Abstract
Abstract 2496
Poster Board II-473
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) have been used to treat hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia for over 20 years. Statins competitively inhibit HMG-CoA reductase thereby blocking the synthesis of mevalonate. They directly inhibit synthesis of steroid hormones and cholesterol but also indirectly inhibit prenylation and ubiqitination. As all currently marketed statins are lipophillic, with the exception of Pravachol (pravastatin), several therapeutic trials have attempted to exploit these indirect actions to treat both neoplastic (glioblastoma, anaplastic astrocytoma) and degenerative (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's) neurologic disease. We studied the impact of incidentally prescribed statins on high-risk patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B cell lymphoma (PCNSL).
We used an IRB-approved clinicopathologic database, derived from comprehensive tumor registry data at the Massachusetts General Hospital, to identify all patients diagnosed with primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL) between 1991 and 2007 (n=118). We excluded pediatric patients, patients who did not receive curative treatment and patients who failed to achieve a CR with initial therapy. Automated analysis of billing and medication administration records was used to identify the administration of statins to these patients. We compared the outcome of patients who were receiving statins to controls with PCNSL who did not receive statins. We excluded patients who did not receive statins within the time interval from 6 months prior to 2 years after their PCNSL diagnosis. As only a single statin pt was less than 50 we excluded all pts below this age from the cases and controls. All patients received high dose MTX based therapy. Overall survival (OS) was calculated from the date of first methotrexate.
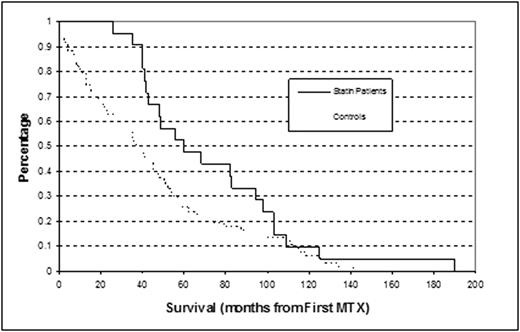
Median age of statin patients was 66 yrs (range 52 – 76); median age of controls was 66 years (range 50 - 86). Nine patients were on atorvastatin, 9 were on simvastatin, 1 each were on pravastatin, rosuvastatin and fluvastatin. At a median follow-up of 47.5 months, concurrent statin therapy was associated with improved OS (62% vs. 37%)(p=0.04 Log-rank test). The median OS for all statin patients > 50 years old (n=21) was 60 months versus 37 months for all other patients > 50 years old (n=67) (p=<0.005 t-test two tailed).
Concurrent prescription of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors is associated with improved outcome in patients with high risk PCNSL compared to controls. Prospective controlled trials will be required to validate this observation.
Hochberg:Amgen: Speakers Bureau; Biogen-Idec: Speakers Bureau; Genentech: Speakers Bureau; Enzon: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal