Abstract
The serine/threonine Pim kinases are up-regulated in specific hematologic neoplasms, and play an important role in key signal transduction pathways, including those regulated by MYC, MYCN, FLT3-ITD, BCR-ABL, HOXA9, and EWS fusions. We demonstrate that SMI-4a, a novel benzylidene-thiazolidine-2, 4-dione small molecule inhibitor of the Pim kinases, kills a wide range of both myeloid and lymphoid cell lines with precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (pre–T-LBL/T-ALL) being highly sensitive. Incubation of pre–T-LBL cells with SMI-4a induced G1 phase cell-cycle arrest secondary to a dose-dependent induction of p27Kip1, apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway, and inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin C1 (mTORC1) pathway based on decreases in phospho-p70 S6K and phospho-4E-BP1, 2 substrates of this enzyme. In addition, treatment of these cells with SMI-4a was found to induce phosphorylation of extracellular signal-related kinase1/2 (ERK1/2), and the combination of SMI-4a and a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) inhibitor was highly synergistic in killing pre–T-LBL cells. In immunodeficient mice carrying subcutaneous pre–T-LBL tumors, treatment twice daily with SMI-4a caused a significant delay in the tumor growth without any change in the weight, blood counts, or chemistries. Our data suggest that inhibition of the Pim protein kinases may be developed as a therapeutic strategy for the treatment of pre–T-LBL.
Introduction
The serine/threonine Pim protein kinase is overexpressed in multiple hematopoietic tumors, with an approximately 3-fold increase in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma,1,2 and many primary human myeloid leukemic samples.3 The level of Pim mRNA correlated with the doubling time of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Likewise, in mantle cell lymphoma the level of Pim protein kinase expression predicted poor patient outcome.4 Pim protein kinase is targeted by aberrant hypermutation in 50% of the cases5 of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas and mutations are detected in primary central nervous system lymphomas6 and AIDS-associated non-Hodgkin lymphoma.6
Murine models point to a role for Pim protein kinases in enhancing the transforming activity of several transcription factors known to be drivers of hematopoietic malignancies. For example, the Pim1 and Pim2 genes were originally cloned as a proviral insertion in murine lymphomas7 that markedly enhanced both the incidence and speed of Myc-driven lymphomagenesis.8 When the Eμ–Pim1 transgene alone is overexpressed in mice, they exhibit a low-level (10%) occurrence of T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma/leukemia.9 Conversely, Eμ–N-myc or Eμ–L-myc transgenic mice develop T-cell or B-cell lymphomas, respectively, and the rate of development of these tumors is greatly enhanced by breeding with Eμ-Pim1 transgenic mice.10 Using a retroviral tagging model in mice transgenic for the E2A-PBX1 fusion oncogenes, the Pim1 locus was targeted in 48% of the T-cell lymphomas and the occurrence of these tumors was greatly accelerated.11 In hematologic malignancies, Pim2 is also identified as a translocation partner of BCL6 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.12 These studies establish that the Pim protein kinases exhibit a dose- and context-dependent transforming activity when paired with other transforming genes and are associated with the development of T-cell leukemia and lymphoma.
Cell culture models also predict an important role for Pim protein kinase in modulating the growth of human leukemias. Constitutively activating internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutations in the tyrosine kinase Fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 (Flt3) is the most commonly mutated tyrosine kinase in human myeloid leukemia.13 Flt3 controls the levels of Pim in myeloid leukemic cells, and the inhibition of Pim1 activity enhances the cytotoxicity of Flt3 inhibitors.14,15 In normal cells, Pim1 expression is a determining factor in the ability of cells to respond to growth factors. In early B-lymphoid progenitors, Pim plays a role in growth mediated by interleukin 7 (IL-7) and c-kit ligand.16 In addition, the Pim1 gene compensates for IL-7 and common γ-chain functions in β-selection in CD4/8 double-negative T cells.17 In cells constitutively expressing other protein tyrosine kinases found in human leukemias (TEL/JAK2, BCR/ABL, and H4/PDGFβR), the levels of Pim1 and Pim2 protein kinases are elevated and knockdown of the Pim protein kinase gene inhibits the growth of these leukemias.18 Thus, the Pim protein kinases have a regulatory role both in normal hematopoietic cell proliferation and the survival of diverse types of hematopoietic malignancies, suggesting that Pim may be an important therapeutic target.
We have developed novel Pim protein kinase small molecule inhibitors, including SMI-4a and SMI-16a, based on the benzylidene-thiazolidine-2, 4-dione chemotype.19 These molecules inhibit Pim kinase activity both in vitro and in vivo in a breast cancer model, and block the ability of Pim to phosphorylate a well-known substrate, the BAD BH3 protein.20 In the current study, we have extended these observations to examine the ability of SMI-4a to kill leukemic cells both in tissue culture and in mice based on the pharmacokinetic properties of this molecule.
Methods
Cell lines
In this study, we have identified cell lines based on the World Health Organization classification instead of the traditional French-American-British. Likewise, murine hematologic malignancies are classified according to the Bethesda proposals, which also follow the World Health Organization classification. The origin of the cell lines used are as follows: (1) ALL-SIL, CEM, DU528, HPB-ALL, HSB2, KOP-TK1, Jurkat, MOLT16, SUPT1, and TALL1 are human pre–T-LBL cell lines; (2) Nalm6 is a human precursor B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (pre-B-LBL) cell line; (3) HEL, HL60, K562, Kasumi1, MV4-11, NB4, THP1, and U937 are human myeloid leukemia cell lines; (4) 6812/2, 6645/4, 6605/4, and St4113 are pre–T-LBL established from transgenic mice that overexpressed both human SCL/TAL1 and LMO1; (5) 12/1 was derived from a pre–T-LBL transgenic mouse that overexpressed the human LMO1 gene; and (6) F4-6 is a murine erythroleukemic cell line that was transformed by the Friend erythroleukemia virus (for detailed information see supplemental Table 1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article). All human leukemic cell lines were cultured at 37°C under 5% CO2 in RPMI1640 supplemented with 2mM Glutamax and 10% fetal calf serum (Mediatech) and supplemented with or without 1mM sodium pyruvate. Murine cell lines were grown in Iscove modified Dulbecco medium supplemented with 2mM Glutamax and 10% fetal calf serum (Invitrogen).
Cell-cycle analysis
6812/2 cells were incubated for 24 hours and Jurkat cells, for 48 hours with SMI-4a (10μM) or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in serum-free medium. After incubation, cells were harvested, washed once in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), fixed in cold 70% ethanol for 45 minutes, stained with propidium iodide solution that contains RNaseA for 30 minutes, and analyzed by flow cytometry.
Apoptosis analysis
After 6 hours of incubation with 5μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium, Jurkat and 6812/2 cells were washed with ice-cold PBS and stained with annexin V–fluorescein isothiocyanate and propidium iodide (PI; Trevigen) to measure the number of apoptotic cells. To measure changes in the activation of Bax proteins, 6812/2 was incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 4 hours. Cells were then harvested and cytoplasmic proteins were separated using a buffer containing 500mM sucrose, 50mM NaCl, 10mM N-2-hydroxyethylpiperazine-N′-2-ethanesulfonic acid, 1mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and 0.21% Triton X-100. Western blotting was carried out using anti-Bax antibody (BD Biosciences) as described in “Western blot analysis.” K562 myeloid leukemic cells were washed with PBS, and then stained with anti-Bak (Calbiochem) and Bax antibody (BD Biosciences), and the level of antibody binding was measured by flourescent-activated cell sorting analysis. For morphologic analysis, 6812/2 and Jurkat cells were fixed on slides using a Shandon Cytospin (Thermo) after a 24-hour incubation with 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium. The fixed cells were then stained for 5 minutes with May-Grünwald solution at room temperature washed with PBS, and stained with Giemsa solution at room temperature for 30 minutes (Sigma). Poly–adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage was examined in 4 × 107 6812/2 and Jurkat cells after incubation with 10μM SMI-4a or DMSO in serum-free medium for 4, 8, 16, and 24 hours. Jurkat cells were incubated with SMI-4a at various concentrations for 8 hours. The caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK (40μM) was added along with SMI-4a (0, 30μM) during the same time period. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to PARP and caspases-3 and -9. Jurkat cells were transfected with either Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL expression vectors and permanent transfectants were established. These transfectants were incubated with 30μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 24 hours, and then viable cells were identified by trypan blue exclusion. The experiment was repeated in triplicate.
Western blot analysis
Cells were harvested, washed with PBS, and resuspended in lysis buffer (20mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane–HCl, pH 7.5, containing 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS], 50mM NaCl, 1mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 1mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 10mM sodium fluoride, and 1mM sodium orthovanadate). Cell samples were then agitated at 4°C for 1 hour followed by centrifugation for 15 minutes. Supernatants were then loaded on SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and the separated proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. Membranes were routinely blocked in 5% nonfat milk in PBS with 0.1% Tween-20 for an hour with agitation and washed, and primary antibodies including p27Kip1, phospho-AKT (Ser473), 4E-BP1, phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr37/46), p70 S6K, phospho-p70 S6K (Thr389), extracellular signal-related kinase1/2 (ERK1/2), phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), MYC, caspase-9, caspase-3 (Cell Signaling), and PARP (BD Biosciences) were added (1:500-1000 dilution in 5% bovine serum albumin in PBS buffer). Membranes were incubated overnight at 4°C with agitation, washed, and then incubated with horseradish peroxidase–conjugated secondary antibodies (1:5000 dilution in 5% bovine serum albumin in PBS with 0.1% Tween-20) for 3 hours at room temperature. Proteins were detected using the Enhanced Chemiluminescence Western Blotting Detection Reagent (GE Healthcare). The x-ray film was scanned at 400 dpi and densitometric analysis was performed using National Institutes of Health ImageJ software to quantify the expression of protein.
Mouse models
The mouse triple knockout (TKO) of the Pim1, 2, and 3 genes was generated by Mikkers et al21 and was a kind gift of Drs Paul B. Rothman, University of Iowa, and Anton Berns, The Netherlands Cancer Institute.
To grow subcutaneous tumors, the 6812/2 murine pre–T-LBL cells were washed with PBS 3×, resuspended, and adjusted to 2 × 106 cells/50 μL in PBS. Matrigel (BD Biosciences) was then added in equal amounts and the cell suspension injected into the dorsal flank of 18 Nu/nu nude mice. All mice were randomly assigned to vehicle only (65% DMSO, 30% PEG-400, 5% Tween-80) or 60 mg/kg SMI-4a once daily (QD) or twice daily treatments. The oral gavage was begun on day 3, and administered 5 of 7 days each week for 21 days. The growth of the subcutaneous tumors was measured twice each week and their body weight was determined on days 0, 7, 14, and 21. On day 24, 60 hours after the final gavage, all 18 mice were killed, tumor was removed, and drug concentrations were determined. Tumor volume was calculated using the equation (L × W2)/2. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Medical University of South Carolina approved the animal experiments.
Additional information can be found in supplemental Methods.
Results
The effect of SMI-4a on leukemic growth in vitro
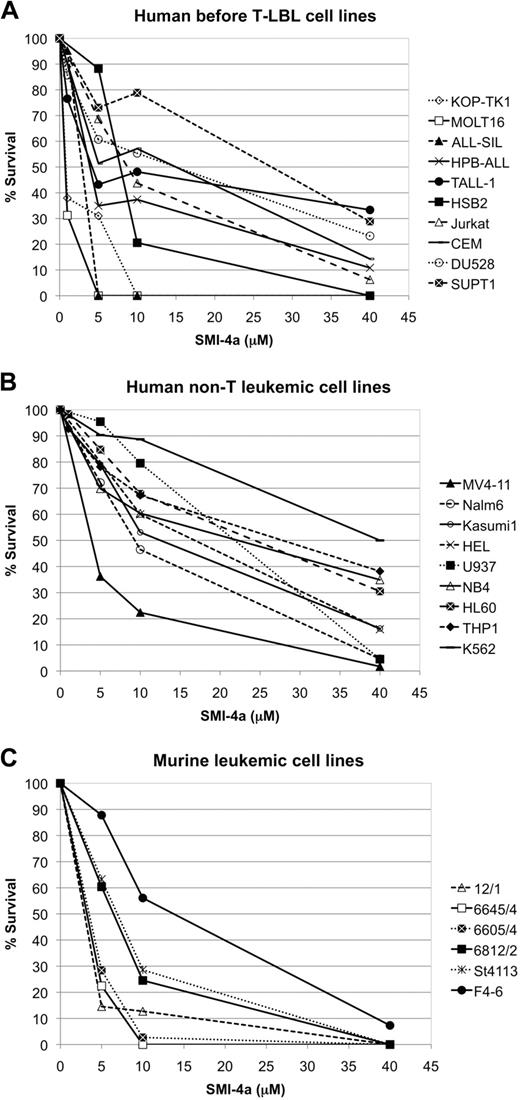
We investigated the ability of varied doses of the Pim kinase inhibitor SMI-4a to block the growth of leukemic cells. Preliminary results demonstrated that this Pim1 and Pim2 inhibitor was more active than SMI-16a, another dual inhibitor, and thus this small molecule was chosen as the focus of these experiments. Twenty-five leukemic cell lines, including human and murine pre–T-LBL cells, myeloid leukemia cells expressing BCR/ABL, PML/RARA, AML/ETO, and mutant FLT3, and human pre-B-LBL cells were killed to various degrees by this agent (Figure 1A-C) and the 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) for each cell line is shown in Table 1. These data demonstrate that pre–T-LBL cell lines are significantly more sensitive to SMI-4a than myeloid leukemic cell lines and at each dose tested the average kill rate was 21% higher for pre–T-LBL cell lines than myeloid leukemia cell lines (P < .001, supplemental Figure 1). The K562 chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line harboring the BCR-ABL fusion and the THP-1 human monocytic leukemia cell line were the least sensitive cells to this agent, although in 24 hours a significant percentage was killed. Among the myeloid cell lines tested, MV4-11, which carries both MLL-AF4 and FLT3-ITD, was the most sensitive. Murine pre–T-LBL cell lines that overexpress both SCL/TAL1 and LMO1 or LMO1 alone showed similar sensitivity to human pre–T-LBL cell lines (Figure 1A,C).
The sensitivity of leukemic cell lines to Pim kinase inhibitor SMI-4a. Human and mouse leukemic cell lines were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SMI-4a for 24 hours in serum-free medium and then viable cells were quantitated by trypan blue exclusion. (A) Human pre–T-LBL cell lines. (B) Human non-T leukemic cell lines. All cell lines except for Nalm 6 pre-B-LBL were derived from a myeloid leukemia. (C) The murine leukemic cell lines tested were established from pre–T-LBL (12/1. 6605/4, 6645/4, 6812/1, St4113) and erythroleukemia (F4-6).
The sensitivity of leukemic cell lines to Pim kinase inhibitor SMI-4a. Human and mouse leukemic cell lines were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SMI-4a for 24 hours in serum-free medium and then viable cells were quantitated by trypan blue exclusion. (A) Human pre–T-LBL cell lines. (B) Human non-T leukemic cell lines. All cell lines except for Nalm 6 pre-B-LBL were derived from a myeloid leukemia. (C) The murine leukemic cell lines tested were established from pre–T-LBL (12/1. 6605/4, 6645/4, 6812/1, St4113) and erythroleukemia (F4-6).
The IC50 was calculated for each of the cell lines from the data presented in Figure 1 and is shown in micromoles
| Line . | IC50, μM . |
|---|---|
| Human pre T-LBL cell lines | |
| KOP-TK1 | 0.83 |
| MOLT16 | 0.83 |
| ALL-SIL | 2.78 |
| HPB-ALL | 3.89 |
| TALL-1 | 4.17 |
| HSB2 | 7.78 |
| Jurkat | 8.89 |
| CEM | 15.0 |
| DU528 | 15.0 |
| SUPT11 | 27.5 |
| Human non-T leukemic cell lines | |
| MV4-11 | 3.89 |
| Nalm6 | 9.17 |
| Kasumi1 | 12.8 |
| HEL | 16.9 |
| U937 | 21.4 |
| NB4 | 22.2 |
| HL60 | 24.4 |
| THP1 | 28.1 |
| K562 | 39.7 |
| Murine leukemic cell lines | |
| 12/1 | 3.06 |
| 6645/4 | 3.38 |
| 6605/4 | 3.61 |
| 6812/2 | 6.67 |
| St4113 | 6.67 |
| F4-6 | 14.4 |
| Line . | IC50, μM . |
|---|---|
| Human pre T-LBL cell lines | |
| KOP-TK1 | 0.83 |
| MOLT16 | 0.83 |
| ALL-SIL | 2.78 |
| HPB-ALL | 3.89 |
| TALL-1 | 4.17 |
| HSB2 | 7.78 |
| Jurkat | 8.89 |
| CEM | 15.0 |
| DU528 | 15.0 |
| SUPT11 | 27.5 |
| Human non-T leukemic cell lines | |
| MV4-11 | 3.89 |
| Nalm6 | 9.17 |
| Kasumi1 | 12.8 |
| HEL | 16.9 |
| U937 | 21.4 |
| NB4 | 22.2 |
| HL60 | 24.4 |
| THP1 | 28.1 |
| K562 | 39.7 |
| Murine leukemic cell lines | |
| 12/1 | 3.06 |
| 6645/4 | 3.38 |
| 6605/4 | 3.61 |
| 6812/2 | 6.67 |
| St4113 | 6.67 |
| F4-6 | 14.4 |
IC50 indicates 50% inhibitory concentration; and pre-T-LBL, precursor T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma.
SMI-4a treatment of leukemic cells induces cell-cycle arrest
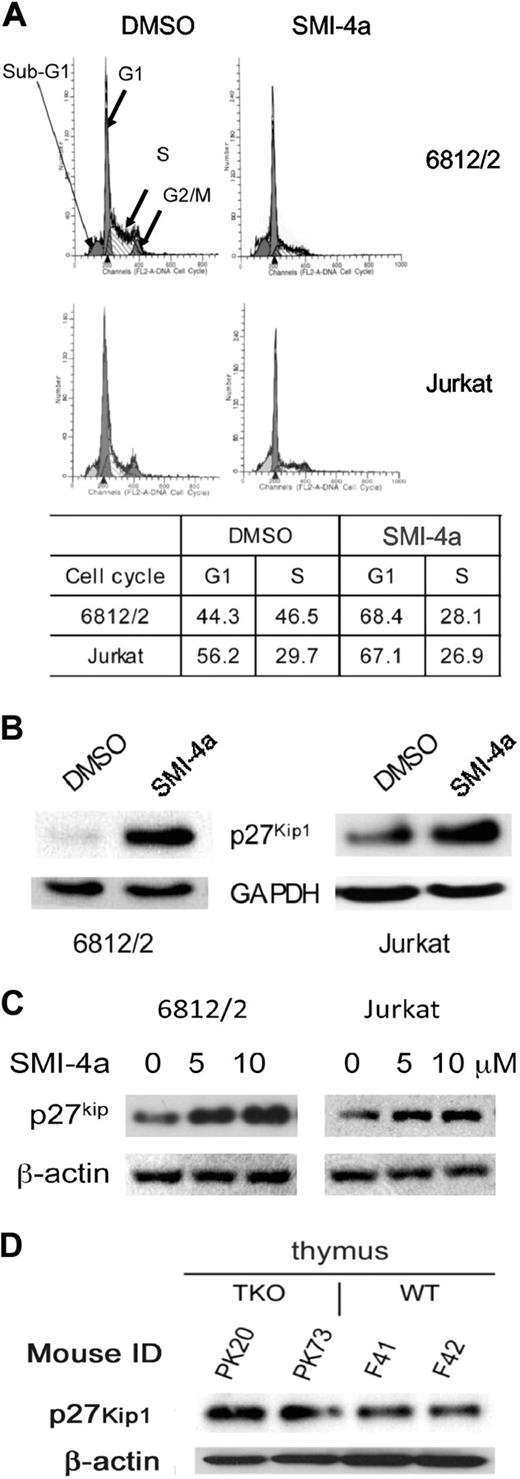
To understand the mechanism by which SMI-4a inhibits leukemic cell growth, we first investigated the ability of this agent to regulate the cell cycle. Because the pre–T-LBL cells were the most sensitive to this agent, they were the focus of these experiments. To analyze the effects of this agent on the cell cycle, the murine cell line 6812/2 that overexpresses human SCL/TAL1 and LMO1, and the human Jurkat cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a for 24 to 48 hours. Treatment with SMI-4a increased the population of cells in the G1 phase from 44.3% to 68.4% and from 56.2% to 67.1% in 6812/2 and Jurkat, respectively (Figure 2A). S-phase cells were decreased in 6812/2, whereas only small changes were seen in Jurkat cells consistent with the lesser G1 block. Because Pim has been shown to regulate the cell cycle by modulating the activity of p27Kip1,22 we evaluated the levels of p27Kip1 in both 6812/2 and Jurkat after incubation with SMI-4a (10μM) for 24 hours (Figure 2B). Our results demonstrate a 5.9- and 1.8-fold increase in p27Kip1 levels in 6812/2 and Jurkat, respectively. Because p27Kip1 is known to inhibit Cdk2 and block cells in G1/S, this result is consistent with the effects of SMI-4a on the cell cycle. When 6812/2 and Jurkat cells were treated with SMI-4a for 24 hours, the induction level of p27Kip1 was found to be dose dependent (Figure 2C). To document that the levels of p27Kip1 were regulated by the Pim protein kinases, we investigated the level of p27Kip1 in the thymus of two 3-month-old Pim1/2/3 TKO mice21 and age-matched wild type (WT)–FVB controls. In the TKO mice, we found an average 1.8-fold increase (Figure 2D) in the level of p27Kip1, suggesting that the absence of Pim activity increases the level of p27Kip1 protein.
SMI-4a inhibition of Pim protein kinase induces cell-cycle arrest in pre–T-LBL. (A) 6812/2 cells were incubated for 24 hours and Jurkat cells for 48 hours with SMI-4a (10μM) or DMSO in serum-free medium. Propidium iodide staining of these cells was followed by cell-cycle quantification performed using flow cytometric analysis. (B) The effect of 24 hours of treatment with SMI-4a (10μM). After treatment of 6812/2 and Jurkat, the cellular levels of p27Kip1 were measured by Western blotting using antibodies to this protein and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a loading control. (C) 6812/2 and Jurkat cells were incubated with increasing doses of SMI-4a for 24 hours in serum-free medium, and the level of p27Kip1 was measured by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using β-actin antibodies as a protein loading control. (D) The thymus was harvested from 2 Pim1/2/3 triple knockout (TKO) mice and WT-FVB mouse controls. Extracts of these organs were Western blotted with antibodies to p27Kip1 and β-actin.
SMI-4a inhibition of Pim protein kinase induces cell-cycle arrest in pre–T-LBL. (A) 6812/2 cells were incubated for 24 hours and Jurkat cells for 48 hours with SMI-4a (10μM) or DMSO in serum-free medium. Propidium iodide staining of these cells was followed by cell-cycle quantification performed using flow cytometric analysis. (B) The effect of 24 hours of treatment with SMI-4a (10μM). After treatment of 6812/2 and Jurkat, the cellular levels of p27Kip1 were measured by Western blotting using antibodies to this protein and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) as a loading control. (C) 6812/2 and Jurkat cells were incubated with increasing doses of SMI-4a for 24 hours in serum-free medium, and the level of p27Kip1 was measured by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting using β-actin antibodies as a protein loading control. (D) The thymus was harvested from 2 Pim1/2/3 triple knockout (TKO) mice and WT-FVB mouse controls. Extracts of these organs were Western blotted with antibodies to p27Kip1 and β-actin.
SMI-4a induces cell death by the induction of apoptosis
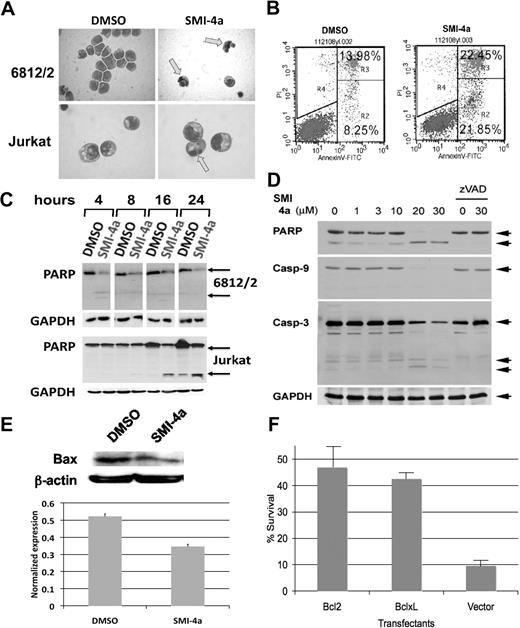
Treatment of both 6812/2 and Jurkat cell lines with 10μM SMI-4a for 24 hours resulted in nuclear condensation consistent with the induction of apoptosis (Figure 3A). To examine the mechanism of cell death in more detail, these cells were subjected to flow cytometric analysis after staining with PI and annexin V–fluorescein isothiocyanate. Treatment with SMI-4a for 6 hours led to an increase in the number of the cells positive for annexin V and negative for PI from 8.25% in the control to 21.85% (Figure 3B). To further evaluate the potential of this compound to induce apoptosis, the cleavage of poly–adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase (PARP),23 a hallmark of apoptosis, was examined. We found that treatment with SMI-4a in 6812/2 or Jurkat cells over 24 hours caused a marked increase in PARP cleavage (Figure 3C). In 6812/2 cells, PARP was largely cleaved by 4 hours. In Jurkat cells, PARP cleavage is clearly activated above 10μM SMI-4a, although the ability of this compound to decrease cell numbers is seen at even lower concentrations (Figure 1). It is possible that at lower doses of SMI-4a the decrease in cell number seen in a dose-response curve does not reflect cell death but is in part secondary to G1/S arrest. PARP cleavage after SMI-4a treatment was also detected in K562 (supplemental Figure 2A). In K562 cells after SMI-4a treatment, the proportion of cells positive for activated Bax and Bak, hallmarks of the induction of apoptosis, increased from 10.68% to 38.26% for Bax and from 15.82% to 42.13% for Bak (supplemental Figure 2B), again suggesting activation of apoptosis by this agent. Western blots shown in Figure 3D demonstrate that PARP cleavage was accompanied by a decrease in the levels of caspase-9 and caspase-3, consistent with activation of these enzymes during apoptosis. A hallmark of apoptosis is the shift of Bax from the cytoplasm to the mitochondrial membrane. To examine the ability of SMI-4a to decrease the levels of cytoplasmic Bax, we treated 6812/2 cells with SMI-4a, separated the cytoplasm, and carried out Western blots. This experiment (Figure 3E) demonstrates that SMI-4a treatment is capable of decreasing the levels of cytoplasmic Bax. To examine whether SMI-4a was activating the mitochondrial pathway24 to induce cell death, we overexpressed the Bcl2 or Bcl-xL proteins, both inhibitors of mitochondrial-mediated cell death, in Jurkat cells. As seen in Figure 3F, the cells overexpressing these proteins become resistant to SMI-4a treatment. Together these findings indicate that SMI-4a induces cell death through the apoptotic machinery.
SMI-4a treatment induces apoptosis in pre–T-LBL. (A) May-Giemsa staining of 6812/2 and Jurkat was carried out after incubation with DMSO or 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 24 hours. Arrows indicate cells with nuclear condensation. (B) Jurkat cells were stained with annexin V and PI after treatment with DMSO or SMI-4a as in panel A. The R2 quadrant contains the cells that have undergone apoptosis. (C) PARP cleavage was examined in 6812/2 and Jurkat after incubation with DMSO or 10μM SMI-4a in the absence of serum for the indicated times. Western blots of extracts of these cells were probed with antibodies to PARP and GAPDH as a control.  denotes holo- and cleaved PARP. (D) Jurkat cells were incubated with SMI-4a for 8 hours at the indicated concentrations. The caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK (40μM) was added along with SMI-4a (0, 30μM) for the same time period. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to PARP and caspases-3 and -9.
denotes holo- and cleaved PARP. (D) Jurkat cells were incubated with SMI-4a for 8 hours at the indicated concentrations. The caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK (40μM) was added along with SMI-4a (0, 30μM) for the same time period. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to PARP and caspases-3 and -9.  denotes the holo- and cleaved enzymes. GAPDH levels were measured as a loading control. (E) 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 4 hours. Cells were lysed and the cytoplasmic proteins were extracted and separated from nuclear protein. Bax protein levels were detected by Western blotting. (F) Jurkat cells were transfected with either Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL expression vectors and permanent transfectants established. These cells were incubated with SMI-4a (30μM) in the absence of serum for 24 hours. Viable cells were identified by trypan blue exclusion. The experiment was repeated in triplicate and the standard deviation of the mean of these determinations is shown.
denotes the holo- and cleaved enzymes. GAPDH levels were measured as a loading control. (E) 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 4 hours. Cells were lysed and the cytoplasmic proteins were extracted and separated from nuclear protein. Bax protein levels were detected by Western blotting. (F) Jurkat cells were transfected with either Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL expression vectors and permanent transfectants established. These cells were incubated with SMI-4a (30μM) in the absence of serum for 24 hours. Viable cells were identified by trypan blue exclusion. The experiment was repeated in triplicate and the standard deviation of the mean of these determinations is shown.
SMI-4a treatment induces apoptosis in pre–T-LBL. (A) May-Giemsa staining of 6812/2 and Jurkat was carried out after incubation with DMSO or 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 24 hours. Arrows indicate cells with nuclear condensation. (B) Jurkat cells were stained with annexin V and PI after treatment with DMSO or SMI-4a as in panel A. The R2 quadrant contains the cells that have undergone apoptosis. (C) PARP cleavage was examined in 6812/2 and Jurkat after incubation with DMSO or 10μM SMI-4a in the absence of serum for the indicated times. Western blots of extracts of these cells were probed with antibodies to PARP and GAPDH as a control.  denotes holo- and cleaved PARP. (D) Jurkat cells were incubated with SMI-4a for 8 hours at the indicated concentrations. The caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK (40μM) was added along with SMI-4a (0, 30μM) for the same time period. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to PARP and caspases-3 and -9.
denotes holo- and cleaved PARP. (D) Jurkat cells were incubated with SMI-4a for 8 hours at the indicated concentrations. The caspase inhibitor zVAD-FMK (40μM) was added along with SMI-4a (0, 30μM) for the same time period. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to PARP and caspases-3 and -9.  denotes the holo- and cleaved enzymes. GAPDH levels were measured as a loading control. (E) 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 4 hours. Cells were lysed and the cytoplasmic proteins were extracted and separated from nuclear protein. Bax protein levels were detected by Western blotting. (F) Jurkat cells were transfected with either Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL expression vectors and permanent transfectants established. These cells were incubated with SMI-4a (30μM) in the absence of serum for 24 hours. Viable cells were identified by trypan blue exclusion. The experiment was repeated in triplicate and the standard deviation of the mean of these determinations is shown.
denotes the holo- and cleaved enzymes. GAPDH levels were measured as a loading control. (E) 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in serum-free medium for 4 hours. Cells were lysed and the cytoplasmic proteins were extracted and separated from nuclear protein. Bax protein levels were detected by Western blotting. (F) Jurkat cells were transfected with either Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL expression vectors and permanent transfectants established. These cells were incubated with SMI-4a (30μM) in the absence of serum for 24 hours. Viable cells were identified by trypan blue exclusion. The experiment was repeated in triplicate and the standard deviation of the mean of these determinations is shown.
SMI-4a treatment of pre–T-LBL inhibits the mTOR pathway
Because the Pim protein kinases have been shown to regulate the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1, eIF4E, and PRAS40,25 and evidence26-28 suggests that activation of phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K)–AKT and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathways occurs in pre–T-LBL, we investigated whether SMI-4a treatment inhibits the mTOR pathway in these leukemic cells. To examine the activity of the mTORC1 pathway,29 the phosphorylation of 2 mTOR substrates, 4E-BP1 and p70 S6K, was examined in Jurkat and 6812/2 cells treated with SMI-4a in serum-free medium. In parallel, the mTORC2 pathway was studied by measuring changes in a known substrate of this complex, Akt. In these 2 cell types (Figure 4A), the results demonstrate that growth factor starvation decreases the phosphorylation of p70 S6K at Thr389 and this decrease in phosphorylation is markedly enhanced by treatment with SMI-4a. Starvation of Jurkat cells alone appears to lead to increases in the levels of 4E-BP1 proteins. A similar result has been reported for human myeloid leukemia cells.30 Hyperphosphorylation of 4E-BP1 disrupts the inhibitory effect of 4E-BP1 over eIF4E and results in activation of cap-dependent translation. Incubation of these cells with SMI-4a prevented the increase in 4E-BP1 protein levels and inhibited mTOR-directed phosphorylation on Thr37/46, preventing decreased mobility in SDS-PAGE (Figure 4B). In comparison with the inhibition of mTORC1 activity, SMI-4a treatment had no effect on the phosphorylation of the mTORC2 substrate AKT on Ser473 (Figure 4C). To examine the ability of Pim to regulate the mTOR pathway, we measured the level of phosphorylation of these substrates in the hematopoietic tissue of Pim TKO mice. In the bone marrow (BM) and spleen, the levels of phospho–p70 S6K but not total p70 S6K protein was decreased, whereas in the BM, spleen, and thymus the amount of both 4E-BP1 protein and phospho–4E-BP1 were down-regulated, although the extent of decrease appears to be organ specific (Figure 4D). These results, as well as previous findings,31 suggest that in hematopoietic cells Pim protein kinases play a role in modulating the mTORC1 pathway consistent with the effects of SMI-4a treatment on leukemic cells.
SMI-4a treatment inhibits the phosphorylation of TORC1 substrates. (A) Jurkat or 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in the absence of serum for the indicated time periods. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to phospho-p70 S6K (Thr389), total p70 S6K, and GAPDH. (B) Jurkat cells were treated with SMI-4a for varied periods of time and extracts were probed with antibodies to phospho–4E-BP1 (Thr37/46), total 4E-BP1, and GAPDH. (C) Identical extracts as in panel B were probed with antibodies to phospho-Akt (Ser473) and GAPDH. (D) Hematopoietic tissue was harvested from TKO mice and WT-FVB mice, and subjected to Western blots using antibodies to phospho–4E-BP1, total 4E-BP1, phospho–p70 S6K, total p70 S6K, and GAPDH as a loading control.
SMI-4a treatment inhibits the phosphorylation of TORC1 substrates. (A) Jurkat or 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in the absence of serum for the indicated time periods. Extracts of these cells were Western blotted with antibodies to phospho-p70 S6K (Thr389), total p70 S6K, and GAPDH. (B) Jurkat cells were treated with SMI-4a for varied periods of time and extracts were probed with antibodies to phospho–4E-BP1 (Thr37/46), total 4E-BP1, and GAPDH. (C) Identical extracts as in panel B were probed with antibodies to phospho-Akt (Ser473) and GAPDH. (D) Hematopoietic tissue was harvested from TKO mice and WT-FVB mice, and subjected to Western blots using antibodies to phospho–4E-BP1, total 4E-BP1, phospho–p70 S6K, total p70 S6K, and GAPDH as a loading control.
SMI-4a reduces MYC protein expression
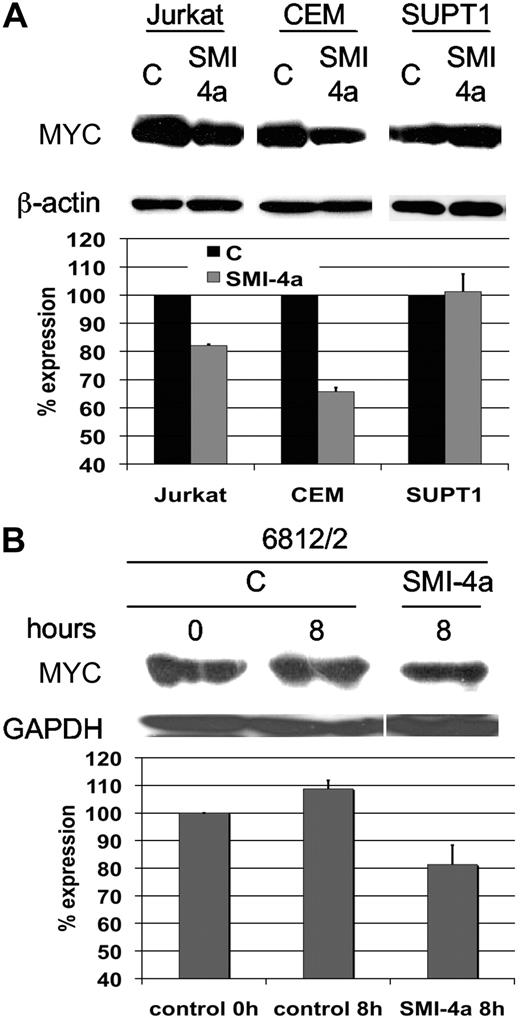
Because MYC and Pim1 collaborate in malignant transformation10,32,33 and MYC protein is essential for the continued growth of pre–T-LBL, we investigated whether SMI-4a affects the level of MYC protein. Three human pre–T-LBL cell lines including Jurkat, CEM, and SUPT1 were treated with 10μM SMI-4a for 8 hours. The expression of MYC was slightly reduced in Jurkat and CEM cells (Figure 5A), which were sensitive to SMI-4a treatment at the 10μM dose level (Figure 1), whereas it was not changed in SUPT1, which was not sensitive to SMI-4a at this dose level. Densitometry analysis of MYC protein expression revealed that MYC levels were reduced to 82.1% (± 0.44%) and 65.8% (± 1.44%) in Jurkat and CEM of control levels, respectively (Figure 5A). Similar results were seen in 6812/2 cells (81.3% ± 7.0% of control; Figure 5B). These findings demonstrate that SMI-4a decreases MYC levels and this decrease may also play a role in blocking cell growth.
SMI-4a treatment of pre–T-LBL down-regulates the level of MYC protein. (A) Human pre–T-LBL cell lines, Jurkat, CEM, and SUPT1 were incubated in the absence of serum with DMSO control (C) or 10μM SMI-4a for 24 hours. The extracts of these cells were evaluated by Western blotting for the expression of MYC. The films were scanned and the levels of MYC protein determined by National Institutes of Health ImageJ software normalized to β-actin expression. The percentage of expression is the ratio of MYC in SMI-4a–treated cells compared with untreated control. The experiment was carried out in triplicate and the error bars show the SD from the mean. (B) The level of MYC after SMI-4a treatment of murine 6812/2 cells was evaluated in an identical fashion as in panel A. The percentage of expression is the ratio of each time point over the control at the 0 time point.
SMI-4a treatment of pre–T-LBL down-regulates the level of MYC protein. (A) Human pre–T-LBL cell lines, Jurkat, CEM, and SUPT1 were incubated in the absence of serum with DMSO control (C) or 10μM SMI-4a for 24 hours. The extracts of these cells were evaluated by Western blotting for the expression of MYC. The films were scanned and the levels of MYC protein determined by National Institutes of Health ImageJ software normalized to β-actin expression. The percentage of expression is the ratio of MYC in SMI-4a–treated cells compared with untreated control. The experiment was carried out in triplicate and the error bars show the SD from the mean. (B) The level of MYC after SMI-4a treatment of murine 6812/2 cells was evaluated in an identical fashion as in panel A. The percentage of expression is the ratio of each time point over the control at the 0 time point.
SMI-4a treatment induces up-regulation of MAPK pathway
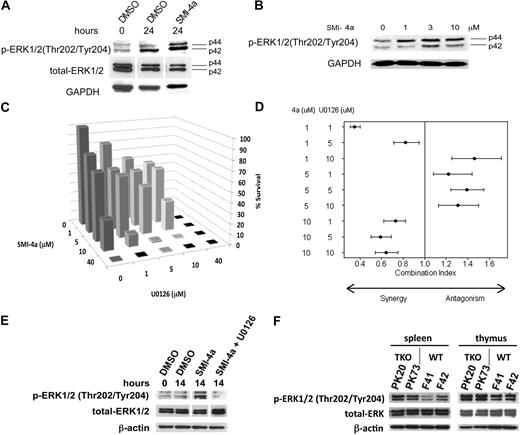
Experiments34 demonstrate that inhibition of the mTORC1 pathway by rapamycin is associated with increased ERK phosphorylation. To examine whether the same phenomenon occurs in leukemic cells, we treated these cells with SMI-4a and investigated the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Figure 6A demonstrates that incubation of 10μM SMI-4a with 6812/2 cells for 24 hours induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2. In Jurkat cells, this increase in ERK phosphorylation was concentration dependent with maximal induction occurring between 3 and 10μM (Figure 6B). Likewise, Western blots of the hematopoietic organs from TKO mice demonstrate that the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was up-regulated in spleen and thymus (Figure 6F), confirming that down-regulation of Pim kinases activated the MAPK pathway. Because several reports demonstrate synergistic killing effects between mTOR and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) inhibitors in multiple cancer types both in vitro and in vivo,34-36 we investigated combination effects of SMI-4a and the MEK1/2 inhibitor U0126 in the cytotoxic effect of 6812/2 cells (Figure 6C). The combination index demonstrates (Figure 6D) that at 1 and 10μM SMI-4a, depending on the U0126 dose, these agents were highly synergistic whereas at 5μM SMI-4a they were not. Figure 6D shows estimated combination indices and their corresponding 95% credible intervals across combined doses for SMI-4a and U0126. Similar results were seen for another MEK 1/2 inhibitor, PD184352, when combined with SMI-4a (data not shown). As would be predicted from this synergistic effect, U0126 treatment in combination with SMI-4a reversed the increase in phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (Figure 6E).
ERK1/2 phosphorylation is increased by SMI-4a treatment. (A) 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in the absence of serum for 24 hours and extracts of these cells subjected to Western blotting with antibodies to p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), total ERK, and GAPDH. (B) Jurkat cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SMI-4a in the serum-free media for 8 hours. Extracts were then probed as in panel A. (C) 6812/2 cells were incubated with varying amounts of SMI-4a and U0126 in serum-free media for 24 hours. Viable cells were then identified by trypan blue exclusion and the percentage of survival compared with the untreated control was plotted. (D) Based on data in panel C, Chou and Talalay's combination index for mutually exclusive agents was constructed across combined doses for SMI-4a and U0126. Estimated indices (●) and corresponding 95% credible intervals (horizontal lines) are shown. The combination index is not estimable for situations in which the kill rates are 100%. Therefore, no index is provided for any combination in which at least one dose was 40μM. (E) 6812/2 cells were treated with DMSO as a control or 10μM SMI-4a with or without 10μM U0126 for 14 hours. Extracts were probed as described in panel A. (F) The spleen and thymus studied in Figure 4D were subjected to Western blotting with antibodies to phospho-ERK1/2, total ERK, and β-actin, as a control.
ERK1/2 phosphorylation is increased by SMI-4a treatment. (A) 6812/2 cells were incubated with 10μM SMI-4a in the absence of serum for 24 hours and extracts of these cells subjected to Western blotting with antibodies to p-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204), total ERK, and GAPDH. (B) Jurkat cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of SMI-4a in the serum-free media for 8 hours. Extracts were then probed as in panel A. (C) 6812/2 cells were incubated with varying amounts of SMI-4a and U0126 in serum-free media for 24 hours. Viable cells were then identified by trypan blue exclusion and the percentage of survival compared with the untreated control was plotted. (D) Based on data in panel C, Chou and Talalay's combination index for mutually exclusive agents was constructed across combined doses for SMI-4a and U0126. Estimated indices (●) and corresponding 95% credible intervals (horizontal lines) are shown. The combination index is not estimable for situations in which the kill rates are 100%. Therefore, no index is provided for any combination in which at least one dose was 40μM. (E) 6812/2 cells were treated with DMSO as a control or 10μM SMI-4a with or without 10μM U0126 for 14 hours. Extracts were probed as described in panel A. (F) The spleen and thymus studied in Figure 4D were subjected to Western blotting with antibodies to phospho-ERK1/2, total ERK, and β-actin, as a control.
SMI-4a decelerates leukemic cell growth in vivo
To investigate the antitumor activity of SMI-4a in vivo, we first determined the oral pharmacokinetics of this agent in WT-FVB mice. We found that after gavage of 60 mg/kg SMI-4a, plasma concentrations could reach a maximum of 200μM in 1 hour and had a half-life of 6 hours and was eliminated from the plasma by 24 hours (supplemental Figure 3A). These data suggested that to inhibit Pim for a longer period of time, twice daily dosing might be significantly more effective. Pharmacokinetics disclosed that in mice treated with 60 mg/kg SMI-4a twice daily for 5 days, there was no buildup of this agent in the plasma, suggesting that the half-life was not prolonged (data not shown).
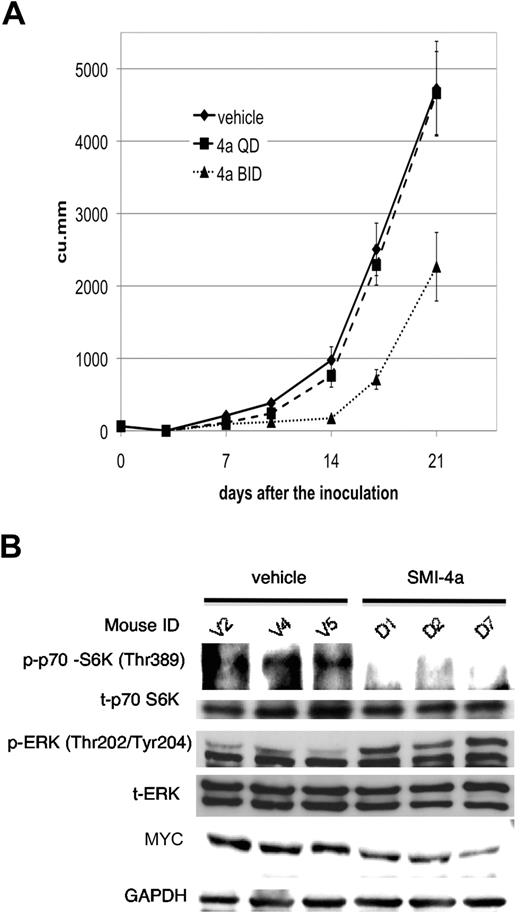
To evaluate the antitumor activity of this agent, we placed 2 × 106 6812/2 cells subcutaneously in Nu/nu nude mice and on day 3 started treatment with this agent. This treatment continued on a twice daily schedule for 5 of 7 days per week until day 21. Although tumor sizes in mice treated with vehicle versus SMI-4a once daily were not significantly different, the differences in the tumor sizes between vehicle and SMI-4a twice daily were statistically significant (P < .05; Figure 7A). There were no statistically significant adverse side effects from this treatment: (1) the mice did not lose body mass (supplemental Figure 3B), (2) the white blood cells were unchanged between vehicle, SMI-4a once daily, or twice daily, and (3) the hemoglobin and platelet counts were not significantly different between the treated and untreated group. Blood smears did not demonstrate morphologic abnormalities in any cell lineage. Because this chemotype has been associated with hepatotoxicity,37 blood chemistry analyses including alanine transferase, albumin, total protein, alkaline phosphatase, amylase, and total bilirubin, were undertaken at the time of killing, but did not disclose any abnormalities. Renal and pancreatic function was also normal.
The in vivo sensitivity of 6812/2 to SMI-4a treatment. (A) To examine the effect of treatment on tumor growth, 18 Nu/nu mice were subcutaneously injected with 2 × 106 cells of 6812/2 on day 0. Mice were then randomly assigned to 3 groups, vehicle, SMI-4a once daily, or SMI-4a twice daily and treatment was initiated on day 3. Tumor size was measured by calipers on day 0, 3, 7, 10, 14, 17, and 21, and calculated as described in “Mouse models.” The statistical difference in the tumor sizes was determined using Mann-Whitney U test. (B) The levels of p70 S6K phosphorylation, total p70 S6K, phospho ERK, total ERK, MYC, and GAPDH were determined by Western blotting in control (V2, V4, and V5) or treated tumors (D1, D2, and D7).
The in vivo sensitivity of 6812/2 to SMI-4a treatment. (A) To examine the effect of treatment on tumor growth, 18 Nu/nu mice were subcutaneously injected with 2 × 106 cells of 6812/2 on day 0. Mice were then randomly assigned to 3 groups, vehicle, SMI-4a once daily, or SMI-4a twice daily and treatment was initiated on day 3. Tumor size was measured by calipers on day 0, 3, 7, 10, 14, 17, and 21, and calculated as described in “Mouse models.” The statistical difference in the tumor sizes was determined using Mann-Whitney U test. (B) The levels of p70 S6K phosphorylation, total p70 S6K, phospho ERK, total ERK, MYC, and GAPDH were determined by Western blotting in control (V2, V4, and V5) or treated tumors (D1, D2, and D7).
Extracts of tumors that were harvested 1 hour after the final oral gavage of SMI-4a demonstrated decreased phosphorylation of p70 S6K compared with tumors from mice treated with vehicle, whereas in comparison total p70 S6K expression was unchanged. In addition, phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was up-regulated in these subcutaneous tumors treated with SMI-4a for 3 weeks (Figure 7B), and the expression of MYC was also slightly reduced to 81.3% (± 12.1%) of control (P < .05; Figure 7B). The biochemical effects of this treatment were gone 60 hours after the last dose of SMI-4a (data not shown), suggesting that continued treatment is needed to inhibit these pathways.
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the ability of a Pim kinase inhibitor SMI-4a to kill leukemic cells. We find that all cell types are sensitive to this agent but pre–T-LBL cells, human and mouse, are significantly more responsive than multiple myeloid or B-cell leukemias. In vivo sensitivity to both chemotherapy38 and apoptosis39 in myeloid and lymphoid malignancies can be regulated by the interactions of the bone marrow with stromal cells. Stromal cells produce IL-3 and IL-7, and bone marrow progenitors from mice lacking specific Pim isoforms are less responsive to these growth factors.21 Thus, it is possible that SMIs of Pim could function to block growth stimulation by these proteins produced by the stroma. Another explanation for the varied sensitivities of different leukemic cells to SMI-4a could be the role of Pim in specific biochemical pathways that drive transformation in each of these cell lines. MV4-11 cells express a FLT3/ITD mutation that regulates Pim levels,15 and Pim inhibitors, including SMI-4a, are highly active in inhibiting the growth of this cell line.14,15 However, the pathways that drive transformation in K562, HEL, and U937 cells (eg, BCR/ABL) may not require Pim to regulate cell growth.
The addition of SMI-4a to pre–T-LBL cells induces a G1 cell-cycle arrest. The addition of this compound to DU145 prostate cancer cells and MV4-11 myeloid leukemia cells induced a similar result.31 This treatment outcome was associated with an inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity, presumably regulated by translocation of p27Kip1 to the nucleus. Now we show that the addition of SMI-4a also markedly increases the levels of p27Kip1, which is consistent with the observed G1 arrest seen in pre–T-LBL cells. The observation that p27Kip1 levels are increased in the thymus of Pim TKO mice compared with WT-FVB controls further substantiates a role for Pim in regulating p27Kip1 and the cell cycle. The effect of these compounds appears to be cell line dependent with 5.9-fold increase in 6812/2 and only a 1.8-fold change in Jurkat. The change in Jurkat is similar to what is seen in TKO mice where organs may contain multiple T cells with different TCR rearrangements that could be differentially affected by absence of Pim protein kinases. Similar results have been seen in the K562 cell line in which overexpression of Pim1 resulted in the down-regulation of p27Kip1 followed by cell-cycle progression.22
Because Pim has been demonstrated to modulate the phosphorylation of both 4E-BP1 and eIF4E,20,40 we investigated the ability of SMI-4a to regulate the mTOR pathway. This was carried out in pre–T-LBL where PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway has been shown to be activated through posttranslational gene inactivation26 or gene deletion (eg, of PTEN). Our results using SMI-4a and analysis of organs from TKO mice again point to a role of Pim in regulating this pathway. Conversely, inhibition of the mTOR pathway with rapamycin decreases the levels of Pim2 in these pre–T-LBL cells (supplemental Figure 4). Interestingly, TKO mice express lower levels of total 4E-BP1 proteins that parallel a decrease in phosphorylation. Further analysis of this observation is under way (Z.M.B., manuscript in preparation). In contrast, the phosphorylation of p70 S6K is clearly decreased in the absence of the Pim proteins.
Pim has been shown to play a role in protection from cell death in multiple cell lines and tumors,11,20,41,42 potentially through phosphorylation of the BH3 protein BAD, inhibiting its activity.43,44 Our results demonstrate that the addition of SMI-4a to cells is capable of reversing this protection and inducing apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway. Unfortunately, the levels of BAD protein in leukemic cell lines are too low to examine changes in phosphorylation of this protein with inhibitor treatment. In addition to its regulation of BH3 proteins, it is possible that inhibition of the mTOR pathway with down-regulation of protein synthesis could also contribute to the apoptotic cell death.45 Further experiments are needed to define how inhibition of Pim regulates the mitochondrial pathway.
Results have demonstrated that inhibition of mTORC1 by RAD001, a rapamycin derivative, led to activation of the MAPK pathway in human breast cancer cells.34 The pathway regulated by this agent involves a reduction in the phosphorylation of p70 S6K followed by a decrease in insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation. This decrease allows higher levels of signal transduction from the insulin-like growth factor receptor with enhanced activation of PI3K, which through the Ras pathway leads to increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2.34 Activation of PI3K was also shown in the BM samples from multiple acute myeloid leukemia patients when cells were treated with RAD001 in vitro.46 Based on these experiments, we investigated the regulation of ERK1/2 phosphorylation by SMI-4a. We found that phosphorylation of ERK1/2 was increased by SMI-4a treatment and was also elevated in the organs of Pim TKO mice, suggesting the Pim protein kinase could play an important role in the feedback regulation of the ERK pathway. As suggested by the regulation of the ERK pathway, combination treatment of animals with subcutaneous tumors of the breast, colorectal cancer, and melanoma34 has been carried out with RAD001 and the MEK1/2 inhibitor PD0325901, and this combination has been shown to be highly synergistic. Likewise, we found that the combination of SMI-4a and a MEK inhibitor is highly synergistic in killing pre–T-LBL. As demonstrated in Figure 6D, combination indices and the upper bounds of corresponding credible intervals were less than 1 for both the 1 and 10mM doses of SMI-4a depending on the dose of U0126, indicating significant synergy between these agents. It is unclear why at 5μM SMI-4a this synergism is not seen. Possibly SMI-4a has an off-target effect at this dose, or inhibition of mTOR by SMI-4a regulates phosphatases that might decrease the activity of the ERK pathway. It is possible that U0126 could have diverse targets at different doses. Unfortunately, a commercial MEK inhibitor was not available for animal testing along with SMI-4a.
Pharmacokinetic analysis allowed us to determine that twice daily dosing of SMI-4a by gavage was superior to once daily administration of this agent. However, even though administration gave a statistical suppression of tumor growth, it was not clear why the results were not more dramatic. In culture, we were able to kill a large percentage of the cells using 40μM SMI-4a when the cells were exposed to this agent for 24 hours. However, unlike in culture, plasma concentrations, even with twice daily dosing, were close to zero by 24 hours, and it is possible that the level of drug in these subcutaneous tumors was lower secondary to poor blood supply to these tumors. Subcutaneous tumors collected 1 hour after the oral gavage of SMI-4a demonstrated a decrease in phospho–p70 S6K and a down-regulation of MYC protein levels, whereas tumors harvested 60 hours after drug administration did not show either of these changes, suggesting that prolonged exposure to this molecule is necessary for biologic activity. Therefore, it is possible that continuous infusion, time-release drug administration, or more frequent dosing might make this agent more effective in killing leukemic cells.
Recent clinical studies suggest that the 5-year survival for patients with precursor lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (LBL) was 84% for children and adolescents less than 19-years old, and 88% for children less than 15-years old (Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results [SEER] Cancer Statistics Review).47 However, the intensification regimens for pre–T-LBL needed to achieve these results have left many children with significant morbidity and long-term side effects. Moreover, the prognosis of adult LBL is still unfavorable, with 5-year survival less than 40%. Therefore, additional clinical treatments are needed for pre–T-LBL patients. More preclinical studies of this small molecule and others targeted at the Pim kinases will be needed to determine whether this protein kinase will be a novel target for therapy of these malignancies.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs Paul B. Rothman, University of Iowa, and Anton Berns, The Netherlands Cancer Institute, for the gift of the Pim knockout mice. We thank Sarah L'Heureux of Harvard Medical School for technical advice on the culture of human pre–T-LBL cell lines. Tracy van den Berg of the Hollings Cancer Center Drug Metabolism & Clinical Pharmacology Shared Resource was very helpful in providing the complete blood count and blood chemistry analysis. We are also grateful to Kylie Martin and Richard Peppler of the Hollings Cancer Center Flow Cytometry & Cell Sorting Shared Resource for carrying out cell-cycle analyses, apoptosis analyses, and phenotyping. These shared resources are supported in part by a Cancer Center Support Grant (P30 CA 138313). We thank Vortex Biotechnology for supplying SMIs of Pim kinases. We also thank our colleagues Drs Bo Cen, Sandeep Mahajan, and Marina Zemskova for discussions during this work.
Authorship
Contribution: Y.-W.L. designed and performed research, analyzed data; and wrote the paper; Z.M.B. performed research and analyzed data; E.G.H. analyzed data; J.H.S. performed research and analyzed data; W.W., Z.X., and Z.Z. performed research; P.D.A., J.C.A., and C.D.S. provided essential reagents; and A.S.K. designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the final draft of the paper.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Correspondence: Andrew S. Kraft, Hollings Cancer Center, Medical University of South Carolina, 86 Jonathan Lucas St, Charleston, SC 29425; e-mail: kraft@musc.edu.