Abstract
Background: Traditionally response to therapy in multiple myeloma (MM) is based on changes in the serum and urine monoclonal protein by immunoelectrophoresis. Immunofixation allows for detection of small amounts of monoclonal protein that cannot be quantitated on immunoelectrophoresis. Serum immunoglobulin free light chain (FLC) assay allows for detection of unbound kappa and lambda free light chain and has allowed disease measurement in patients with oligosecretory myelomas and can potentially allow detection of low levels of tumor burden, below the threshold of the standard tests. We examined this hypothesis in patients who had obtained a negative immunofixation in serum and urine following treatment of their MM.
Methods: For the purposes of the study, we included selected patients with MM who had measurable monoclonal (M) protein levels at baseline (defined as >1 gm/dL in the serum or >200 mg/24 hour in the urine or involved free light chain > 10 mg/dL) on protein electrophoresis; patients with non-secretory and oligo-secretory myeloma were excluded. We then identified patients who since 1995 had a negative immunofixation in the serum and urine, all done at the same time (within 30 days of each other). Baseline demographics and clinical characteristics; date of diagnosis, last follow up, and follow up status; serum and urine M protein levels at diagnosis; and results of serum and urine immunofixation, and serum free light chain (FLC) ratio within 30 days of the immunofixation were all collected from the existing databases.
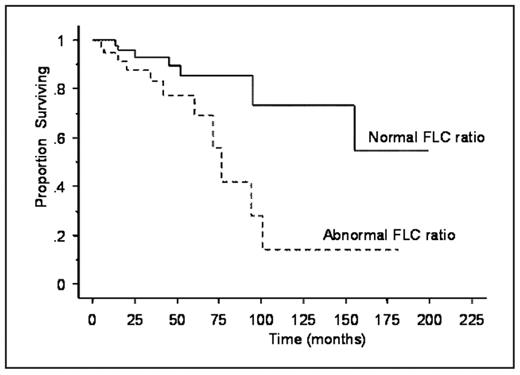
Results: Eighty-four patients met the criteria for the study, all of whom had measurable disease at baseline and subsequently achieved negative immunofixation in serum and urine. Among these, 46 patients (55%) also had a normal FLC ratio (K/L ratio; 0.26–1.65). Th median time from diagnosis to the documented immunofixation was 7.5 months (range, 1–157). The median overall survival from diagnosis among those with a normal FLC ratio along with negative immunofixation was not reached compared to 76 months for those with abnormal FLC ratio, P = 0.02. The median overall survival from the documentation of negative immunofixation was not reached for the group with normal FLC ratio compared to 46.5 months for those with an abnormal FLC, P = 0.03.
Conclusion: Attainment of a normal FLC ratio at the time of serum and urine immunofixation negative status identifies a group of patients with better outcome. The presence of an abnormal FLC ratio likely represents persistence of the clonal population that is secreting none or very small amounts of monoclonal protein. The data presented here supports the inclusion of FLC measurements as part of response criteria for MM as has been done for the definition of stringent CR in the IMWG response criteria.
Overall survival from diagnosis in patients with or with out a normal FLC ratio at the time of serum and urine immunofixation.
Overall survival from diagnosis in patients with or with out a normal FLC ratio at the time of serum and urine immunofixation.
Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal