from the 35-day coculture (Figure 4C inset). While the levels of expression of the β-globin gene were low, never reaching more than 2%, these experiments demonstrated that the β-globin gene is strongly up-regulated with increasing time in coculture, because expression of this gene was virtually undetectable in the 14-day cocultures.
Discussion
In summary, we have established culture systems to produce 2 distinct types of early human erythroid cells. Fourteen-day cocultures yielded megaloblastic, nucleated red cells that are similar to cells produced in the yolk sac and that undergo a dramatic switch during late erythroid maturation, with pro- and basophilic erythroblasts expressing mostly ζ-globin, and polychromatophilic and orthochromatic erythroblasts expressing mostly α-globin. A switch of smaller amplitude between the ϵ- and γ-globin genes could also be detected in these cells. Thirty-five-day cocultures yielded cells that could enucleate and that were similar to cells produced in the early fetal liver. These cells expressed much higher α/ζ and γ/ϵ ratios at the pro- and the basophilic erythroblast stages, but nevertheless underwent a maturation switch of lesser amplitude as they matured to orthochromatic and enucleated red blood cells.
Circulation in human embryos starts at the fourth to fifth week of gestation and involves almost exclusively yolk sac–derived erythroblasts until the release of the first cells produced in the liver during the eighth week of gestation.25 Because differentiation of the primitive erythroblasts is intravascular, the degree of maturation of these cells changes over time, as pro- and basophilic erythroblasts, which predominate at week 4 to 5, progressively mature into orthochromatic erythroblasts, the major cell type at week 7 to 8.25 The first major hemoglobin switch in human involves the progressive replacement of Hb Gower I (ζ2ϵ2) by Hb Gower II (α2ϵ2) between week 4 to 5 and week 6 to 7. This switch is followed by the progressive replacement of Hb Gower II with Hb F (α2γ2) at around week 9.1,26,–28
The globin switches that we observed in vitro are strikingly similar to this sequence of events, suggesting that hESC-derived erythropoiesis in our system closely recapitulates early human erythropoiesis. We propose that the replacement of hemoglobin Gower I by Gower II during early human development is a maturation switch within the primitive lineage and that the replacement of Hb Gower II by Hb F is a lineage switch associated with a switch from primitive to definitive erythropoiesis. However, careful determination of globin expression in early human embryos will be necessary to demonstrate this point.
We propose that the cells obtained after 35 days of coculture are definitive because of their similarity to fetal liver–derived cells. They are, however, very different from red cells found in adults because they express only very low levels of β-globin.
Kingsley et al recently reported a maturation switch in the murine β-globin cluster in the primitive lineage.29 Therefore, globin switching during early development before the onset of definitive erythropoiesis is a conserved mechanism, perhaps because rapid modulation of hemoglobin composition during early development is essential in mammals and must occur before cells produced in the liver are ready to be released. Whether the function of switch from Hb Gower I to Gower II is due to differential oxygen affinity, nitric oxide transport capacity, or some other characteristics of these tetramers is unclear.
Both the α- and β-globin clusters are regulated by upstream enhancers or locus control regions (LCR), and considerable efforts have been devoted to understanding the mechanism of interaction between the enhancers and the genes. The maturation switch is compatible with several proposed models of regulation (Hu et al30 and reference therein). However, our finding that the human ζ-globin gene is expressed mostly at the basophilic stage of maturation in the primitive lineage suggests that transcriptional interferences and competition for interaction with the LCR might not be major factors in the regulation of the α-globin locus in the primitive lineage.
The mechanisms that control the timing of hemoglobin switching remain unclear. Erythroid cells of increasing developmental age can be obtained from both human and mouse ES cells by simply lengthening the time in culture after removal of the cells from self-renewal conditions, as if, once differentiation of the ES cells is initiated, an autonomous development program is set in motion. But so far, in vitro cultures can only recapitulate the first few weeks of development because only small amounts of β-globin expression can be obtained. It has been proposed that a molecular developmental clock, maybe a chromatin mark, might be located on chromosome 11 near or in the β-globin cluster.31,32 The culture systems that we have developed here might prove very useful to test this hypothesis.
Finally, the method described here has important potential applications, but a method to produce erythroid cells with an adult phenotype is needed.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Sanjeev Gupta for providing us with the FH-B-hTERT cells.
E.E.B. is supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants R01 DK56845 and P20 GM075037. C.Q. is supported by NIH grant T32 HL07556-19.
National Institutes of Health
Authorship
Contribution: C.Q. and E.N.O. helped design and perform most of the experiments. M.V. grew a lot of the cells, performed HPLC, and help troubleshoot the experiments. E.E.B. heads the laboratory and contributed to all aspects of the work. All authors contributed to either the preparation of the manuscript or the figures.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Dr Eric Bouhassira, Department of Medicine, Division of Hematology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, 1300 Morris Park Ave, Bronx, NY 10461; e-mail: bouhassi@aecom.yu.edu.
References
Author notes
C.Q. and E.N.O. contributed equally to this work.