Abstract
Introduction/Methods: A key component of improving the success rate of allogeneic HSCT for AML in CR1 is to reduce non-relapse mortality (NRM), which, if excessive, will deny the benefit of the graft-versus-leukemia effect. UD HSCT has traditionally been associated with high NRM rates. We reported previously on the significant reduction of NRM using the conditioning regimen of fludarabine 40mg/m2, IV busulfan 130 mg/m2 for 4 days and thymoglobulin. Here we analyze the outcomes of all patients (n=37) with AML in CR1 treated with this regimen and UD HSCT in our institution from January 2002 to December 2007. High-resolution allele level HLA typing was performed for all donorrecipient pairs for HLA-A, -B, -C, DRB1 and DQB1; up to one mismatch was allowed (9/10). Median follow up is 30 months (range, 9–72).
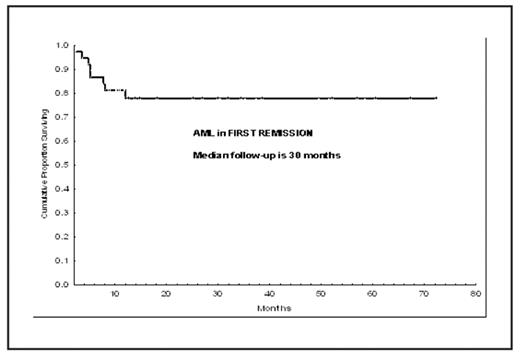
Results: Median age was 48 years (range, 13–68); 30% (n=11) were older than 54 years and 51% (n=19) were male. Eleven patients (30%) had secondary AML. Prognostic cytogenetics classification was poor and intermediate in 53% and 47% of the cases, respectively. Stem cell source was bone marrow (BM) in 68% (n=25) and peripheral blood (PB) in 32% (n=12). Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) prophylaxis was tacrolimus and mini-methotrexate with and without pentostatin (1 or 1.5 mg/m2 on days 8, 15, 22 and 30) in 46% (n=17) and 54% of the cases (n=20), respectively. Donor-recipient HLA match was 9/10 and 10/10 in 14% and 86% of the cases. Median infused total nucleated and CD34+ cells was 3.72 x 108 (range, 0.57 – 11.78) and 3.77 x 106 (range, 0.45 – 12.4), respectively. Median time to neutrophil and platelet engraftment was 12 days (range, 8–18) and 14 days (range, 8–101), respectively. All but one patient engrafted. Grade II–IV acute (a) GVHD rate was 13% (n=2) and 50% (n=10) for patients that received and not received pentostatin-based prophylaxis. Grade III–IV aGVHD rate was 0% versus 15% (n=3) for patients receiving and not receiving pentostatin. Chronic GVHD was diagnosed in 55% (n=18) of all patients (extensive in 10). 100-day and 3-year NRM rate was 11% (n=4) and 20% (n=4), respectively, and was due to engraftment failure (n=1) and aGVHD (n=3). Eight patients (22%) have relapsed, and 8 (22%) have died (4 of relapse, and 4 of NRM causes). Relapse rate was 18% (3/17) and 25% (5/20) for patients that received and not received pentostatin as part of GVHD prophylaxis. Actuarial 3-year event-free and overall survival (figure) is 68% and 78%, respectively. Actuarial 3-year overall survival for patients receiving BM and PB is 80% and 75%, respectively.
Conclusion: Long-term disease control can be achieved in a significant fraction of high-risk AML patients undergoing UD transplants as described in this abstract. Use of pentostatin in this context deserves further prospective evaluation.
Disclosures: No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Corresponding author

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal