Abstract
Abstract 4931
Cellular therapy using dendritic cells (DCs) is emerging as the one of useful immunotherapeutic modality in multiple myeloma (MM). In order to generate potent functional DCs, alternative approaches for using appropriate and effective tumor antigens, such as myeloma cell lysates, myeloma apoptotic bodies, DC-myeloma cell hybrids or DC-transfected with myeloma-derived RNA, in steady of idiotype protein having with weak antigenicity are tried in MM. However, it is laborious work to obtain sufficient autologous tumor cells as a source of tumor antigen in the clinical setting. We investigated the feasibility of immunotherapy in patients with MM using myeloma-specific CTLs, which were generated in vitro by alpha-type 1-polarized DCs (αDC1s) pulsed with UVB-irradiated allogeneic myeloma cell line, ARH77 cells.
Material and
Peripheral blood (PB) was collected from MM patients (IgG, Ü-type) or normal healthy donors with HLA-A0201+ with informed consent according to the protocol approved by the institutional ethical committee of the Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital. Phenotypic analysis of aDC1s was performed using a FACS Aria cell sorter. Tumor antigen uptakes (CD83+/PKH67+), allogeneic mixed lymphocyte reaction (MLR) and induction of myeloma-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) were analyzed.
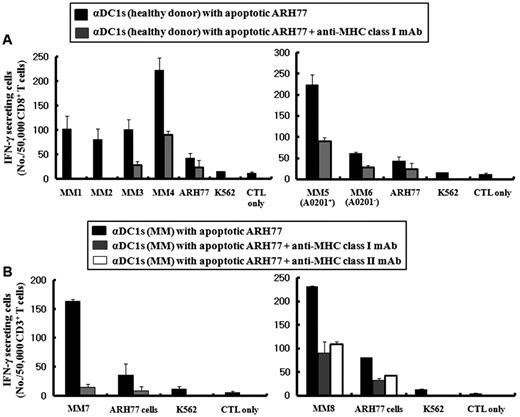
αDC1s were significantly increased the expression of several molecules without differences by loading tumor antigens. αDC1s showed high production of IL-12 during maturation and after subsequent stimulation of CD40L, but were not significantly affected by loading tumor antigens. Myeloma-specific CTLs against autologous myeloma cells from MM patients were induced by αDC1s pulsed with allogeneic apoptotic ARH77 cells. Autologous CTLs generated by pulsed αDC1s displayed a larger number of IFN-g secreting cells against autologous myeloma cells as a target cell for ELISPOT assay. Pre-incubation of the target cells with an anti-MHC class I or II mAb inhibited the IFN-g release, indicating MHC class molecule-dependent cytotoxicity (figure)
We suggested that autologous DCs pulsed with allogeneic myeloma cell line could generate potent myeloma-specific CTLs against autologous myeloma cells and could be practicable method for approaching cellular immunotherapy in MM.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal