Abstract
Cytomegalovirus (CMV), an important cause of mortality after allogeneic HSCT in the past, is now controllable with sensitive monitoring techniques and drugs such as valganciclovir and foscarnet. However, some groups still report that CMV seropositivity influences the outcome adversely. The outcome of 130 reduced-intensity allograft recipients treated uniformly (2001–7) was studied to determine the effect of CMV.
Table 1: Patient characteristics
| Age (y) . | 19–71 (median 55) . | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 55% | |
| Refractory disease | 57% | |
| ECOG performance status | 0 | 34% |
| 1 | 48% | |
| 2 | 14% | |
| 3 | 4% | |
| Diagnosis | Lymphoma | 42% |
| Leukemia | 36% | |
| Myeloma | 22% | |
| Donor | Matched sibling | 49% |
| Mismatched sibling | 2% | |
| Matched unrelated | 33% | |
| Mismatched unrelated | 15% | |
| Donor age (y) | 21–71 (median 44) | |
| Male donor | 65% | |
| CMV IgG-seropositive | Patient | 59% |
| Donor | 32% | |
| CMV serostatus | P+D+ | 21% |
| P+D− | 38% | |
| P−D+ | 11% | |
| P−D− | 30% | |
| Prior autograft | 45% | |
| Age (y) . | 19–71 (median 55) . | |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 55% | |
| Refractory disease | 57% | |
| ECOG performance status | 0 | 34% |
| 1 | 48% | |
| 2 | 14% | |
| 3 | 4% | |
| Diagnosis | Lymphoma | 42% |
| Leukemia | 36% | |
| Myeloma | 22% | |
| Donor | Matched sibling | 49% |
| Mismatched sibling | 2% | |
| Matched unrelated | 33% | |
| Mismatched unrelated | 15% | |
| Donor age (y) | 21–71 (median 44) | |
| Male donor | 65% | |
| CMV IgG-seropositive | Patient | 59% |
| Donor | 32% | |
| CMV serostatus | P+D+ | 21% |
| P+D− | 38% | |
| P−D+ | 11% | |
| P−D− | 30% | |
| Prior autograft | 45% | |
Table 2: CMV prophylaxis, monitoring and therapy employed
| Prophylaxis (patient and/or donor CMV-seropositive): |
| - Valacyclovir 500 mg TID from the start of the conditioning regimen |
| ○ Tapered to BID after 100–120 days and to QD at 5–6 months |
| ○ Stopped one month after stopping all immunosuppression |
| - No regular IVIG infusion |
| Monitoring (all patients): |
| - CMV quantitative PCR (previously antigenemia) at each visit |
| ○ Once a week for at least 2 months |
| ○ Subsequently, every 2–4 weeks |
| Therapy: production |
| - Viremia |
| ○ Valganciclovir 900 mg BID (previously ganciclovir 5 mg/kg BID IV) for 1 week (1 more week if viremia persistent) and then 900 mg QD (ganciclovir 5 mg/kg QD IV) for 2 weeks; adjusted for kidney function |
| ○ Foscarnet 100 mg/kg for persistent viremia or ANC <1 × 109/L on G-CSF |
| ○ Combination valganciclovir/ganciclovir and foscarnet for resistant viremia |
| - Organ involvement (disease) by the manufacturer. |
| ○ As above with added IVIG 500 mg/kg once a week |
| - Precautions while on valganciclovir/ganciclovir |
| ○ Blood counts twice a week if within the normal range |
| ○ Blood counts daily if absolute neutrophil count <2 × 109/L |
| ○ G-CSF or pegfilgrastim if absolute neutrophil count <1.5 × 10 9/L |
| ○ Stop drug if absolute neutrophil count <1.5 × 109/L despite growth factor |
| ○ Broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone prophylaxis if ANC <1.5 × 10 9/L |
| ○ Prophylaxis with mold-active triazole (itraconazole in the past; voriconazole or reliable test for risk of viremia after alloHSCT, but patients posaconazole now) |
| - CMV hyperimmune globulin not used under any circumstances |
| Transfusions: |
| - Leukocyte-filtered blood products (all patients) |
| - CMV-seronegative blood products (both patient and donor CMV-seronegative) |
| Prophylaxis (patient and/or donor CMV-seropositive): |
| - Valacyclovir 500 mg TID from the start of the conditioning regimen |
| ○ Tapered to BID after 100–120 days and to QD at 5–6 months |
| ○ Stopped one month after stopping all immunosuppression |
| - No regular IVIG infusion |
| Monitoring (all patients): |
| - CMV quantitative PCR (previously antigenemia) at each visit |
| ○ Once a week for at least 2 months |
| ○ Subsequently, every 2–4 weeks |
| Therapy: production |
| - Viremia |
| ○ Valganciclovir 900 mg BID (previously ganciclovir 5 mg/kg BID IV) for 1 week (1 more week if viremia persistent) and then 900 mg QD (ganciclovir 5 mg/kg QD IV) for 2 weeks; adjusted for kidney function |
| ○ Foscarnet 100 mg/kg for persistent viremia or ANC <1 × 109/L on G-CSF |
| ○ Combination valganciclovir/ganciclovir and foscarnet for resistant viremia |
| - Organ involvement (disease) by the manufacturer. |
| ○ As above with added IVIG 500 mg/kg once a week |
| - Precautions while on valganciclovir/ganciclovir |
| ○ Blood counts twice a week if within the normal range |
| ○ Blood counts daily if absolute neutrophil count <2 × 109/L |
| ○ G-CSF or pegfilgrastim if absolute neutrophil count <1.5 × 10 9/L |
| ○ Stop drug if absolute neutrophil count <1.5 × 109/L despite growth factor |
| ○ Broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone prophylaxis if ANC <1.5 × 10 9/L |
| ○ Prophylaxis with mold-active triazole (itraconazole in the past; voriconazole or reliable test for risk of viremia after alloHSCT, but patients posaconazole now) |
| - CMV hyperimmune globulin not used under any circumstances |
| Transfusions: |
| - Leukocyte-filtered blood products (all patients) |
| - CMV-seronegative blood products (both patient and donor CMV-seronegative) |
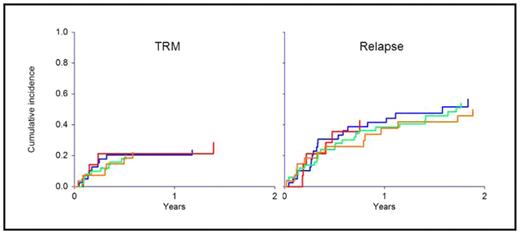
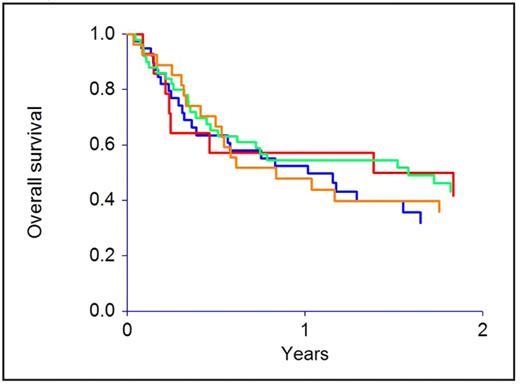
CMV reactivation was seen in 40 patients, and was influenced by serostatus (12 P+D+, 26 P+D−, 1 P−D+, 1 P−D−; P<0.0001). Patient or donor CMV status did not affect transplant-related mortality, relapse, or survival, and the outcome of the P+D+, P+D−, P−D+ and P−D− groups was identical. Not a single death was attributable to CMV infection or adverse effects of anti-viral therapy.
The effect of patient and donor cytomegalovirus serostatus on TRM (P=0.58) and relapse (P=0.97)
The effect of patient and donor cytomegalovirus serostatus on TRM (P=0.58) and relapse (P=0.97)
The effect of patient and donor cytomegalovirus serostatus on overall survival (P=0.67)
The effect of patient and donor cytomegalovirus serostatus on overall survival (P=0.67)
Outcome was influenced by factors described previously in a subgroup of these patients (Mehta et al. Does younger donor age affect the outcome of reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for hematologic malignancies beneficially?
Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal